SNAS558N January 2000 – March 2024 LMC555
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Parameter Measurement Information
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
- P|8
- YPB|8
- DGK|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.4.2 Astable Operation
If the circuit is connected as shown in Figure 7-5 (TRIGGER and THRESHOLD pins connected together), the circuit triggers and free runs as a multivibrator. The external capacitor charges through RA + RB and discharges through RB. Thus, the duty cycle can be precisely set by the ratio of these two resistors.
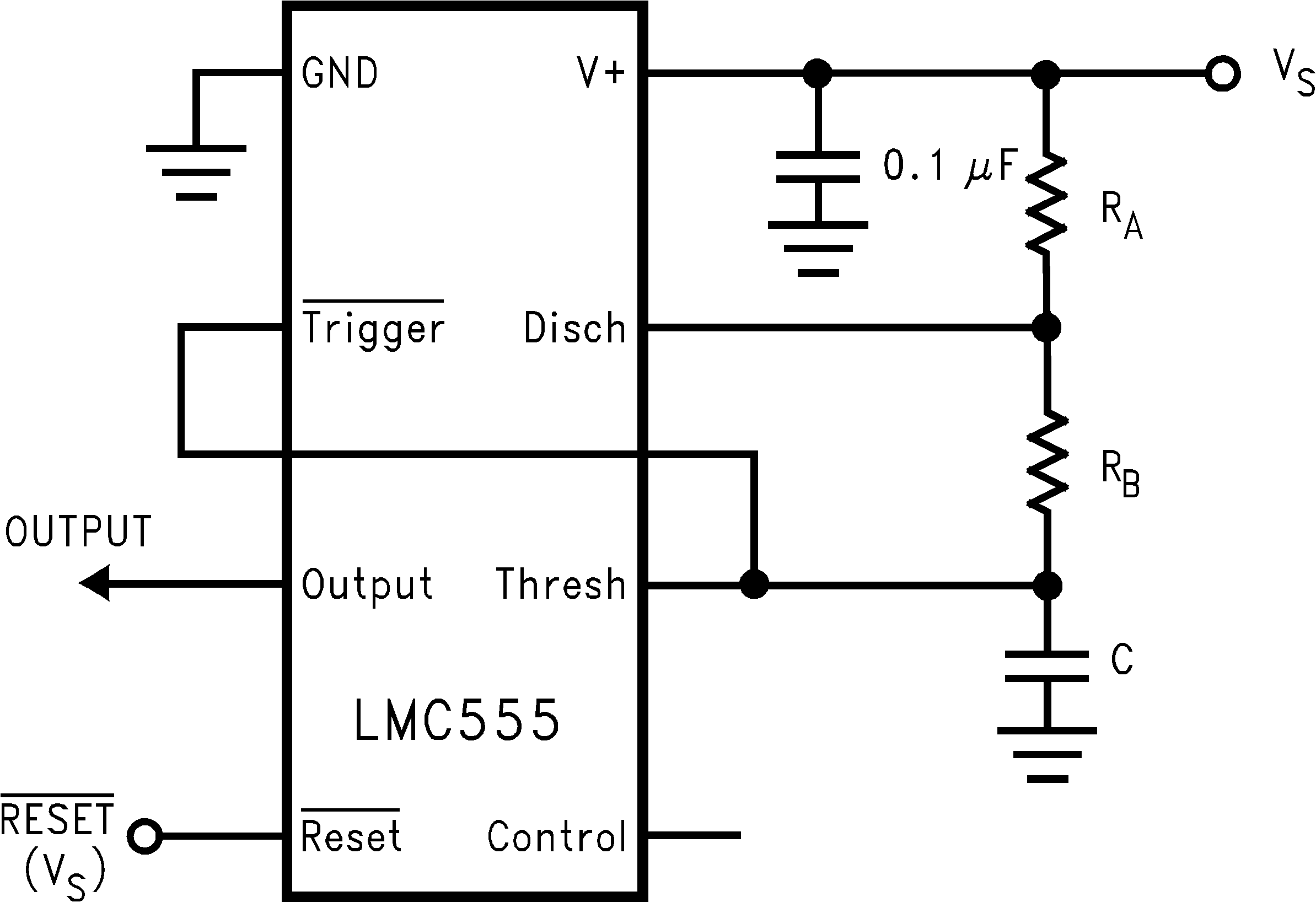 Figure 7-5 Astable (Variable Duty Cycle Oscillator)
Figure 7-5 Astable (Variable Duty Cycle Oscillator)In this mode of operation, the capacitor charges and discharges between 1/3 VS and 2/3 VS. As in the triggered mode, the charge and discharge times, and therefore, the frequency are independent of the supply voltage.
