SNVS191F November 2002 – October 2016 LM2705
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBV|5
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
The input bypass capacitor CIN, as shown in Figure 25, must be placed close to the device. This reduces copper trace resistance, which effects input voltage ripple of the LM2705 device. For additional input voltage filtering, a 100-nF bypass capacitor can be placed in parallel with CIN to shunt any high frequency noise to ground. The output capacitor, COUT, must also be placed close to the device. Any copper trace connections for the COUT capacitor can increase the series resistance, which directly effects output voltage ripple. Keep the feedback network, resistors R1 and R2, close to the FB pin to minimize copper trace connections that can inject noise into the system. The ground connection for the feedback resistor network must connect directly to an analog ground plane. Tie the analog ground plane directly to the GND pin. If no analog ground plane is available, the ground connection for the feedback network must tie directly to the GND pin. Minimize trace connections made to the inductor and Schottky diode to reduce power dissipation and increase overall efficiency.
10.2 Layout Example
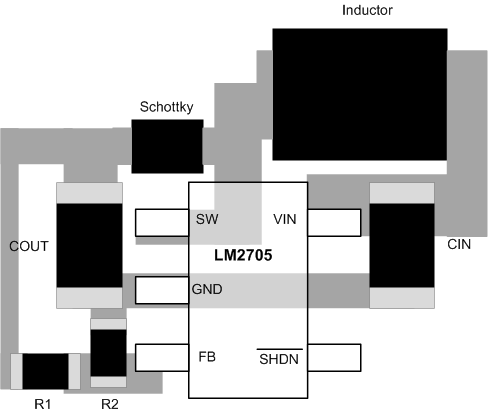 Figure 25. LM2705 Layout Example
Figure 25. LM2705 Layout Example