SLES275A January 2015 – December 2017 VSP5324-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: Dynamic Performance
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: General
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: Digital
- 6.8 Timing Requirements
- 6.9 LVDS Timing at Different Sampling Frequencies (One-Lane Interface, 12x Serialization)
- 6.10 LVDS Timing at Different Sampling Frequencies (Two-Lane Interface, 6x Serialization)
- 6.11 Serial Interface Timing Requirements
- 6.12 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1
Serial Registers
- 7.6.1.1 Register 00h (offset = 00h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.2 Register 01h (offset = 01h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.3 Register 02h (offset = 02h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.4 Register 0Ah (offset = 0Ah) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.5 Register 0Fh (offset = 0Fh) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.6 Register 14h (offset = 14h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.7 Register 1Ch (offset = 1Ch) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.8 Register 23h (offset = 23h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.9 Register 24h (offset = 24h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.10 Register 25h (offset = 25h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.11 Register 26h (offset = 26h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.12 Register 27h (offset = 27h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.13 Register 28h (offset = 28h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.14 Register 29h (offset = 29h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.15 Register 2Ah (offset = 2Ah) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.16 Register 2Bh (offset = 2Bh) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.17 Register 2Eh (offset = 2Eh) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.18 Register 30h (offset = 30h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.19 Register 33h (offset = 33h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.20 Register 35h (offset = 35h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.21 Register 38h (offset = 38h) [reset = 0x0000]
- 7.6.1.22 Register 42h (offset = 42h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.23 Register 45h (offset = 45h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.24 Register 46h (offset = 46h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.25 Register 50h (offset = 50h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.26 Register 51h (offset = 51h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.27 Register 53h (offset = 53h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.28 Register 54h (offset = ) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.29 Register 55h (offset = 55h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1.30 Register F0h (offset = F0h) [reset = 0]
- 7.6.1
Serial Registers
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGC|64
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGC|64
Orderable Information
7 Detailed Description
7.1 Overview
The VSP5324-Q1 device is a high-performance, 12-bit, quad-channel, analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with sample rates up to 80 MSPS. The conversion process is initiated by a rising edge of the external input clock and when the analog input signal is sampled. The sampled signal is sequentially converted by a series of small resolution stages, with the outputs combined in a digital correction logic block. At every clock edge the sample propagates through the pipeline, resulting in a data latency of 11 clock cycles. The output is available as 12-bit data, in serial (low-voltage differential signaling) LVDS format, coded in either offset binary or binary twos complement format.
7.2 Functional Block Diagrams
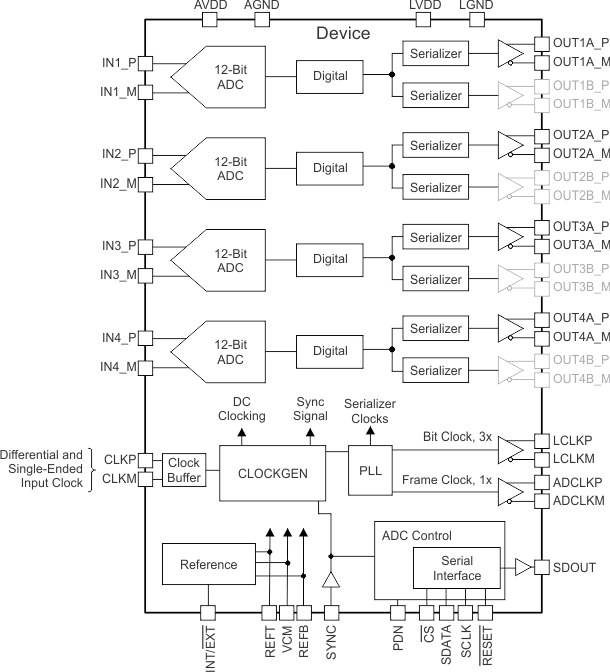 Figure 40. Quad ADC, One-Lane Configuration
Figure 40. Quad ADC, One-Lane Configuration
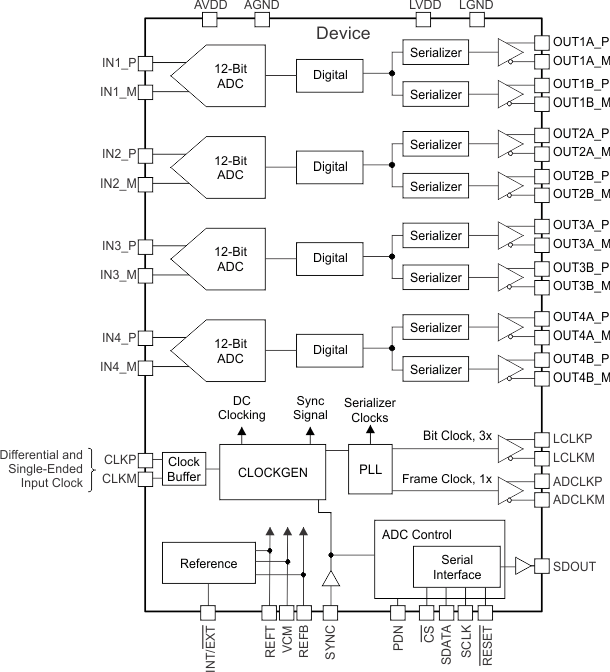 Figure 41. Quad ADC, Two-Lane Configuration
Figure 41. Quad ADC, Two-Lane Configuration
7.3 Feature Description
7.3.1 Analog Input
The analog input consists of a switched-capacitor-based differential sample-and-hold architecture, as shown in Figure 42. This differential topology results in very good AC performance even for high-input frequencies at high sampling rates. The INx_P and INx_M pins must be externally biased around a common-mode voltage of 0.95 V, available on the VCM pin. For a full-scale differential input, each input pin (INx_P, INx_M) must swing symmetrically between VCM + 0.5 V and VCM – 0.5 V, resulting in a 2-VPP differential input swing. The input sampling circuit has a high 3-dB bandwidth that extends up to 550 MHz (measured from the input pins to the sampled voltage).
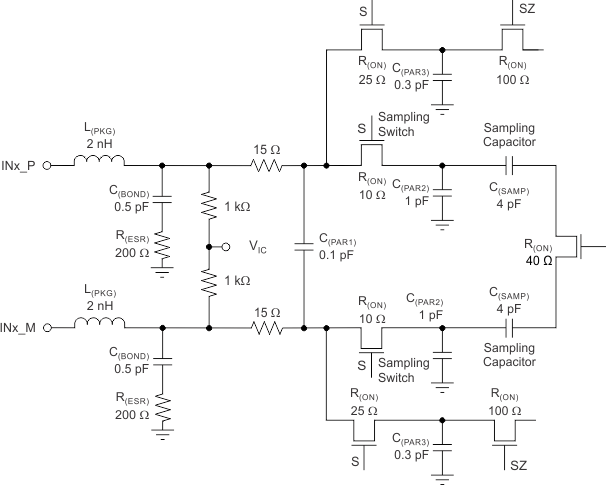 Figure 42. Analog Input Equivalent Circuit
Figure 42. Analog Input Equivalent Circuit
7.3.1.1 Large- and Small-Signal Input Bandwidth
The analog input circuit small-signal bandwidth is high, approximately 550 MHz. When using an amplifier to drive the VSP5324-Q1 device, the total amplifier noise up to small-signal bandwidth must be considered. The device large-signal bandwidth depends on the input signal amplitude. The VSP5324-Q1 device supports 2-VPP amplitude for input signal frequencies up to 80 MHz. For higher frequencies (greater than 80 MHz), the input signal amplitude must be decreased proportionally. For example, at 160 MHz, the device supports a maximum of 1-VPP signal.