Figure 7-6 shows the waveform generated in this mode of operation.
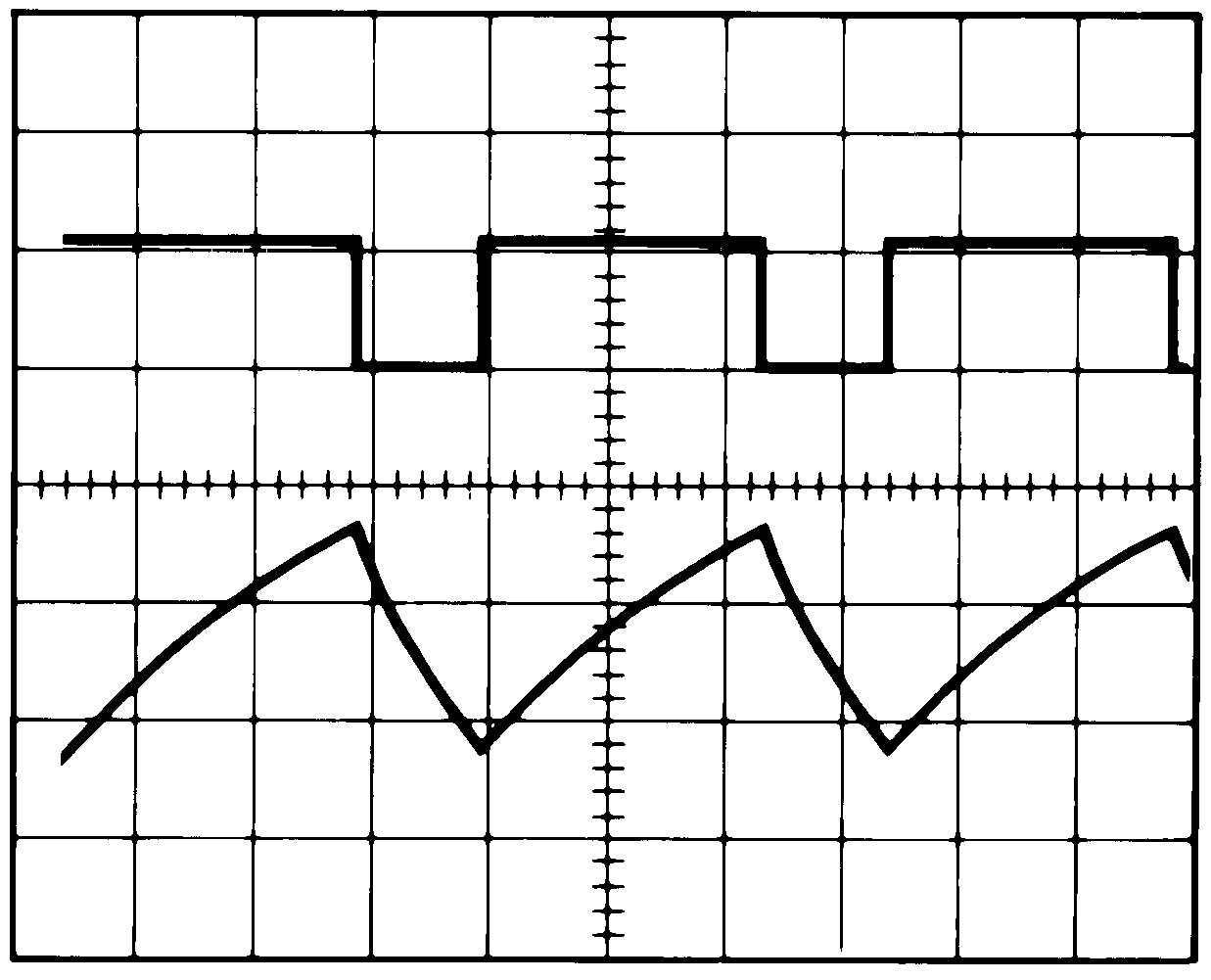
| VS = 5 V | Top trace: Output 5 V/div | RA = 1.78 kΩ |
| TIME = 20 µs/div | Bottom trace: Capacitor voltage 1 V/div | RB = 4.12 kΩ |
| C = 0.01 µF |
The charge time (output high) is given by
And the discharge time (output low) by:
Thus the total period is:
