SBOU257 June 2021 PGA2500
1 Product Overview
The PGA2500 is a digitally-controlled, microphone preamplifier integrated circuit designed for amplifying the output of dynamic and condenser microphones and driving high-performance audio analog-to-digital (A/D) converters. Figure 1-1 shows a functional block diagram of the PGA2500.
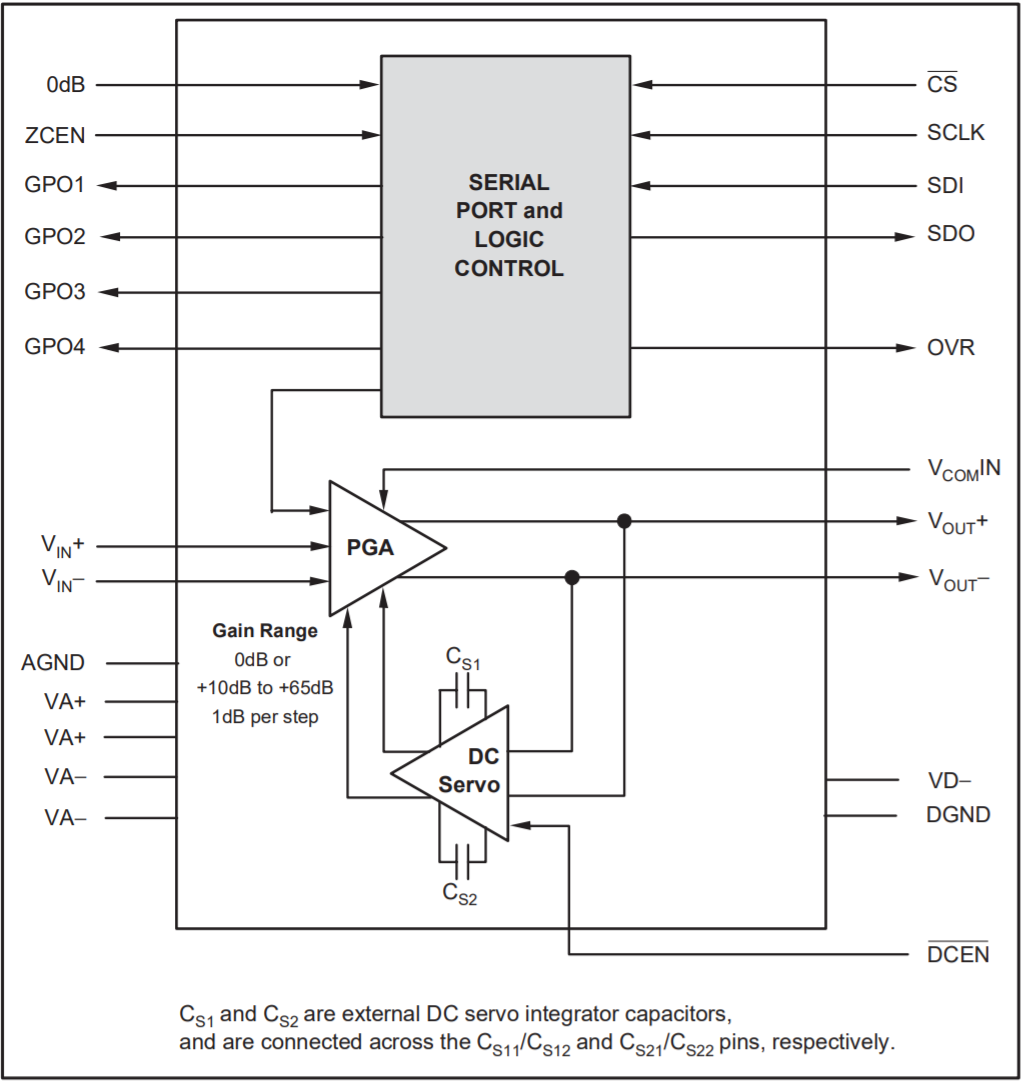 Figure 1-1 PGA2500 Functional Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 PGA2500 Functional Block DiagramThe analog input to the preamplifier is provided differentially at the VIN+ and VIN− inputs (pins 27 and 26, respectively). The programmable gain amplifier can be programmed to either pass through the signal at unity gain, or apply 10 dB to 65 dB of gain to the input signal. The gain of the amplifier is adjustable over the full 10 dB to 65 dB range in 1-dB steps. The differential output of the PGA2500 is made available at VOUT+ and VOUT− (pins 17 and 16, respectively). Gain is controlled using a MSP430F5529 microcontroller and PGA2500EVMV2 Graphical User Interface (GUI), which can be accessed here. The microcontroller and GUI are used to program the PGA2500 gain and support functions, see Figure 1-2.
