JAJSE50 November 2017 TLA2021 , TLA2022 , TLA2024
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 概要(続き)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Register Maps
- 11Application and Implementation
- 12Power Supply Recommendations
- 13Layout
- 14デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 15メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
9.5.2.2 Writing the Configuration Register
Write the configuration register as shown in Figure 13 using a single I2C communication frame. The R/W bit at the end of the salve address is 0 to indicate a write. The host first sends the register pointer that points to the configuration register, followed by two bytes that represent the register content to write. The TLA202x acknowledge each received byte.
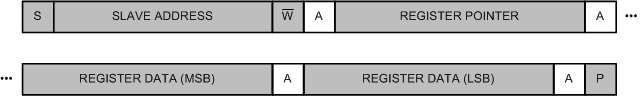 Figure 13. Writing Register Data
Figure 13. Writing Register Data Figure 14 provides a legend for Figure 12 and Figure 13.
 Figure 14. Legend for the I2C Sequence Diagrams
Figure 14. Legend for the I2C Sequence Diagrams