SLAA600E June 2013 – January 2024
- 1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2Implementation
- 3Customization of MSPBoot
- 4Building MSPBoot
- 5References
- 6Revision History
2.2.2 Vector Redirection
MSPBoot cannot erase or reprogram the bootloader area. This limitation provides a more secure implementation, because the bootloader is always accessible, and the MCU can be recovered by forcing bootloader mode.
The reset vector is an integral part of the bootloader, because it forces the MCU to always jump to the bootloader entry sequence, and thus it should not be erased. Because the reset vector resides in the top of 16-bit flash space (0xFFFE), the bootloader code is placed in the contiguous locations (see Figure 2-4).
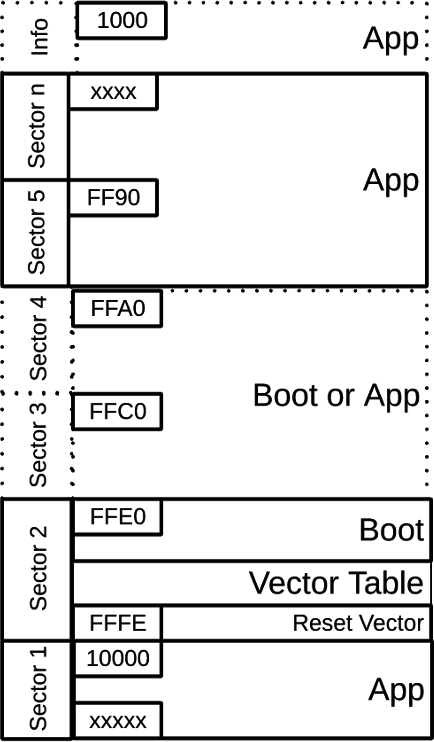 Figure 2-4 Memory Assignment
Figure 2-4 Memory AssignmentThe interrupt vector table also resides in protected Boot area. Because the value of the interrupt table is expected to change based on the application, this means that special considerations must be followed to allow for application interrupts. Additional 20-bit space is available for the application in large memory model devices (0x10000 and above).