SLOS993A March 2018 – June 2018 TPA3138D2
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Analog Gain
- 9.3.2 SD/FAULT Operation
- 9.3.3 PLIMIT
- 9.3.4 Spread Spectrum and De-Phase Control
- 9.3.5 GVDD Supply
- 9.3.6 DC Detect
- 9.3.7 PBTL Select
- 9.3.8 Short-Circuit Protection and Automatic Recovery Feature
- 9.3.9 Over-Temperature Protection (OTP)
- 9.3.10 Over-Voltage Protection (OVP)
- 9.3.11 Under-Voltage Protection (UVP)
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Applications
- 10.2.1 Design Requirements
- 10.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 10.2.2.1 Ferrite Bead Filter Considerations
- 10.2.2.2 Efficiency: LC Filter Required with the Traditional Class-D Modulation Scheme
- 10.2.2.3 When to Use an Output Filter for EMI Suppression
- 10.2.2.4 Input Resistance
- 10.2.2.5 Input Capacitor, Ci
- 10.2.2.6 BSN and BSP Capacitors
- 10.2.2.7 Differential Inputs
- 10.2.2.8 Using Low-ESR Capacitors
- 10.2.3 Application Performance Curves
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|28
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|28
Orderable Information
9.4.2 MODE_SEL = HIGH: Low-Idle-Current 1SPW Modulation
The 1SPW mode alters the normal modulation scheme in order to achieve higher efficiency with a slight penalty in THD degradation and more attention required in the output filter selection. In 1SPW mode the outputs operate at ~15% modulation during idle conditions. When an audio signal is applied one output decreases and the other output increases. The decreasing output signal rails to GND. At which point all the audio modulation takes place through the rising output. The result is that only one output is switching during a majority of the audio cycle. Efficiency is improved in this mode due to the reduction of switching losses.
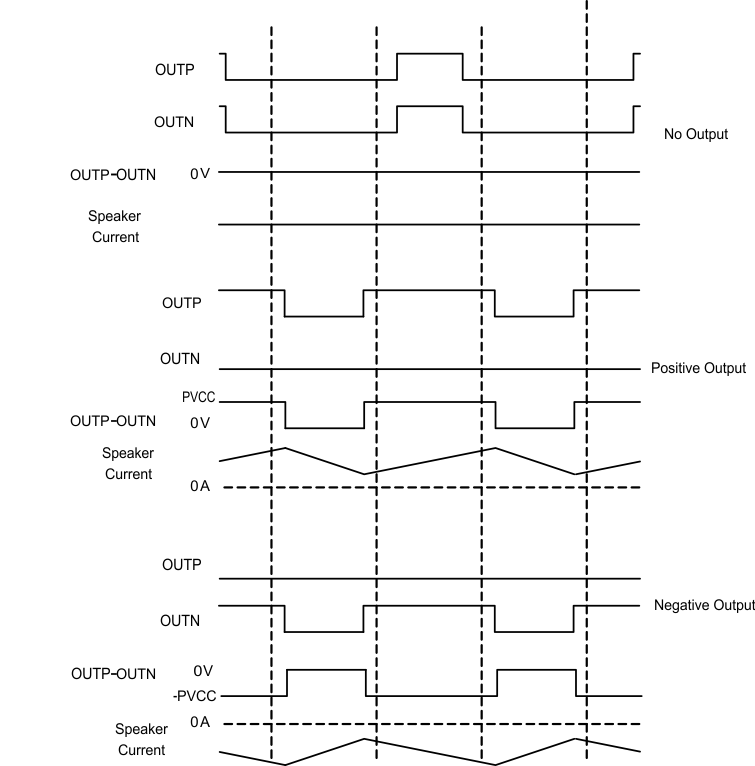 Figure 19. Low-Idle-Current 1SPW Modulation
Figure 19. Low-Idle-Current 1SPW Modulation