7.3.2 Digital Processing Block
The VSP5324-Q1 device integrates a set of commonly-used digital functions that can be used to ease system design such as test patterns and gain.
7.3.2.1 Digital Gain
The VSP5324-Q1 device includes programmable digital gain settings from 0 dB to 12 dB in 1-dB steps. The benefit of digital gain is to obtain improved SFDR performance. SFDR improvement is achieved at the expense of SNR; for each gain setting, SNR degrades by approximately 1 dB. Therefore, gain can be used to trade-off between SFDR and SNR.
For each gain setting, the analog input full-scale range support scales proportionally, as shown in Table 1. After reset, the device is in 0-dB gain mode. To use other gain settings, program the GAIN_CHx bits in registers 2Ah (see the Register 2Ah (offset = 2Ah) [reset = 0] section) and 2Bh (see the Register 2Bh (offset = 2Bh) [reset = 0] section).
Table 1. Analog Input Full-Scale Range Across Gains
| DIGITAL GAIN (dB) | FULL-SCALE (VPP) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 2 |
| 1 | 1.78 |
| 2 | 1.59 |
| 3 | 1.42 |
| 4 | 1.26 |
| 5 | 1.12 |
| 6 | 1.00 |
| 7 | 0.89 |
| 8 | 0.80 |
| 9 | 0.71 |
| 10 | 0.63 |
| 11 | 0.56 |
| 12 | 0.50 |
7.3.2.2 ADC Input Polarity Inversion
Normally, the INx_P pin represents the positive analog input pin and INx_M represents the complementary negative input. Setting the INVERT_ CH[4:1] bits listed in Table 2 (which provide individual control for each channel) causes the inputs to be swapped. INN now represents the positive input and INx_P represents the negative input.
Table 2. Polarity Inversion
| ADDRESS (HEX) | D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 | PRBS_SEED[22:16] | X(1) | INVERT_CH4 | X | INVERT_CH3 | X | X | INVERT_CH2 | X | INVERT_CH1 | ||||||
7.3.2.3 SYNC Function
The SYNC function can be used to synchronize the RAMP test patterns across channels. This function can be enabled using either the hardware pin (SYNC) or software register bits.
To enable the software sync, set the register bit, EN_SYNC. To use the SYNC pin, set the EN_SYNC and HARD_SYNC_TP register bits. Note that SYNC pin is disabled after reset.
7.3.2.4 Output Data Format
Two output data formats are supported: twos complement and offset binary. These modes can be selected using the BTC_MODE serial interface register bit.
For a positive overload, the D[11:0] output data bits are FFFh in offset binary output format and 7FFh in twos complement output format. For a negative input overload, the output code is 000h in offset binary output format and 800h in twos complement output format.
7.3.3 Serial LVDS Interface
The VSP5324-Q1 device offers several flexible output options which makes interfacing to an (application-specific integrated circuit) ASIC or an (field-programmable gate array) FPGA easy. Each option can be easily programmed using the serial interface. Table 3 lists a summary of all options. This table also lists the default values after power-up and reset and a detailed description of each option. The output interface options are one-lane and two-lane serialization, and are described in the One-Lane, 12x Serialization with DDR Bit Clock and 1x Frame Clock and Two-Lane, 6x Serialization with DDR Bit Clock and 0.5x Frame Clock sections, respectively.
Table 3. Summary of Output Interface Options
| FEATURE | OPTIONS | AVAILABLE IN | DEFAULT AFTER RESET | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ONE-LANE | TWO-LANE | ||||
| Lane interface | One and two lanes | Yes | Yes | One-lane | One-lane: ADC data are sent serially over one pair of LVDS pins Two-lane: ADC data are split and sent serially over two pairs of LVDS pins |
| Serialization factor | 12x | Yes | No | 12x | — |
| DDR bit clock frequency | 6x | Yes | No | 6x | — |
| 3x | No | Yes | — | Only with two-lane interface | |
| Frame clock frequency | 1x sample rate | Yes | No | 1x | — |
| 1/2x sample rate | No | Yes | — | Only with two-lane interface | |
| Bit sequence | Byte-wise | No | Yes | Byte-wise | These options are available only with two-lane interface. Byte wise: ADC data are split into upper and lower bytes that are output on separate lanes. Bit wise: ADC data are split into even and odd bits that are output on separate lanes. Word wise: Successive ADC data samples are sent over separate lanes. |
| Bit-wise | No | Yes | Byte-wise | ||
| Word-wise | No | Yes | Byte-wise | ||
7.3.3.1 One-Lane, 12x Serialization with DDR Bit Clock and 1x Frame Clock
The 12-bit ADC data are serialized and output over one LVDS pair per channel along with a 6x bit clock and 1x frame clock, as shown in Figure 43. The output data rate is 12x sample rate and is therefore suited for low sample rates (typically up to 50 MSPS).
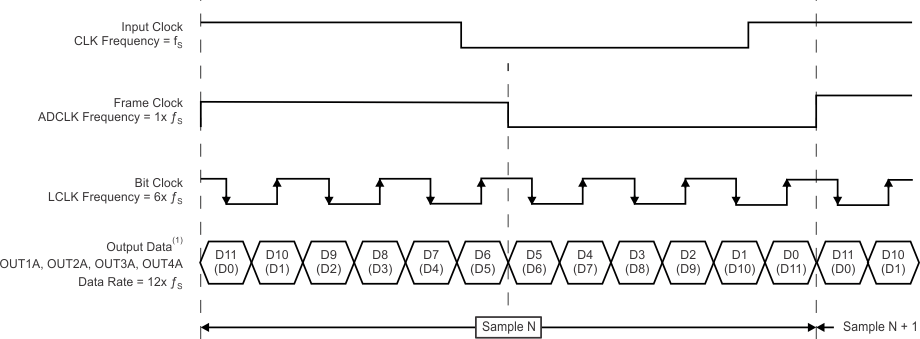
NOINDENT:
Upper number is the data bit in MSB-first mode. Lower number in parenthesis is the data bit in LSB-first mode.7.3.3.2 Two-Lane, 6x Serialization with DDR Bit Clock and 0.5x Frame Clock
In the two-lane serialization option, the 12-bit ADC data are serialized and output over two LVDS pairs per channel. The output data rate is a 6x sample rate with a 3x bit clock and a 1x frame clock.
Compared to the one-line scenario, the two-line output data rate is half the amount. This difference allows the device to be used up to the maximum sampling rate. Two-lane serialization is available in bit-, byte-, and word-wise modes. Figure 44 shows the bit- and byte-wise modes and Figure 45 shows the word-wise mode.
