SLOS073G March 1976 – November 2014 RC4558
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
- P|8
- DGK|8
- PS|8
- PW|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PS|8
Orderable Information
7 Detailed Description
7.1 Overview
The RC4558 device is a dual general-purpose operational amplifier, with each half electrically similar to the μA741, except that offset null capability is not provided.
The high common-mode input voltage range and the absence of latch-up make this amplifier ideal for voltage-follower applications. The device is short-circuit protected, and the internal frequency compensation ensures stability without external components.
7.2 Functional Block Diagram
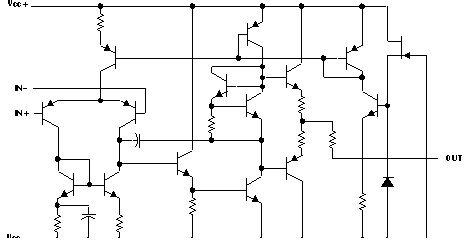
7.3 Feature Description
7.3.1 Unity-Gain Bandwidth
The unity-gain bandwidth is the frequency up to which an amplifier with a unity gain may be operated without greatly distorting the signal. The RC4558 device has a 3-MHz unity-gain bandwidth.
7.3.2 Common-Mode Rejection Ratio
The common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR) of an amplifier is a measure of how well the device rejects unwanted input signals common to both input leads. It is found by taking the ratio of the change in input offset voltage to the change in the input voltage, then converting to decibels. Ideally the CMRR is infinite, but in practice, amplifiers are designed to have it as high as possible. The CMRR of the RC4558 device is 90 dB.
7.3.3 Slew Rate
The slew rate is the rate at which an operational amplifier can change its output when there is a change on the input. The RC4558 device has a 1.7 V/μs slew rate.
7.4 Device Functional Modes
The RC4558 device is powered on when the supply is connected. Each of these devices can be operated as a single supply operational amplifier or dual supply amplifier depending on the application.