SLAA649G October 2014 – August 2021 MSP430F2001 , MSP430F2002 , MSP430F2003 , MSP430F2011 , MSP430F2012 , MSP430F2013 , MSP430F2013-EP , MSP430F2101 , MSP430F2111 , MSP430F2112 , MSP430F2121 , MSP430F2122 , MSP430F2131 , MSP430F2132 , MSP430F2232 , MSP430F2234 , MSP430F2252 , MSP430F2254 , MSP430F2272 , MSP430F2274 , MSP430F2274-EP , MSP430F233 , MSP430F2330 , MSP430F235 , MSP430F2350 , MSP430F2370 , MSP430F2410 , MSP430F2416 , MSP430F2417 , MSP430F2418 , MSP430F2419 , MSP430F247 , MSP430F2471 , MSP430F248 , MSP430F2481 , MSP430F249 , MSP430F249-EP , MSP430F2491 , MSP430F2616 , MSP430F2617 , MSP430F2618 , MSP430F2619 , MSP430F2619S-HT , MSP430FR2032 , MSP430FR2033 , MSP430FR2110 , MSP430FR2111 , MSP430FR2153 , MSP430FR2155 , MSP430FR2310 , MSP430FR2311 , MSP430FR2353 , MSP430FR2355 , MSP430FR2433 , MSP430FR2475 , MSP430FR2476 , MSP430FR2532 , MSP430FR2533 , MSP430FR2632 , MSP430FR2633 , MSP430FR2672 , MSP430FR2673 , MSP430FR2675 , MSP430FR2676 , MSP430FR4131 , MSP430FR4132 , MSP430FR4133 , MSP430G2001 , MSP430G2101 , MSP430G2102 , MSP430G2111 , MSP430G2112 , MSP430G2121 , MSP430G2131 , MSP430G2132 , MSP430G2152 , MSP430G2153 , MSP430G2201 , MSP430G2202 , MSP430G2203 , MSP430G2210 , MSP430G2211 , MSP430G2212 , MSP430G2213 , MSP430G2221 , MSP430G2230 , MSP430G2230-EP , MSP430G2231 , MSP430G2231-EP , MSP430G2232 , MSP430G2233 , MSP430G2252 , MSP430G2253 , MSP430G2302 , MSP430G2302-EP , MSP430G2303 , MSP430G2312 , MSP430G2313 , MSP430G2332 , MSP430G2332-EP , MSP430G2333 , MSP430G2352 , MSP430G2353 , MSP430G2402 , MSP430G2403 , MSP430G2412 , MSP430G2413 , MSP430G2432 , MSP430G2433 , MSP430G2444 , MSP430G2452 , MSP430G2453 , MSP430G2513 , MSP430G2533 , MSP430G2544 , MSP430G2553 , MSP430G2744 , MSP430G2755 , MSP430G2855 , MSP430G2955 , MSP430I2020 , MSP430I2021 , MSP430I2030 , MSP430I2031 , MSP430I2040 , MSP430I2041
- Trademarks
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Comparison of MSP430FR4xx and MSP430FR2xx Devices
- 3 In-System Programming of Nonvolatile Memory
- 4 Hardware Migration Considerations
- 5 Device Calibration Information
- 6 Important Device Specifications
- 7 Core Architecture Considerations
- 8 Peripheral Considerations
- 9 ROM Libraries
- 10Conclusion
- 11References
- 12Revision History
7.1.1 Core LDO and LPM3.5 LDO
The F2xx family devices use a single voltage rail to power the chip, that is, a single power rail supplies both the analog peripherals and the digital core on the chip. The FR4xx family also uses a single voltage supply. However unlike F2xx, there are no AVCC and AVSS pins, only DVCC and DVSS. The external voltage supply on the DVCC pin is fed to an internal low-dropout voltage regulator (LDO) (see Figure 7-1).