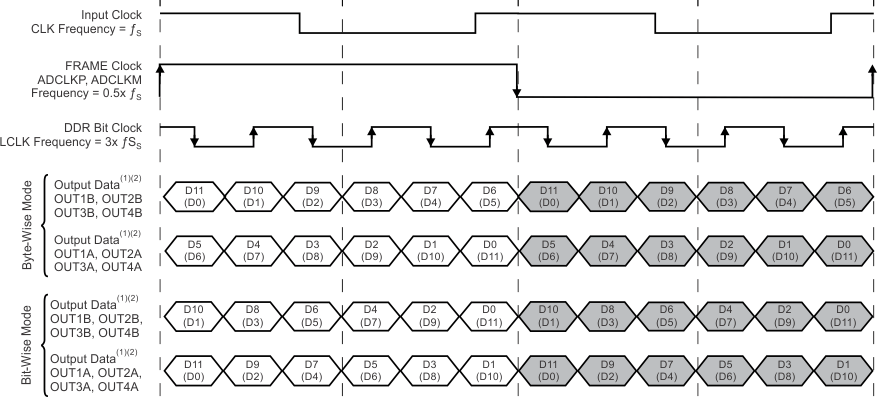
NOINDENT:
The upper number is the data bit in MSB-first mode. The lower number in parenthesis is the data bit in LSB-first mode.NOINDENT:
The unshaded cells indicate sample N data. The shaded cells indicate sample N + 1 data.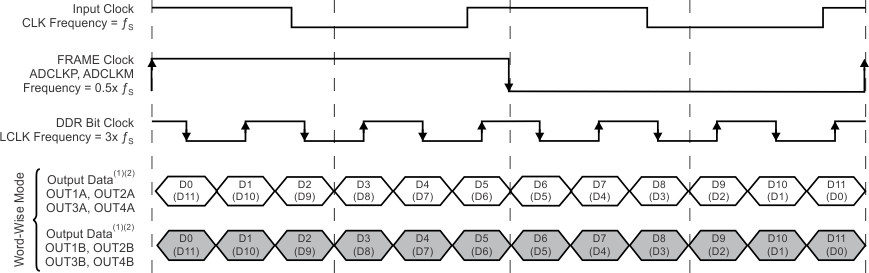
NOINDENT:
The upper number is the data bit in MSB-first mode. The lower number in parenthesis is the data bit in LSB-first mode.NOINDENT:
The unshaded cells indicate sample N data. The shaded cells indicate sample N + 1 data.7.3.4 Bit Clock Programmability
The VSP5324-Q1 output interface is normally a DDR interface with the LCLK rising and falling edge transitions in the middle of alternate data windows. Figure 46 shows this default phase.
![VSP5324-Q1 LCLK Default Phase
(PHASE_DDR[1:0] = 10) VSP5324-Q1 ai_tim_lclk_default_sles275.gif](/ods/images/SLES275A/ai_tim_lclk_default_sles275.gif) Figure 46. LCLK Default Phase (PHASE_DDR[1:0] = 10)
Figure 46. LCLK Default Phase (PHASE_DDR[1:0] = 10)
The LCLK phase can be programmed relative to the output frame clock and data using the PHASE_DDR[1:0] bits in Table 4. Figure 47 shows the LCLK phase modes.
Table 4. Clock Programmability
| ADDRESS (HEX) | D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 42 | EN_REF_VCM0 | X(1) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | PHASE_DDR[1:0] | X | EN_REF_VCM1 | X | X | X | |
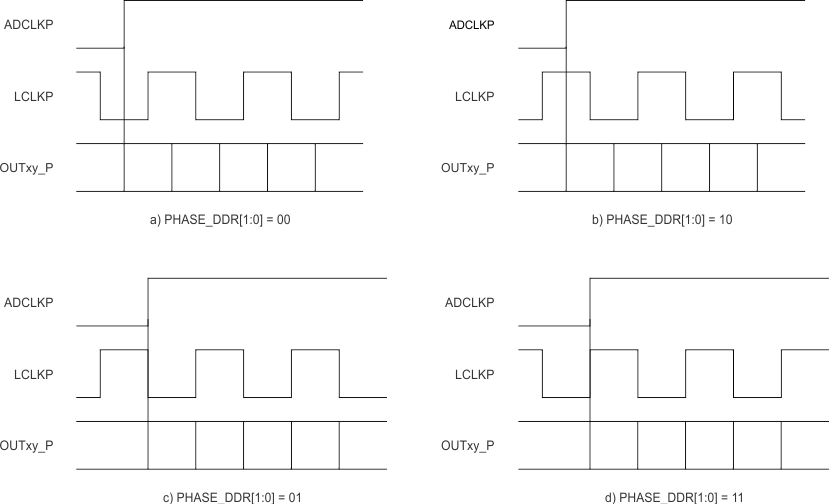 Figure 47. LCLK Phase Programmability Modes
Figure 47. LCLK Phase Programmability Modes
7.3.5 LVDS Output Data and Clock Buffers
Figure 48 shows the equivalent circuit of each LVDS output buffer. After reset, the buffer presents a 100-Ω output impedance to match the external 100-Ω termination.
The VID voltage is nominally 350 mV, resulting in an output swing of ±350 mV with 100-Ω external termination. The buffer output impedance behaves in the same way as a source-side series termination. By absorbing reflections from the receiver end, the buffer helps improve signal integrity.
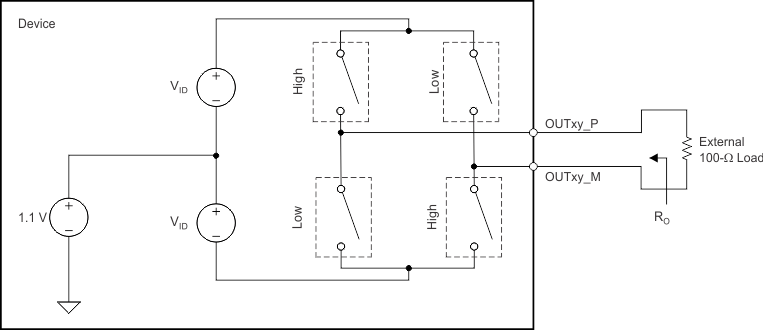 Figure 48. LVDS Buffer Equivalent Circuit
Figure 48. LVDS Buffer Equivalent Circuit
7.4 Device Functional Modes
7.4.1 External Reference Mode Of Operation
The VSP5324-Q1 device supports an external reference mode of operation either by:
- Forcing the reference voltages on the REFT and REFB pins, or by
- Applying the reference voltage on the VCM pin.
This mode can be used to operate multiple VSP5324-Q1 chips with the same (externally applied) reference voltage.
7.4.1.1 Using the REF Pins
For normal operation, the device requires two reference voltages, REFT and REFB. By default, the device generates these two voltages internally. To enable the external reference mode, set the register bits as listed in Table 5. This procedure powers down the internal reference amplifier and the two reference voltages can be forced directly on the REFT and REFB pins as (V(REFT) = 1.45 V ± 50 mV) and (V(REFB) = 0.45 V ±50 mV).
Use to calculate the relationship between the ADC full-scale input voltage (VFS) and the applied reference voltages.
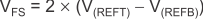
7.4.1.2 Using the VCM Pin
In this mode, an external reference voltage (VREFIN) can be applied to the VCM pin. UseEquation 2 to calculate the relationship between the ADC full-scale input voltage and VREFIN.
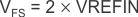
To enable this mode, set the register bits as listed in Table 5. This action changes the function of the VCM pin to an external reference input pin. The voltage applied on VCM must be 1.5 V ±50 mV.
