SBOS160A November 1993 – January 2015 ISO122
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Simplified Schematic
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2 Typical Application
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
To maintain the isolation barrier of the device, the distance between the high-side ground (pin 16 or 28) and the low-side ground (pin 8 or 14) should be kept at maximum; that is, the entire area underneath the device should be kept free of any conducting materials.
11.2 Layout Example
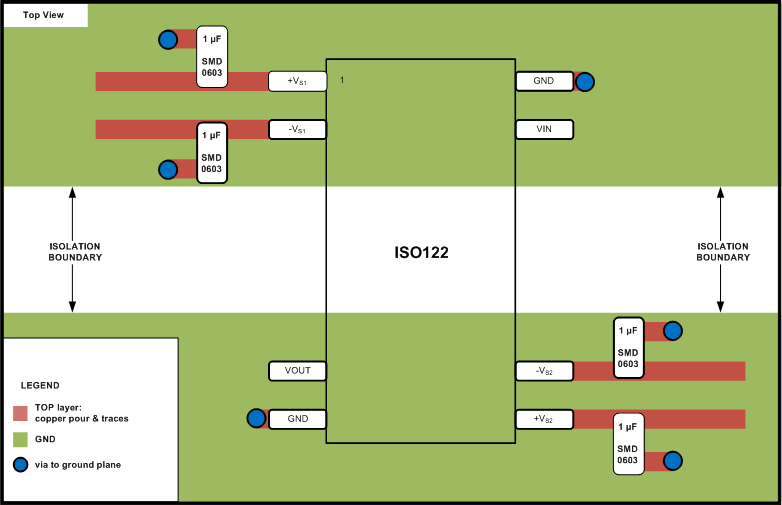 Figure 25. Typical Layout
Figure 25. Typical Layout