SSZT408 september 2019 CC1352P
Building security systems come in many system topologies, ranging from a simple alarm system to a complicated network of sensors that all report to a main security panel acting as a hub. These systems are either wired or wireless based on their deployment, and when wireless leverage many different types of connectivity to achieve their specific application. Some applications (like security cameras) use Wi-Fi® for a native connection to the cloud, while some smart applications (like door locks) use Bluetooth® low energy in order to connect to phones and tablets. Security systems based on sensor networks, such as smoke detectors, motion detectors, door/window sensors, temp / humidity sensors, and glass-break detectors, can benefit from using Sub-1 GHz networks.
Sub-1 GHz technology offers many advantages when designing a building security system, including achieving much longer range and better wall penetration than 2.4 GHz technology. This enables whole building coverage without the need for repeaters and without having to use a complicated mesh network topology. Sub-1 GHz is also very low power, enabling remote sensors to operate for 10 years on a coin-cell battery. This benefit offers system design flexibility, eliminating the need to route wires inside ceilings and walls.
One essential point when designing building security systems is that the communication must be reliable. Sub-1 GHz systems offer high robustness by taking advantage of the Sub-1 GHz frequency band, which is less crowded than the 2.4 GHZ band.
While it is clear that Sub-1 GHz has many key advantages for building security design, often security systems and sensors must have a cloud connection or a smart device interface requiring Wi-Fi and Bluetooth low energy. However, it is very complicated to design a system that sends and receives sensor data over a Sub-1 GHz star network, connects to the cloud, and provides a smart device interface. Thanks to the dual-band capabilities and flexible radio features of the CC1352P wireless microcontroller (MCU) and the Sub-1 GHz Linux Gateway solution, you can easily develop products that seamlessly connect to both smart devices and the cloud while still leveraging the benefits of Sub-1 GHz technology with an integrated, low power 20dBm PA for longer range.
The Sub-1 GHz Linux Gateway SDKscales to many different applications. For instance, imagine designing a building security system including smoke detectors, motion detectors, door & window sensors, and glass-break detectors covering a whole building, and all communicating with a centralized security panel. The system design requires that consumers view sensor data on the web or a smart device. The solution can help achieve this use case, while supporting a fast time to market and being flexible enough to enable various solution architectures.
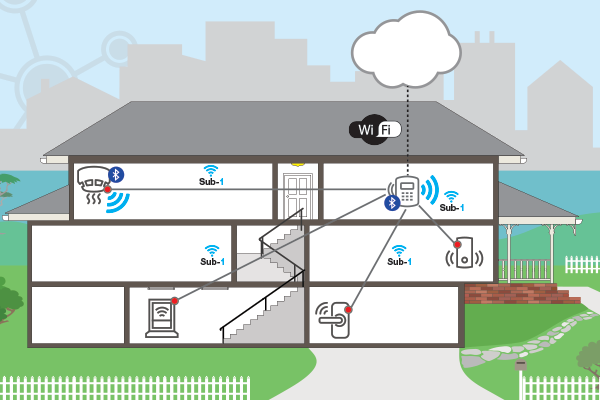 Figure 1 Home security system example
Figure 1 Home security system exampleAs Figure 1 shows, the peripheral sensors (smoke detector, motion detector, door/window sensors and glass-break detectors) all talk to the central security panel over a Sub-1 GHz star network. The security system leverages the long range and wall penetration of Sub-1 GHz to cover the whole building. Additionally, you can place sensors that don’t have access to AC power, like the door and window sensors, remotely; they can run for 10 years on a coin-cell battery. Using the CC13152P dual-band MCU, the smoke detector can connect over Bluetooth low energy to a phone or tablet and send users alerts on their smart device.
These alerts can report battery life or any danger detected, while the smoke detectors communicate to the main security panel over the Sub-1 GHz network. The security panel can collect data from all of the sensors and, using Wi-Fi, connect to the cloud to report to the security company or enable visualization of the data on the web. Users can also update the system firmware by connecting to the panel with Bluetooth low energy or receiving the updates from the cloud. The panel can then push those updates out to the peripherals and update the firmware of each node over the Sub-1 GHz network.
This building security system example is just one use case enabled by TI’s Sub-1 GHz gateway solution. The gateway architecture is flexible, enabling interfaces to multiple cloud providers andthe design is based on proven hardware and software from the SimpleLink MCU platform, which will shorten development time and enable quick time to market. Take advantage of the solution and start your design today.