Table 5. External Reference Function
| FUNCTION | EN_HIGH_ADDRS | EN_EXT_REF | EXT_REF_VCM |
|---|---|---|---|
| External reference using the REFT and REFB pins | 1 | 1 | 00 |
| External reference using the VCM pin | 1 | 1 | 11 |
7.5 Programming
7.5.1 Serial Interface
The VSP5324-Q1 device has a set of internal registers that can be accessed by the serial interface formed by the CS (serial interface enable), SCLK (serial interface clock), and SDATA (serial interface data) pins. When CS is low the following occurs:
- The serial shift of bits into the device is enabled.
- Serial data (on the SDATA pin) are latched at every SCLK rising edge.
- The serial data are loaded into the register at every 24th SCLK rising edge.
If the word length exceeds a multiple of 24 bits, the excess bits are ignored. Data can be loaded in multiples of 24-bit words within a single active CS pulse.
The first eight bits form the register address and the remaining 16 bits form the register data. The interface can function with SCLK frequencies from 15 MHz down to very low speeds (of few Hertz) and also with a non-50% SCLK duty cycle.
7.5.2 Register Initialization
After power-up, the internal registers must be initialized to the default values. This reset can be accomplished in one of two ways:
- A hardware reset is applied by a low-going pulse on the RESET pin (widths greater than 10 ns), as shown in Figure 3 and Serial Interface Timing Requirements.
- A software reset is applied by using the serial interface and setting the RST bit (register 00h, bit D0) high. This setting initializes the internal registers to default values and then self-resets the RST bit low. In this case, the RESET pin is kept high (inactive).
See the Serial Interface Timing Requirements section and Figure 3 for timing information.
7.5.3 Serial Register Readout
The device includes a mode where the contents of the internal registers can be readback on the SDOUT pin, as shown in Figure 49. This mode can useful as a diagnostic check to verify the serial interface communication between the external controller and ADC.
By default, after power-up and device reset, the SDOUT pin is high-impedance. When readout mode is enabled using the READOUT register bit, the SDOUT pin outputs the contents of the selected register serially in the following sequence:
- The READOUT register bit must be set to 1 in order for the device to enter readout mode. This setting disables any further writes into the internal registers, except for the register at address 01h. Note that the READOUT bit is also located in this register. The device can exit readout mode by writing the READOUT bit to 0. Only the register contents of address 01h are unable to be read in register readout mode.
- The read cycle is initiated by clocking the register address A[7:0] on the SDIN pin.
- The device serially outputs the contents (D[15:0]) of the selected register on the SDOUT pin.
- The external controller latches the contents at the SCLK rising edge.
- The READOUT register bit is set to 0 to exit serial readout mode, which enables all registers of the device to be written to. At this point, the SDOUT pin enters a high-impedance state.
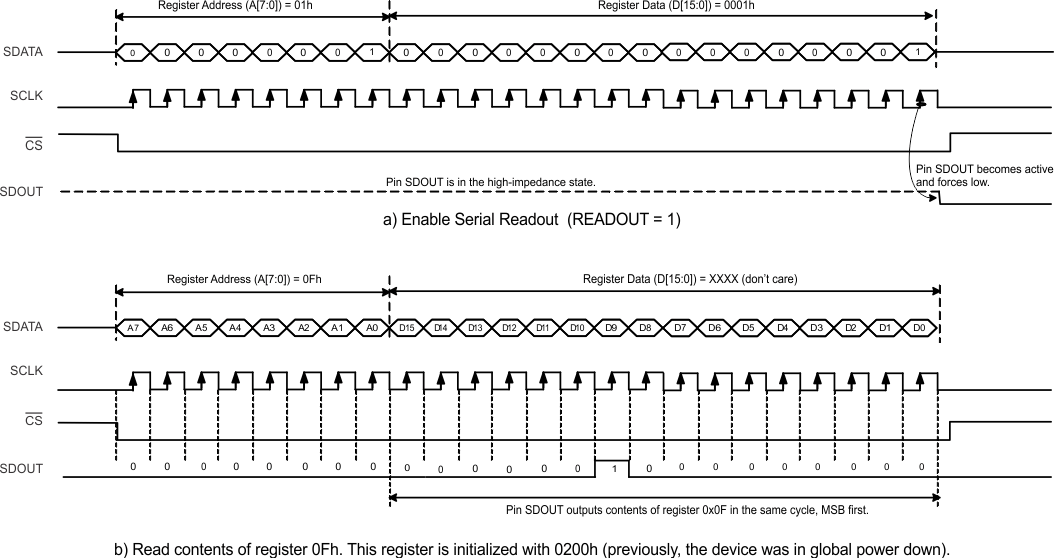 Figure 49. Serial Readout Timing
Figure 49. Serial Readout Timing
After reset, the device default states include the following:
- The device is in normal operation mode with 12x serialization enabled for all channels.
- Output interface is one-lane, 12x serialization with a 6x bit clock and a 1x frame clock frequency.
- Data format is LSB-first and offset binary.
- Serial readout is disabled.
- The PD pin is configured as a global power-down pin.
- Digital gain is set to 0 dB.
7.6 Register Maps
Table 6. Serial Register Memory Map
| ADDRESS | D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | X(1) | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | RST |
| 01 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | EN_HIGH_ ADDRS |
X | X | X | READOUT |
| 02 | X | X | EN_SYNC | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| 0A | RAMP_PAT_RESET_VAL | |||||||||||||||
| 0F | X | X | X | X | X | PDN_PIN_ CFG |
PDN_ COM PLETE |
PDN_ PARTIAL |
PDN_CH4 | X | PDN_CH3 | X | PDN_CH2 | X | PDN_CH1 | X |
| 14 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | LFNS_CH4 | X | LFNS_CH3 | X | X | LFNS_CH2 | X | LFNS_CH1 |
| 1C | X | EN_ FRAME_ PAT |
ADCLKOUT[11:0] | X | X | |||||||||||
| 23 | PRBS_SEED[15:0] | |||||||||||||||
| 24 | PRBS_SEED[22:16] | X | INVERT_ CH4 |
X | INVERT_ CH3 |
X | X | INVERT_ CH2 |
X | INVERT_ CH1 |
||||||
| 25 | HARD_ SYNC_TP |
PRBS_ SEED_ FROM_ REG |
X | PRBS_ TP_EN |
X | X | X | TP_SOFT_SYNC | X | EN_RAMP | DUAL_ CUSTOM_ PAT |
SINGLE_ CUSTOM_ PAT |
BITS_CUSTOM2[13:12] | BITS_CUSTOM1[13:12] | ||
| 26 | BITS_CUSTOM1[9:0] | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||
| 27 | BITS_CUSTOM2[9:0] | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||
| 28 | EN_BIT ORDER |
X | X | X | X | X | X | BIT_WISE | EN_WORDWISE_BY_CH[7:0] | |||||||
| 29 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | GLOBAL_ EN_FILTER |
X |
| 2A | X | X | X | X | GAIN_CH2[3:0] | X | X | X | X | GAIN_CH1[3:0] | ||||||
| 2B | X | X | X | X | GAIN_CH3[3:0] | X | X | X | X | GAIN_CH4[3:0] | ||||||
| 2E | X | HPF_EN_ CH1 |
HPF_CORNER _CH1[3:0] | FILTER1_COEFF_SET[2:0] | FILTER1_RATE[2:0] | X | ODD_TAP1 | X | USE_ FILTER1 |
|||||||
| 30 | X | HPF_EN_ CH2 |
HPF_CORNER _CH2[3:0] | FILTER2_COEFF_SET[2:0] | FILTER2_RATE[2:0] | X | ODD_TAP2 | X | USE_ FILTER2 |
|||||||
| 33 | X | HPF_EN_ CH3 |
HPF_CORNER _CH3[3:0] | FILTER3_COEFF_SET[2:0] | FILTER3_RATE[2:0] | X | ODD_TAP3 | X | USE_ FILTER3 |
|||||||
| 35 | X | HPF_EN_ CH4 |
HPF_CORNER _CH4[3:0] | FILTER4_COEFF_SET[2:0] | FILTER4_RATE[2:0] | X | ODD_TAP4 | X | USE_ FILTER4 |
|||||||
| 38 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | DATA_RATE[1:0] | |
| 42 | EN_REF_ VCM0 |
X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | PHASE_DDR[1:0] | X | EN_REF_ VCM1 |
X | X | X | |
| 45 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | PAT_SYNC | PAT_ DESKEW |
| 46 | ENABLE 46 | X | FALL_SDR | X | EN_16BIT | EN_14BIT | EN_12BIT | X | X | X | X | EN_SDR | MSB_ FIRST |
BTC_ MODE |
X | EN_2LANE |
| 50 | ENABLE 50 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | MAP_CH12_TO_OUT1B[3:0] | MAP_CH12_TO_OUT1A[3:0] | ||||||
| 51 | ENABLE 51 | X | X | X | MAP_CH12_TO_OUT2B[3:0] | MAP_CH12_TO_OUT2A[3:0] | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| 53 | ENABLE 53 | X | X | X | MAP_CH34_TO_OUT3B[3:0] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||
| 54 | ENABLE 54 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | MAP_CH34_TO_OUT3A[3:0] | |||
| 55 | ENABLE 55 | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | MAP_CH34_TO_OUT4A[3:0] | MAP_CH34_TO_OUT4B[3:0] | ||||||
| F0 | EN_EXT_ REF |
X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
7.6.1 Serial Registers
7.6.1.1 Register 00h (offset = 00h) [reset = 0]
This is a general register.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| X | |||||||
| W-0 | |||||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| X | RST | ||||||
| W-0 | W-0 | ||||||
Table 7. Register 00h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15-D1 | X | W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D0 | RST | W | 0 |
