SBOS464B september 2019 – june 2023 INA333-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DGK|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DGK|8
Orderable Information
8.2.2.6 Single-Supply Operation
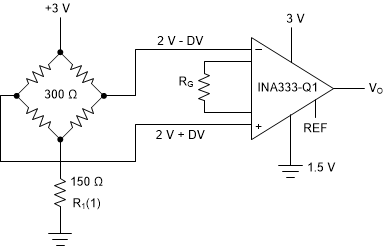
The INA333-Q1 can be used on single power supplies of 1.8 V to 5.5 V. Figure 8-4 shows a basic single-supply circuit. The output REF pin is connected to midsupply. Zero differential input voltage demands an output voltage of midsupply. Actual output voltage swing is limited to approximately 50 mV more than ground, when the load is referred to ground as shown. Figure 6-29 shows how the output voltage swing varies with output current.
With single-supply operation, VIN+ and VIN– must both be 0.1 V greater than ground for linear operation. For instance, the inverting input cannot be connected to ground to measure a voltage connected to the noninverting input.
To show the issues affecting low-voltage operation, consider the circuit in Figure 8-4 that shows the device operating from a single 3-V supply. A resistor in series with the low side of the bridge makes sure that the bridge output voltage is within the common-mode range of the amplifier inputs.