The frequency of oscillation is:
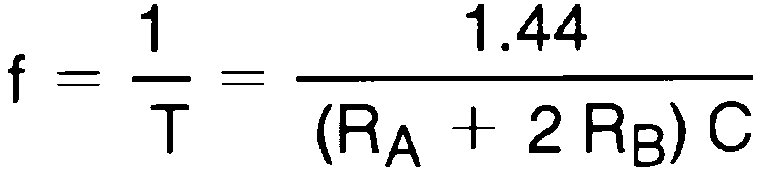
Figure 7-7 can be used for quick determination of these RC Values. The duty cycle, as a fraction of total period that the output is low, is:
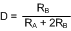
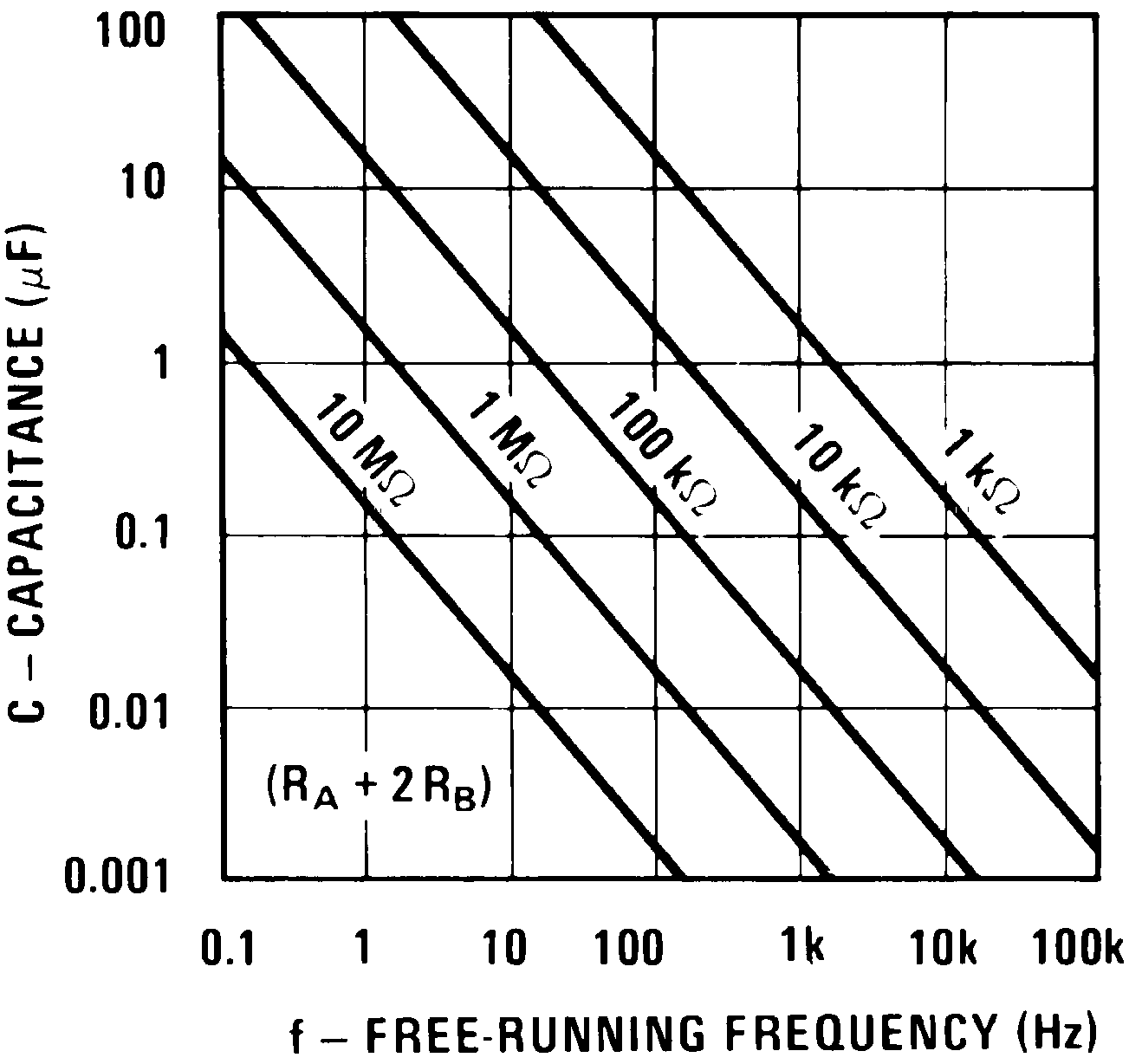 Figure 7-7 Free-Running Frequency
Figure 7-7 Free-Running Frequency