Reset 0 = Normal operation (default) 1 = Self-clearing software reset (after reset, this bit is set to 0) |
7.6.1.2 Register 01h (offset = 01h) [reset = 0]
This is a general register.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| X | |||||||
| W-0 | |||||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| X | EN_HIGH_ADDRS | X | READOUT | ||||
| W-0 | W-0 | W-0 | W-0 | ||||
Table 8. Register 01h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15-D5 | X | W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D4 | EN_HIGH_ADDRS | W | 0 |
Register F0h access 0 = Disables access to register F0h (default) 1 = Enables access to register F0h |
| D3-D1 | X | W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D0 | READOUT | W | 0 |
Register mode readout 0 = Normal operation (default) 1 = Register mode readout |
7.6.1.3 Register 02h (offset = 02h) [reset = 0]
This is a general register.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| X | EN_SYNC | X | |||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | |||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| X | |||||||
| R/W-0 | |||||||
Table 9. Register 02h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15-D14 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D13 | EN_SYNC | R/W | 0 |
SYNC enable(1) 0 = Normal operation; SYNC feature disabled (default) 1 = SYNC feature enabled to synchronize test patterns |
| D12-D0 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
7.6.1.4 Register 0Ah (offset = 0Ah) [reset = 0]
This is a general register.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| RAMP_PAT_RESET_VAL | |||||||
| R/W-0 | |||||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| RAMP_PAT_RESET_VAL | |||||||
| R/W-0 | |||||||
Table 10. Register 0Ah Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15-D0 | RAMP_PAT_RESET_VAL | R/W | 0 | These bits determine the initial value of the ramp pattern after reset. |
7.6.1.5 Register 0Fh (offset = 0Fh) [reset = 0]
This is a power-down mode register. All bits default to 0 after reset.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| X | PDN_PIN_CFG | PDN_ COMPLETE | PDN_PARTIAL | ||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| PDN_CH4 | X | PDN_CH3 | X | PDN_CH2 | X | PDN_CH1 | |
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | |
Table 11. Register 0Fh Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15-D11 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D10 | PDN_PIN_CFG | R/W | 0 |
PD pin configuration 0 = PD pin configured for complete power-down mode 1 = PD pin configured for partial power-down mode |
| D9 | PDN_ COMPLETE | R/W | 0 |
Complete power-down 0 = Normal operation 1 = Register mode for complete power-down (slower recovery) |
| D8 | PDN_PARTIAL | R/W | 0 |
Partial power-down 0 = Normal operation 1 = Partial power-down mode (fast recovery from power-down) |
| D7 | PDN_CH4 | R/W | 0 |
ADC power-down mode for channel 4 0 = Normal operation 1 = Partial power-down mode (fast recovery from power-down) |
| D6 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D5 | PDN_CH3 | R/W | 0 |
ADC power-down mode for channel 3 0 = Normal operation 1 = ADC power-down mode for channel 3 |
| D4-D3 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D2 | PDN_CH2 | R/W | 0 |
ADC power-down mode for channel 2 0 = Normal operation 1 = ADC power-down mode for channel 2 |
| D1 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D0 | PDN_CH1 | R/W | 0 |
ADC power-down mode for channel 1 0 = Normal operation 1 = ADC power-down mode for channel 1 |
7.6.1.6 Register 14h (offset = 14h) [reset = 0]
This is a general register.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| X | |||||||
| R/W-0 | |||||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| LFNS_CH4 | X | LFNS_CH3 | X | LFNS_CH2 | X | LFNS_CH1 | |
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | |
Table 12. Register 14h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15-D8 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D7 | LFNS_CH4 | R/W | 0 |
Noise-suppression mode selection for channel 4 0 = LFNS disabled (default) 1 = Low-frequency noise-suppression mode enable for channel 4 |
| D6 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D5 | LFNS_CH3 | R/W | 0 |
Noise-suppression mode selection for channel 3 0 = LFNS disabled (default) 1 = Low-frequency noise-suppression mode enable for channel 3 |
| D4-D3 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D2 | LFNS_CH2 | R/W | 0 |
Noise-suppression mode selection for channel 2 0 = LFNS disabled (default) 1 = Low-frequency noise-suppression mode enable for channel 2 |
| D1 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D0 | LFNS_CH1 | R/W | 0 |
Noise-suppression mode selection for channel 1 0 = LFNS disabled (default) 1 = Low-frequency noise-suppression mode enable for channel 1 |
7.6.1.7 Register 1Ch (offset = 1Ch) [reset = 0]
This is a test pattern register. All bits default to 0 after reset.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| X | EN_FRAME_PAT | ADCLKOUT[11:0] | |||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | |||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| ADCLKOUT[11:0] | X | ||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||||
Table 13. Register 1Ch Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D14 | EN_FRAME_PAT | R/W | 0 |
Frame pattern enable 0 = Normal frame clock operation 1 = Enables the output frame clock to be programmed through a pattern |
| D13-D2 | ADCLKOUT[11:0] | R/W | 0 |
ADCLK pin frame clock pattern These bits determine the 12-bit pattern for the frame clock on the ADCLKP and ADCLKN pins. |
| D1-D0 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
7.6.1.8 Register 23h (offset = 23h) [reset = 0]
This is a test pattern register.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| PRBS_SEED[15:0] | |||||||
| R/W-0 | |||||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| PRBS_SEED[15:0] | |||||||
| R/W-0 | |||||||
Table 14. Register 23h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15-D0 | PRBS_SEED[15:0] | R/W | 0 |
PRBS pattern seed value, lower bits These bits determine the PRBS pattern starting seed value of the lower 16 bits. (Default = 0) |
7.6.1.9 Register 24h (offset = 24h) [reset = 0]
This is a test pattern register. All bits default to 0 after reset.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| PRBS_SEED[22:16] | X | ||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| INVERT_CH4 | X | INVERT_CH3 | X | INVERT_CH2 | X | INVERT_CH1 | |
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | |
Table 15. Register 24h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15-D9 | PRBS_SEED[22:16] | R/W | 0 |
PRBS pattern seed value, upper bits These bits determine the PRBS pattern starting seed value of the upper seven bits. |
| D8 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D7 | INVERT_CH4 | R/W | 0 |
Analog input pin polarity for channel 4 0 = Normal configuration (default) 1 = Electrically swaps the analog input pin polarity for channel 4 |
| D6 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D5 | INVERT_CH3 | R/W | 0 |
Analog input pin polarity for channel 3 0 = Normal configuration (default) 1 = Electrically swaps the analog input pin polarity for channel 3 |
