SBOU124B march 2012 – july 2023 INA230
- 1
- INA230EVM Evaluation Board and Software Tutorial
- Trademarks
- 1Overview
- 2INA230EVM Hardware
- 3INA230EVM (Rev A) Hardware Setup
- 4INA230EVM Software Setup
- 5INA230EVM Software Overview
- 6INA230EVM Documentation
- 7Revision History
5.2.1 I2C Address Selection
The INA230 device has a flexible I2C address configuration that allows multiple devices on the same I2C lines. By moving the A0 and A1 addresses on jumpers J3-J6 to either GND, VS, SDA or SCL, the user can change the INA230 to a total of 16 I2C addresses (see Table 5-1).
Table 5-1 INA230 I2C Address Configuration
| A1 | A0 | TARGET ADDRESS |
|---|---|---|
| GND | GND | 1000000 |
| GND | VS+ | 1000001 |
| GND | SDA | 1000010 |
| GND | SCL | 1000011 |
| VS+ | GND | 1000100 |
| VS+ | VS+ | 1000101 |
| VS+ | SDA | 1000110 |
| VS+ | SCL | 1000111 |
| SDA | GND | 1001000 |
| SDA | VS+ | 1001001 |
| SDA | SDA | 1001010 |
| SDA | SCL | 1001011 |
| SCL | GND | 1001100 |
| SCL | VS+ | 1001101 |
| SCL | SDA | 1001110 |
| SCL | SCL | 1001111 |
Figure 5-3 shows how to configure the I2C addresses. Click the A0 or A1 box and select how to configure the hardware on the EVM. Failure to select the correct address prevents the INA230 device from communicating with the software.
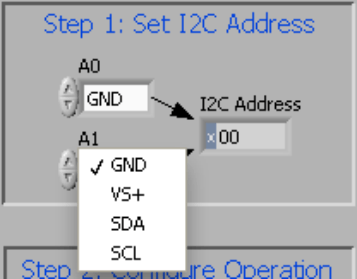 Figure 5-3 Setting the A1 Address
Figure 5-3 Setting the A1 Address