SLOA227B October 2015 – March 2019 TRF7964A , TRF7964A , TRF7970A , TRF7970A
-
NFC/HF RFID reader/writer using the TRF7970A
- Trademarks
- 1 Terms, Definitions, and Symbols
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Initial RF Collision
- 4 TRF7970A Register Settings
- 5 Reader/Writer Mode
- 6 Hardware Description
- 7 Reader/Writer Firmware Example
- 8 Quick Start Guide
- 9 Operational Overview
- 10 Reader/Writer Interoperability Results
- 11 Conclusion
- 12 References
- Revision History
5.2.3.2 NDEF Format
To read an NDEF message from a Type 4 tag, a series of selections and reads must be performed to properly access the data. The first step is to select the NDEF Application, which is signified by an Application ID of 0xD2760000850101. The second step is to select the Capability Container file. NDEF applications must contain the Capability Container file with a File ID of 0xE103.
To read the contents of the CC, the first two bytes must be read first to determine the length of the CC, and then the rest of the CC must be read. The CC contains the File ID information for the NDEF data, and that must be used to read the correct File IDs to read all of the NDEF data from the tag. The CC also contains the TLV fields for each NDEF message stored.
There may be multiple files present in a single tag, so the information for each individual file must be stored within the CC. See Figure 19 and Figure 20 for an example of how the tag memory of a properly formatted NDEF message looks.
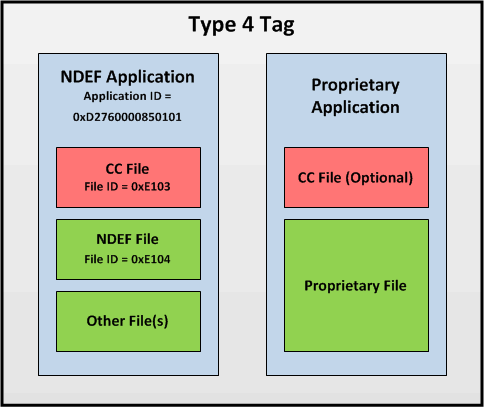 Figure 19. Type 4 Tag NDEF Structure
Figure 19. Type 4 Tag NDEF Structure 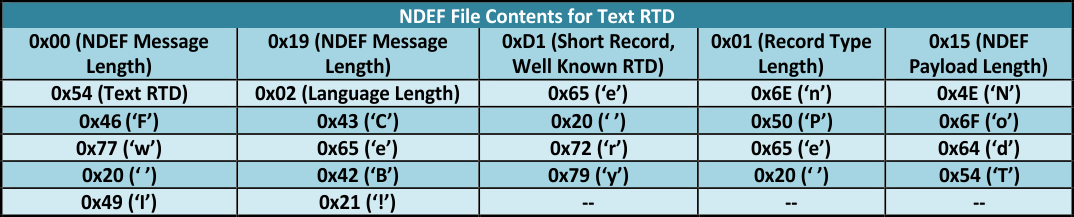 Figure 20. Type 4 NDEF File Example for Text RTD
Figure 20. Type 4 NDEF File Example for Text RTD