SLAS844A May 2012 – January 2016 TAS5624A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics - Audio Specification Stereo (BTL)
- 7.7 Electrical Characteristics - Audio Specification 4 Channels (SE)
- 7.8 Electrical Characteristics - Audio Specification Mono (PBTL)
- 7.9 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 System Power-Up and Power-Down Sequence
- 9.3.2 Start-Up and Shutdown Ramp Sequence
- 9.3.3 Unused Output Channels
- 9.3.4 Device Protection System
- 9.3.5 Pin-to-Pin Short-Circuit Protection (PPSC)
- 9.3.6 Overtemperature Protection
- 9.3.7 Overtemperature Warning, OTW
- 9.3.8 Undervoltage Protection (UVP) and Power-On Reset (POR)
- 9.3.9 Error Reporting
- 9.3.10 Fault Handling
- 9.3.11 Device Reset
- 9.3.12 System Design Consideration
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDV|44
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DDV|44
Orderable Information
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
DDV Package
44-Pin HTSSOP
Top View
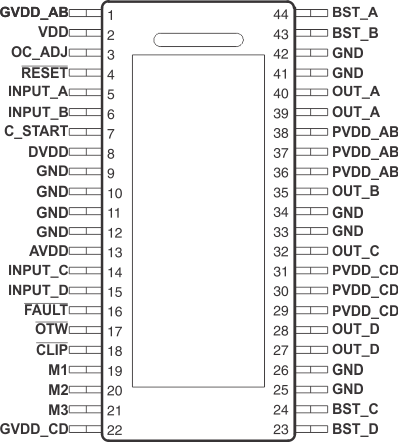
Pin Functions
| PIN | TYPE(1) | DESCRIPTION(2) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| AVDD | 13 | P | Internal voltage regulator, analog section |
| BST_A | 44 | P | Bootstrap pin, A-side |
| BST_B | 43 | P | Bootstrap pin, B-side |
| BST_C | 24 | P | Bootstrap pin, C-side |
| BST_D | 23 | P | Bootstrap pin, D-side |
| C_START | 7 | O | Start-up ramp |
| CLIP | 18 | O | Clipping warning; open-drain; active-low |
| DVDD | 8 | P | Internal voltage regulator, digital section |
| FAULT | 16 | O | Shutdown signal, open-drain; active-low |
| GND | 9, 10, 11, 12, 25, 26, 33, 34, 41, 42 |
P | Ground |
| GVDD_AB | 1 | P | Gate-drive voltage supply; AB-side |
| GVDD_CD | 22 | P | Gate-drive voltage supply; CD-side |
| INPUT_A | 5 | I | PWM Input signal for half-bridge A |
| INPUT_B | 6 | I | PWM Input signal for half-bridge B |
| INPUT_C | 14 | I | PWM Input signal for half-bridge C |
| INPUT_D | 15 | I | PWM Input signal for half-bridge D |
| M1 | 19 | I | Mode selection 1 (LSB) |
| M2 | 20 | I | Mode selection 2 |
| M3 | 21 | I | Mode selection 3 (MSB) |
| OC_ADJ | 3 | O | Overcurrent threshold programming pin |
| OTW | 17 | O | Overtemperature warning; open-drain; active-low |
| OUT_A | 39, 40 | O | Output, half-bridge A |
| OUT_B | 35 | O | Output, half-bridge B |
| OUT_C | 32 | O | Output, half-bridge C |
| OUT_D | 27, 28 | O | Output, half-bridge D |
| PowerPAD™ | — | P | Ground, connect to grounded heat sink |
| PVDD_AB | 36, 37, 38 | P | PVDD supply for half-bridge A and B |
| PVDD_CD | 29, 30, 31 | P | PVDD supply for half-bridge C and D |
| RESET | 4 | I | Device reset Input; active-low |
| VDD | 2 | P | Input power supply |
(1) I = Input, O = Output, and P = Power
(2) Located on the top side of the device for convenient thermal coupling to the heat sink.
Mode Selection Pins
| MODE PINS | PWM Input(1) | OUTPUT CONFIGURATION | INPUT A | INPUT B | INPUT C | INPUT D | MODE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M3 | M2 | M1 | |||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 2N + 1 | 2 × BTL | PWMa | PWMb | PWMc | PWMd | AD Mode |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1N + 1(2) | 2 × BTL | PWMa | Unused | PWMc | Unused | AD Mode |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 2N + 1 | 2 × BTL | PWMa | PWMb | PWMc | PWMd | BD Mode |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1N + 1(2) | 1 × BTL + 2 × SE | PWMa | Unused | PWMc | PWMd | AD Mode |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 2N + 1 | 1 × PBTL | PWMa | PWMb | 0 | 0 | AD Mode |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1N + 1(2) | 1 × PBTL | PWMa | Unused | 0 | 1 | AD Mode |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 2N + 1 | 1 × PBTL | PWMa | PWMb | 1 | 0 | BD Mode |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1N + 1 | 4 × SE(3) | PWMa | PWMb | PWMc | PWMd | AD Mode |
(1) The 1N and 2N naming convention is used to indicate the number of PWM lines to the power stage per channel in a specific mode.
(2) Using 1N interface in BTL and PBTL mode results in increased DC offset on the output terminals.
(3) The 4 × SE mode can be used as 1 × BTL + 2 × SE configuration by feeding a 2N PWM signal to either INPUT_AB or INPUT_CD for improved DC offset accuracy