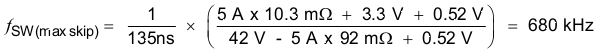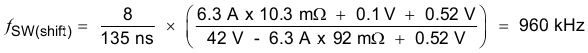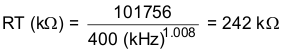SLVSEZ9 January 2019 TPS54540B
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope Compensation Output Current
- 7.3.3 Pulse Skip Eco-mode
- 7.3.4 Low Dropout Operation and Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 7.3.5 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.6 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.7 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.8 Internal Soft Start
- 7.3.9 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK) pin)
- 7.3.10 Accurate Current-Limit Operation and Maximum Switching Frequency
- 7.3.11 Synchronization to RT/CLK pin
- 7.3.12 Overvoltage Protection
- 7.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.14 Small Signal Model for Loop Response
- 7.3.15 Simple Small Signal Model for Peak-Current-Mode Control
- 7.3.16 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design with WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.3 Output Inductor Selection (LO)
- 8.2.2.4 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.5 Catch Diode
- 8.2.2.6 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.8 Undervoltage Lockout Set Point
- 8.2.2.9 Output Voltage and Feedback Resistors Selection
- 8.2.2.10 Minimum VIN
- 8.2.2.11 Compensation
- 8.2.2.12 Discontinuous Conduction Mode and Eco-mode Boundary
- 8.2.2.13 Power Dissipation Estimate
- 8.2.2.14 Safe Operating Area
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.3 Other System Examples
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDA|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DDA|8
Orderable Information
8.2.2.2 Selecting the Switching Frequency
The first step is to choose a switching frequency for the regulator. Typically, the designer uses the highest switching frequency possible because this produces the smallest solution size. High switching frequency allows for lower value inductors and smaller output capacitors compared to a power supply that switches at a lower frequency. The switching frequency that can be selected is limited by the minimum on-time of the internal power switch, the input voltage, the output voltage and the frequency foldback protection.
Use Equation 9 and Equation 10 to calculate the upper limit of the switching frequency for the regulator. Choose the lower value result from the two equations. Switching frequencies higher than these values results in pulse skipping or the lack of overcurrent protection during a short circuit.
The typical minimum on time, tonmin, is 135 ns for the TPS54540. For this example, the output voltage is 3.3 V, and the maximum input voltage is 42 V. Assuming a diode voltage of 0.52 V, inductor DC resistance of 10.3 mΩ, typical switch resistance of 92 mΩ, and 5-A load, using Equation 25 the maximum switch frequency to avoid pulse skipping is 680 kHz. To ensure overcurrent runaway is not a concern during short circuits use Equation 26 to determine the maximum switching frequency for frequency foldback protection. With a current limit value of 6.3 A and short-circuit output voltage of 0.1 V, the maximum switching frequency is 960 kHz.
For this design, a lower switching frequency of 400 kHz is chosen to operate comfortably below the calculated maximums. To determine the timing resistance for a given switching frequency, use Equation 27 or the curve in Figure 6. The switching frequency is set by resistor R3 shown in Figure 32. For 400 kHz operation, the closest standard value resistor is 243 kΩ.