| D4-D3 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D2 | INVERT_CH2 | R/W | 0 |
Analog input pin polarity for channel 2 0 = Normal configuration (default) 1 = Electrically swaps the analog input pin polarity for channel 2 |
| D1 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D0 | INVERT_CH1 | R/W | 0 |
Analog input pin polarity for channel 1 0 = Normal configuration (default) 1 = Electrically swaps the analog input pin polarity for channel 1 |
7.6.1.10 Register 25h (offset = 25h) [reset = 0]
This is a test pattern register. All bits default to 0 after reset.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| HARD_SYNC_TP | PRBS_SEED_FROM_REG | PRBS_MODE_2 | PRBS_TP_EN | X | TP_SOFT_SYNC | ||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| X | EN_RAMP | DUAL_CUSTOM_PAT | SINGLE_CUSTOM_PAT | BITS_CUSTOM2[13:12] | BITS_CUSTOM1[13:12] | ||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||
Table 16. Register 25h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15 | HARD_SYNC_TP | R/W | 0 |
Sync test pattern selection 0 = Inactive 1 = External SYNC feature enabled for syncing test patterns |
| D14 | PRBS_SEED_FROM_REG | R/W | 0 |
PRBS seed selection 0 = Disabled 1 = Selection of PRBS seed from registers 23h and 24h enabled |
| D13 | PRBS_MODE_2 | R/W | 0 |
PRBS mode selection This bit sets the PRBS mode of the 9-bit LFSR (the 23-bit LFSR is default). |
| D12 | PRBS_TP_EN | R/W | 0 |
PRBS test pattern selection 0 = PRBS test pattern disabled 1 = PRBS test pattern enable bit |
| D11-D9 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D8 | TP_SOFT_SYNC | R/W | 0 |
Test pattern software sync 0 = No sync 1 = Software sync bit for test patterns on all eight channels |
| D7 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D6 | EN_RAMP | R/W | 0 |
Ramp pattern enable 0 = Normal operation 1 = Enables a repeating full-scale ramp pattern on the outputs. Ensure that bits D4 and D5 are 0. |
| D5 | DUAL_CUSTOM_PAT | R/W | 0 |
Output toggles between two codes 0 = Normal operation 1 = Enables mode where the output toggles between two defined codes. Ensure that bits D4 and D6 are 0. |
| D4 | SINGLE_CUSTOM_PAT | R/W | 0 |
Output is defined code 0 = Normal operation 1 = Enables mode where the output is a constant specified code. Ensure that bits D5 and D6 are 0. |
| D3-D2 | BITS_CUSTOM2[13:12] | R/W | 0 |
MSB selection for dual patterns These bits determine two MSBs for the second code of the dual custom patterns. |
| D1-D0 | BITS_CUSTOM1[13:12] | R/W | 0 |
MSB selection for single patterns These bits define two MSBs for the single custom pattern (and for the first code of the dual custom patterns). |
7.6.1.11 Register 26h (offset = 26h) [reset = 0]
This is a test pattern register.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| BITS_CUSTOM1[9:0] | |||||||
| R/W-0 | |||||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| BITS_CUSTOM1[9:0] | X | ||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||||
Table 17. Register 26h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15-D6 | BITS_CUSTOM1[9:0] | R/W | 0 |
Lower single custom pattern bits These bits determine the 10 lower bits for the single custom pattern (and the first code of the dual custom pattern). |
| D5-D0 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
7.6.1.12 Register 27h (offset = 27h) [reset = 0]
This is a test pattern register.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| BITS_CUSTOM2[9:0] | |||||||
| R/W-0 | |||||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| BITS_CUSTOM2[9:0] | X | ||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||||
Table 18. Register 27h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15-D6 | BITS_CUSTOM2[9:0] | R/W | 0 | Lower dual custom pattern bits These bits determine the 10 lower bits for the second code of the dual custom pattern. |
| D5-D0 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
7.6.1.13 Register 28h (offset = 28h) [reset = 0]
This is an output interface mode register. All bits default to 0 after reset.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| EN_BITORDER | X | BIT_WISE | |||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | |||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| EN_WORDWISE_BY_CH[7:0] | |||||||
| R/W-0 | |||||||
Table 19. Register 28h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15 | EN_BITORDER | R/W | 0 |
Bit order enable(1) This bit enables the bit order output in two-lane mode. 0 = Byte-wise 1 = Word-wise |
| D14-D9 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D8 | BIT_WISE | R/W | 0 |
Bit- or byte-wise selection This bit selects between byte-wise and bit-wise format. 0 = Byte-wise, the upper bits come are on one lane and the lower bits are on other lane 1 = Bit-wise, the odd bits come out on one lane and the even bits come out on other lane |
| D7-D0 | EN_WORDWISE_BY_CH[7:0] | R/W | 0 |
Word-wise enable with channels 7 to 0 0 = Data comes out in two-lane mode with the upper set of bits on one channel and the lower set of bits on the other channel 1 = Output format is one sample on one LVDS lane with the next sample on the other LVDS lane |
7.6.1.14 Register 29h (offset = 29h) [reset = 0]
This is a digital filter mode register. All bits default to 0 after reset.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| X | |||||||
| R/W-0 | |||||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| X | GLOBAL_EN_FILTER | X | |||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | |||||
Table 20. Register 29h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15-D2 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D1 | GLOBAL_EN_FILTER | R/W | 0 |
Filter block enable 0 = Inactive 1 = Global control filter blocks enabled |
| D0 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
7.6.1.15 Register 2Ah (offset = 2Ah) [reset = 0]
This is a digital gain mode register. All bits default to 0 after reset.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| X | GAIN_CH2[3:0] | ||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| X | GAIN_CH1[3:0] | ||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||||
Table 21. Register 2Ah Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15-D12 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D11-D8 | GAIN_CH2[3:0] | R/W | 0 |
Channel 2 gain These bits set the programmable gain of channel 2 |
| D7-D4 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D3-D0 | GAIN_CH3[3:0] | R/W | 0 |
Channel 1 gain These bits set the programmable gain of channel 1 |
7.6.1.16 Register 2Bh (offset = 2Bh) [reset = 0]
This is a digital gain mode register. All bits default to 0 after reset.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| X | GAIN_CH3[3:0] | ||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| X | GAIN_CH4[3:0] | ||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||||
Table 22. Register 2Bh Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15-D12 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D11-D8 | GAIN_CH3[3:0] | R/W | 0 |
Channel 3 gain These bits set the programmable gain of channel 3 |
| D7-D4 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D3-D0 | GAIN_CH4[3:0] | R/W | 0 |