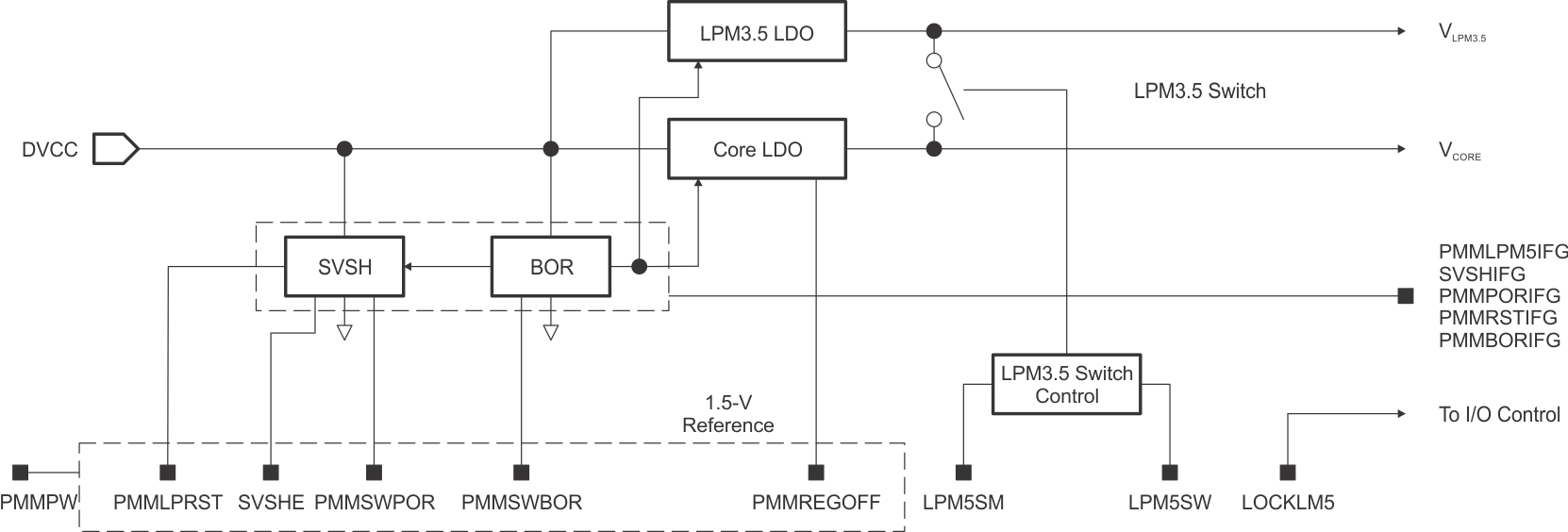 Figure 7-1 PMM Block Diagram
Figure 7-1 PMM Block DiagramThe PMM manages all functions related to the core voltage and its supervision. Its primary functions are, first, to generate a supply voltage for the core logic and, second, to provide several mechanisms for the supervision of both the voltage supplied to the device (DVCC) and the voltage generated for the core (VCORE).
Using the PMM is especially advantageous as it allows the core to operate at a lower voltage, which brings significant power savings. It also ensures that the core receives a stable and regulated voltage over a wide supply range.
This allows the FR4xx devices to operate across the entire voltage range of the device at the maximum device frequency of 16 MHz. In comparison, F2xx devices have a relationship between system frequency and supply voltage that must be followed to ensure proper operation of the device (see Table 6-1).
There is a second LDO integrated in FR4xx, the LPM3.5 LDO. This LDO supplies the current for the LPM3.5 power domain logic, which contains the RTC and LCD modules (only the MSP430FR4xx MCUs have the LCD module). In LPMx.5 low-power modes, the core LDO is turned off. When entering LPM3.5, the LPM3.5 switch is turned off to save power consumption. When exiting LPM3.5 power mode, the LPM3.5 switch is turned on so that the core LDO can supply power to the LPM3.5 domain logic to support high-frequency operation (see Figure 7-1).