SCES503J NOVEMBER 2003 – June 2015 SN74AUP1G57
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 Switching Characteristics, CL = 5 pF
- 6.7 Switching Characteristics, CL = 10 pF
- 6.8 Switching Characteristics, CL = 15 pF
- 6.9 Switching Characteristics, CL = 30 pF
- 6.10 Operating Characteristics
- 6.11 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
9.1 Application Information
The SN74AUP1G57 features configurable multiple functions. The output state is determined by eight patterns of 3-bit input. The user can choose the logic functions AND, NAND, NOR, XNOR, inverter, and noninverter. All inputs can be connected to VCC or GND.
This part can be used in any application where an equivalent single gate would work. The biggest benefit to this part is that it can be used for multiple functions on the same board, reducing the total number of part numbers to be used.
9.2 Typical Application
This application shows how the SN74AUP1G57 can be configured to work as an AND logic gate. This part can The capacitor shown is 0.1 uF and should be placed as close as possible to the part.
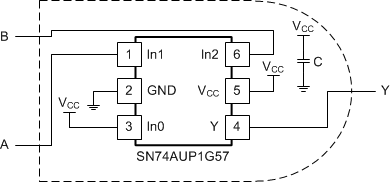 Figure 9. Schematic for AND Gate Configuration of SN74AUP1G57
Figure 9. Schematic for AND Gate Configuration of SN74AUP1G57
9.2.1 Design Requirements
This device uses CMOS technology and has balanced output drive. Take care to avoid bus contention because it can drive currents that would exceed maximum limits.
9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- Recommended Input conditions
- Rise time and fall time specs. See (Δt/ΔV) in Recommended Operating Conditions
- Specified high and low levels. See (VIH and VIL) in Recommended Operating Conditions
- Inputs are overvoltage tolerant allowing them to go as high as 4.6 V at any valid VCC
- Recommend output conditions
- Load currents should not exceed 20 mA on the output and 50 mA total for the part
- Outputs should not be pulled above VCC + 0.5 V.
9.2.3 Application Curve
The AUP family of single gate logic makes excellent translators for the new lower voltage microprocessors that typically are powered from 0.8 V to 1.2 V. They can drop the voltage of peripheral drivers and accessories that are still powered by 3.3 V to the new microcontroller power levels.
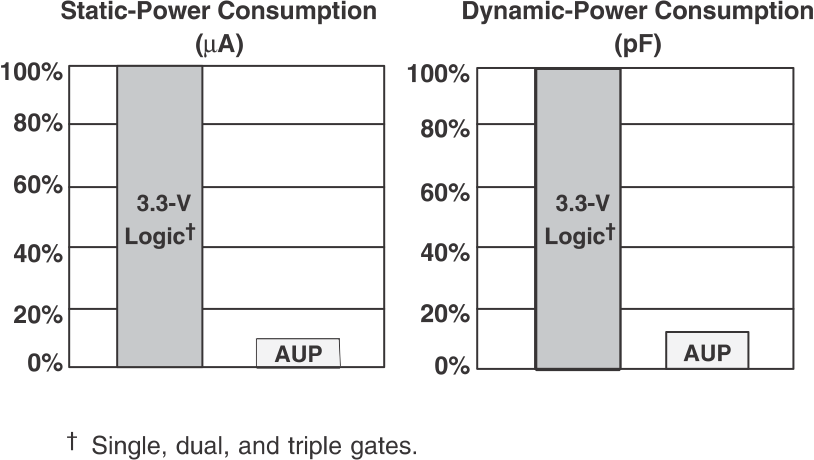 Figure 10. AUP – The Lowest-Power Family
Figure 10. AUP – The Lowest-Power Family