Channel 4 gain These bits set the programmable gain of channel 4 |
7.6.1.17 Register 2Eh (offset = 2Eh) [reset = 0]
This is a digital filter mode register. All bits default to 0 after reset.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| X | HPF_EN_CH1 | HPF_CORNER _CH1[3:0] | FILTER1_COEFF_SET[2:0] | ||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| FILTER1_COEFF_SET[2:0] | FILTER1_RATE[2:0] | X | ODD_TAP1 | X | USE_FILTER1 | ||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||
Table 23. Register 2Eh Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D14 | HPF_EN_CH1 | R/W | 0 |
Channel 1 HPF filter enable 0 = Disabled 1 = HPF filter enable for channel 1 |
| D13-D10 | HPF_CORNER _CH1[3:0] | R/W | 0 |
HPF corner for channel 1 These bits set the HPF corner in values from 2k to 10k. |
| D9-D7 | FILTER1_COEFF_SET[2:0] | R/W | 0 |
Filter 1 coefficient set These bits select the stored coefficient set for filter 1. |
| D6-D4 | FILTER1_RATE[2:0] | R/W | 0 |
Filter 1 decimation factor These bits set the decimation factor for filter 2. |
| D3 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D2 | ODD_TAP1 | R/W | 0 |
Filter 1 odd tap This bit uses odd tap filter 1. |
| D1 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D0 | USE_FILTER1 | R/W | 0 |
Channel 1 filter 0 = Disabled 1 = Enables filter for channel 1 |
7.6.1.18 Register 30h (offset = 30h) [reset = 0]
This is a digital filter mode register. All bits default to 0 after reset.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| X | HPF_EN_CH2 | HPF_CORNER _CH2[3:0] | FILTER2_COEFF_SET[2:0] | ||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| FILTER2_COEFF_SET[2:0] | FILTER2_RATE[2:0] | X | ODD_TAP2 | X | USE_FILTER2 | ||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||
Table 24. Register 30h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D14 | HPF_EN_CH2 | R/W | 0 |
Channel 2 HPF filter enable 0 = Disabled 1 = HPF filter enable for channel 2 |
| D13-D10 | HPF_CORNER _CH2[3:0] | R/W | 0 |
HPF corner for channel 2 These bits set the HPF corner in values from 2k to 10k. |
| D9-D7 | FILTER2_COEFF_SET[2:0] | R/W | 0 |
Filter 2 coefficient set These bits select the stored coefficient set for filter 2. |
| D6-D4 | FILTER2_RATE[2:0] | R/W | 0 |
Filter 2 decimation factor These bits set the decimation factor for filter 2. |
| D3 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D2 | ODD_TAP2 | R/W | 0 |
Filter 2 odd tap This bit uses odd tap filter 2. |
| D1 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D0 | USE_FILTER2 | R/W | 0 |
Channel 2 filter 0 = Disabled 1 = Enables filter for channel 2 |
7.6.1.19 Register 33h (offset = 33h) [reset = 0]
This is a digital filter mode register. All bits default to 0 after reset.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| X | HPF_EN_CH3 | HPF_CORNER _CH3[3:0] | FILTER3_COEFF_SET[2:0] | ||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| FILTER3_COEFF_SET[2:0] | FILTER3_RATE[2:0] | X | ODD_TAP3 | USE_FILTER3 | |||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | |||
Table 25. Register 33h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D14 | HPF_EN_CH3 | R/W | 0 |
Channel 3 HPF filter enable 0 = Disabled 1 = HPF filter enable for channel 3 |
| D13-D10 | HPF_CORNER _CH3[3:0] | R/W | 0 |
HPF corner for channel 3 These bits set the HPF corner in values from 2k to 10k. |
| D9-D7 | FILTER3_COEFF_SET[2:0] | R/W | 0 |
Filter 3 coefficient set These bits select the stored coefficient set for filter 3. |
| D6-D4 | FILTER3_RATE[2:0] | R/W | 0 |
Filter 3 decimation factor These bits set the decimation factor for filter 3. |
| D3 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D2 | ODD_TAP3 | R/W | 0 |
Filter 3 odd tap This bit uses odd tap filter 3. |
| D1 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D0 | USE_FILTER3 | R/W | 0 |
Channel 3 filter 0 = Disabled 1 = Enables filter for channel 3 |
7.6.1.20 Register 35h (offset = 35h) [reset = 0]
This is a digital filter mode register. All bits default to 0 after reset.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| X | HPF_EN_CH4 | HPF_CORNER _CH4[3:0] | FILTER4_COEFF_SET[2:0] | ||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| FILTER4_COEFF_SET[2:0] | FILTER4_RATE[2:0] | X | ODD_TAP4 | X | USE_FILTER4 | ||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||
Table 26. Register 35h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D14 | HPF_EN_CH4 | R/W | 0 |
Channel 4 HPF filter enable 0 = Disabled 1 = HPF filter enable for channel 4 |
| D13-D10 | HPF_CORNER _CH4[3:0] | R/W | 0 |
HPF corner for channel 4 These bits set the HPF corner in values from 2k to 10k. |
| D9-D7 | FILTER4_COEFF_SET[2:0] | R/W | 0 |
Filter 4 coefficient set These bits select the stored coefficient set for filter 4. |
| D6-D4 | FILTER4_RATE[2:0] | R/W | 0 |
Filter 4 decimation factor These bits set the decimation factor for filter 4. |
| D3 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D2 | ODD_TAP4 | R/W | 0 |
Filter 4 odd tap This bit uses odd tap filter 4. |
| D1 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D0 | USE_FILTER4 | R/W | 0 |
Channel 4 filter 0 = Disabled 1 = Enables filter for channel 4 |
7.6.1.21 Register 38h (offset = 38h) [reset = 0x0000]
This is an output interface mode register.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| X | |||||||
| R/W- | |||||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| X | DATA_RATE[1:0] | ||||||
| R/W- | R/W- | ||||||
Table 27. Register 38h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15-D2 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D1-D0 | DATA_RATE[1:0] | R/W | 0 |
Clock rate selection These bits select the output frame clock rate. (Default = 0) |
7.6.1.22 Register 42h (offset = 42h) [reset = 0]
This is an output interface mode register.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| EN_REF_VCM0 | X | ||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| X | PHASE_DDR[1:0] | X | EN_REF_VCM1 | X | |||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | |||
Table 28. Register 42h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15 | EN_REF_VCM0 | R/W | 0 |
To enable the external reference mode, the EN_EXT_REF register bit (register F0h) must be set to 1. 00 = In external reference mode, apply the reference on the REFT, REFB pins 01, 10 = Don't use 11 = In external reference mode, apply the reference on the VCM pin |
| D14-D7 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D6-D5 | PHASE_DDR[1:0] | R/W | 0 | These bits control the LCLK output phase relative to data. (Default = 10) |
| D4 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D3 | EN_REF_VCM1 | R/W | 0 |
To enable the external reference mode, the EN_EXT_REF register bit (register F0h) must be set to 1. 00 = In external reference mode, apply the reference on the REFT, REFB pins 01, 10 = Don't use 11 = In external reference mode, apply the reference on the VCM pin |
| D2-D0 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
7.6.1.23 Register 45h (offset = 45h) [reset = 0]
This is a test pattern register. All bits default to 0 after reset.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| X | |||||||
| R/W-0 | |||||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| X | PAT_SYNC | PAT_DESKEW | |||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | |||||
Table 29. Register 45h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15-D2 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D1 | PAT_SYNC | R/W | 0 |
Sync pattern enable 0 = Inactive 1 = Sync pattern mode enabled; ensure that D0 is 0 |
| D0 | PAT_DESKEW | R/W | 0 |
Deskew pattern enable 0 = Inactive 1 = Deskew pattern mode enabled; ensure that D1 is 0 |
7.6.1.24 Register 46h (offset = 46h) [reset = 0]
This is an output interface mode register. All bits default to 0 after reset.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| ENABLE 46 | X | FALL_SDR | X | EN_16BIT | EN_14BIT | EN_12BIT | X |
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 |
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| X | EN_SDR | MSB_FIRST | BTC_MODE | X | EN_2LANE | ||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||
Table 30. Register 46h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15 | ENABLE 46 | R/W | 0 |
Enable register 46(1) This bit enables register 46. |
| D14 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D13 | FALL_SDR | R/W | 0 |
SDR output mode 0 = At data window edge 1 = The LCLK rising or falling edge control comes in the middle of the data window when operating in SDR output mode |
| D12 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D11 | EN_16BIT | R/W | 0 |
16-bit mode enable 0 = Inactive 1 = 16-bit serialization mode enabled; ensure bits D[10:9] are 0 |
| D10 | EN_14BIT | R/W | 0 |
14-bit mode enable 0 = Inactive 1 = 14-bit serialization mode enabled; ensure bits D11 and D9 are 0 |
| D9 | EN_12BIT | R/W | 0 |
12-bit mode enable 0 = Inactive 1 = 12-bit serialization mode enabled; ensure bits D[11:10] are 0 |
| D8-D5 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D4 | EN_SDR | R/W | 0 |
Bit clock selection 0 = DDR bit clock 1 = SDR bit clock |
| D3 | MSB_FIRST | R/W | 0 |
MSB first selection 0 = LSB first 1 = MSB first |
| D2 | BTC_MODE | R/W | 0 |
Binary mode selection 0 = Binary offset (ADC data output format) 1 = Binary twos complement (ADC data output format) |
| D1 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bit |
| D0 | EN_2LANE | R/W | 0 |
LVDS output lane selection 0 = One-lane LVDS output 1 = Two-lane LVDS output |
7.6.1.25 Register 50h (offset = 50h) [reset = 0]
This is a programmable LVDS mapping mode register. All bits default to 0 after reset.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| ENABLE 50 | X | ||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| MAP_CH12_TO_OUT1B[3:0] | MAP_CH12_TO_OUT1A[3:0] | ||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||||
Table 31. Register 50h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15 | ENABLE 50 | R/W | 0 |
Enable for register 50h(1) This bit enables register 50h. |
| D14-D8 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D7-D4 | MAP_CH12_TO_OUT1B[3:0] | R/W | 0 |
OUT1B pin to channel mapping These bits select the OUT1B pin pair to channel data mapping. |
| D3-D0 | MAP_CH12_TO_OUT1A[3:0] | R/W | 0 |
OUT1A pin to channel mapping These bits select the OUT1A pin pair to channel data mapping. |
7.6.1.26 Register 51h (offset = 51h) [reset = 0]
This is a programmable LVDS mapping mode register. All bits default to 0 after reset.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| ENABLE 51 | X | MAP_CH12_TO_OUT2B[3:0] | |||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | |||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| MAP_CH12_TO_OUT2A[3:0] | X | ||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||||
Table 32. Register 51h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15 | ENABLE 51 | R/W | 0 |
Enable for register 51h(1) This bit enables register 51h. |
| D14-D12 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D11-D8 | MAP_CH12_TO_OUT2B[3:0] | R/W | 0 |
OUT2B pin to channel mapping These bits select the OUT2B pin pair to channel data mapping. |
| D7-D4 | MAP_CH12_TO_OUT2A[3:0] | R/W | 0 |
OUT2A pin to channel mapping These bits select the OUT2A pin pair to channel data mapping. |
| D3-D0 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
7.6.1.27 Register 53h (offset = 53h) [reset = 0]
This is a programmable LVDS mapping mode register. All bits default to 0 after reset.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| ENABLE 53 | X | MAP_CH34_TO_OUT3B[3:0] | |||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | R/W-0 | |||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| X | |||||||
| R/W-0 | |||||||
Table 33. Register 53h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15 | ENABLE 53 | R/W | 0 |
Enable register 53h(1) This bit enables register 53h. |
| D14-D12 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D11-D8 | MAP_CH34_TO_OUT3B[3:0] | R/W | 0 |
OUT3B pin to channel mapping These bits select the OUT3B pin pair to channel data mapping. |
| D7-D0 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
7.6.1.28 Register 54h (offset = ) [reset = 0]
This is a programmable LVDS mapping mode register. All bits default to 0 after reset.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| ENABLE 54 | X | ||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| X | MAP_Ch34_to_OUT3A[3:0] | ||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||||
Table 34. Register 54h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15 | ENABLE 54 | R/W | 0 |
Enable register 54h(1) This bit enables register 54h. |
| D14-D4 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D3-D0 | MAP_Ch34_to_OUT3A[3:0] | R/W | 0 |
OUT3A pin to channel mapping These bits select the OUT3A pin pair to channel data mapping. |
7.6.1.29 Register 55h (offset = 55h) [reset = 0]
This is a programmable LVDS mapping mode register. All bits default to 0 after reset.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| ENABLE 55 | X | ||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| MAP_CH34_TO_OUT4A[3:0] | MAP_CH34_TO_OUT4B[3:0] | ||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||||
Table 35. Register 55h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15 | ENABLE 55 | R/W | 0 |
Enable register 55h(1) This bit enables register 55h. |
| D14-D8 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |
| D7-D4 | MAP_CH34_TO_OUT4A[3:0] | R/W | 0 |
OUT4A pin to channel mapping These bits select the OUT4A pin pair to channel data mapping. |
| D3-D0 | MAP_CH34_TO_OUT4B[3:0] | R/W | 0 |
OUT4B pin to channel mapping These bits select the OUT4B pin pair to channel data mapping. |
7.6.1.30 Register F0h (offset = F0h) [reset = 0]
This is a general register.
NOTE
The EN_HIGH_ADDRS bit (register 01h, bit D4) must be set to 1 in order to access this register.
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 |
| EN_EXT_REF | X | ||||||
| R/W-0 | R/W-0 | ||||||
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| X | |||||||
| R/W-0 | |||||||
Table 36. Register F0h Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Type | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15 | EN_EXT_REF | R/W | 0 |
Reference mode selection 0 = Internal reference mode enabled (default) 1 = External reference mode enabled. The voltage reference can be applied on either the REFP and REFB pins or the VCM pin. |
| D7-D0 | X | R/W | 0 | Don't care bits |