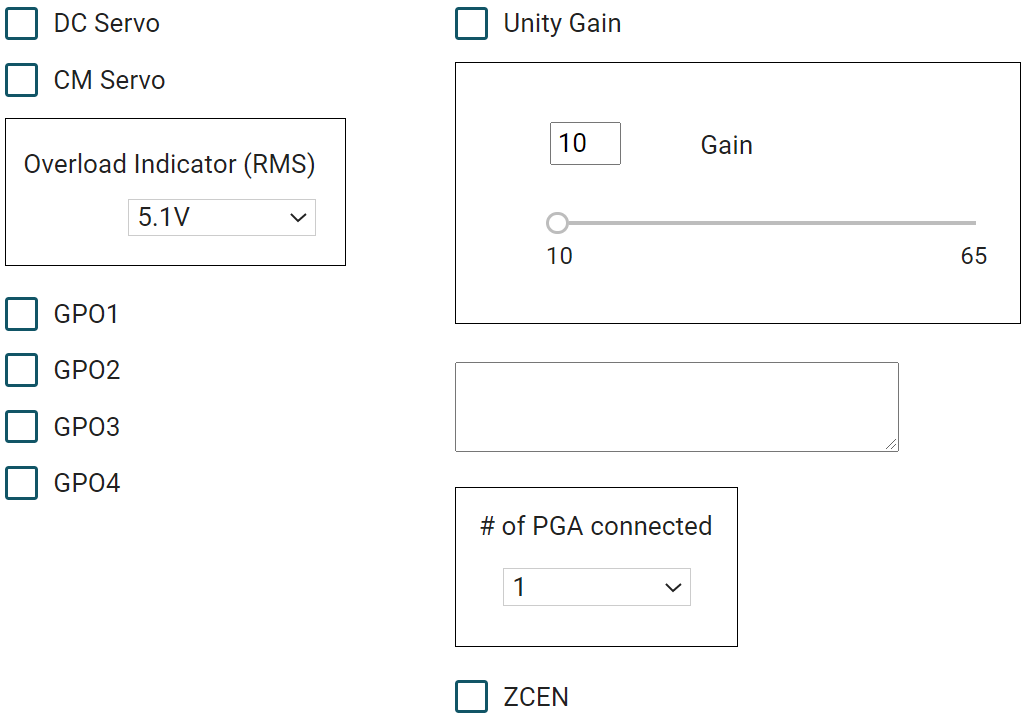 Figure 1-2 PGA2500EVMV2 GUI
Figure 1-2 PGA2500EVMV2 GUIA 16-bit control word is utilized to program these functions; see Figure 1-3.
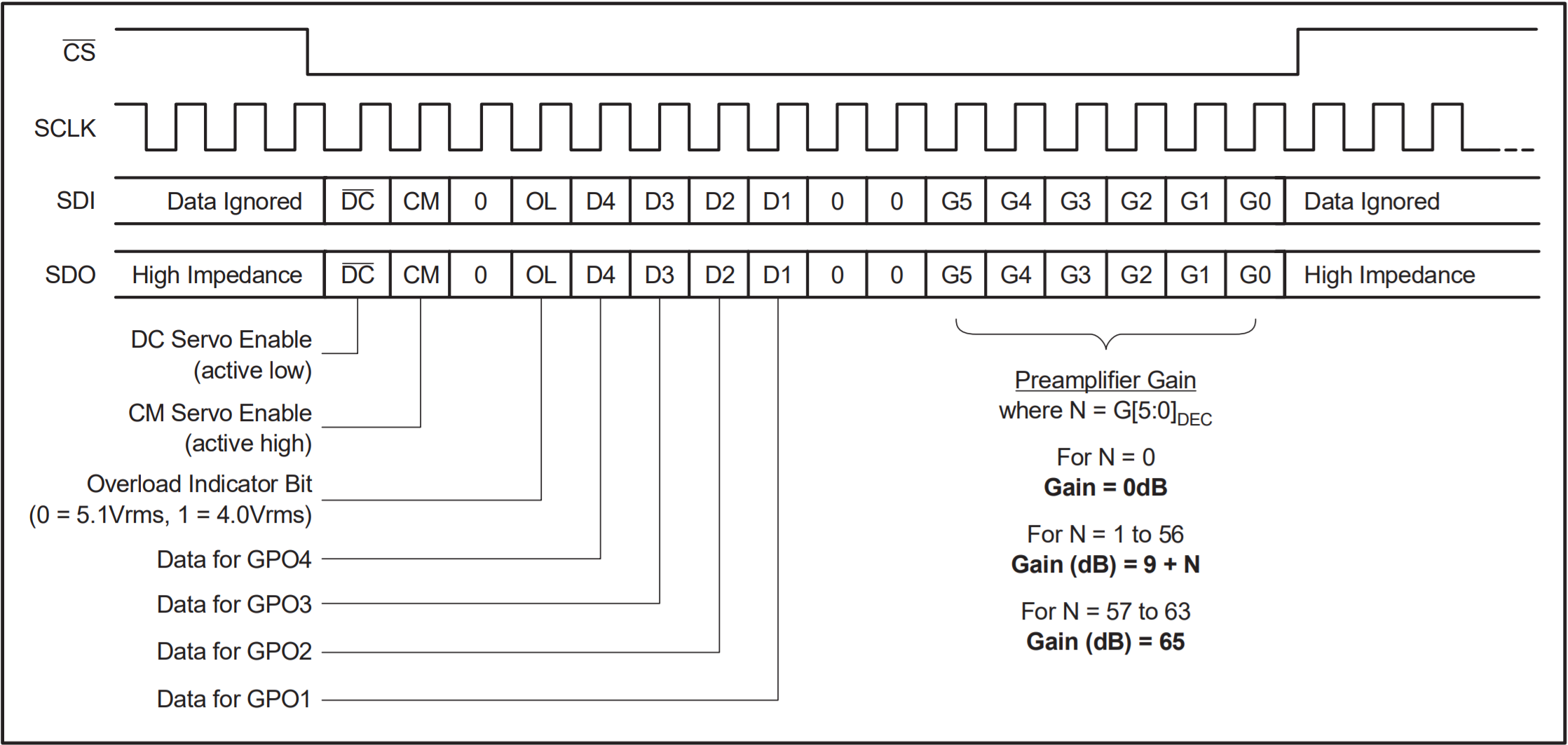 Figure 1-3 PGA2500 16-bit Control
Figure 1-3 PGA2500 16-bit ControlThe differential analog output of the PGA2500 is constantly monitored by a DC servo amplifier loop. The purpose of the servo loop is to minimize the DC offset voltage present at the analog outputs by feeding back an error signal to the input stage of the programmable gain amplifier. The error signal is then used to correct the offset. The DC servo may be enabled by checking the DC Servo checkbox in the GUI. To disable this function, leave the DC Servo checkbox in the GUI unchecked.
Two external capacitors are required for the DC servo function, with one capacitor connected between CS11 and CS12 (pins 24 and 23), and the second capacitor connected between CS21 and CS22 (pins 22 and 21). Capacitor values up to 4.7 µF may be utilized. However, larger valued capacitors will result in longer settling times for the DC servo loop. A value of 1 µF is recommended for use in most microphone preamplifier applications.
The PGA2500 includes a common-mode servo function. This function is enabled and disabled using the CM bit in the serial control word, as shown in Figure 1-3, or by checking the CM Servo checkbox in the GUI. When enabled, the servo provides common-mode negative feedback at the input differential pair, resulting in very low common-mode input impedance. The differential input impedance is not affected by this feedback. This function is useful when the source is floating, or has a high common-mode output impedance. In this case, the only connection between the source and the ground will be through the PGA2500 preamplifier input resistance.
In this case, input common-mode parasitic current is determined by high output impedance of the source, not by input impedance of the amplifier. Therefore, input common-mode interference can be reduced by lowering the common-mode input impedance while not increasing the input common-mode current. Increasing common-mode current degrades common-mode rejection. Using the common-mode servo, overall common-mode rejection can be improved by suppressing low and medium frequency common-mode interference.
The common-mode servo function is designed to operate with a total common mode input capacitance (including the microphone cable capacitance) of up to 10 nF. Beyond this limit, stable servo operation is not ensured.
The common-mode voltage control input, named VCOMIN (pin 25), allows the PGA2500 output and input to be DC biased to a common-mode voltage between 0 V and +2.5 V. This allows for a DC-coupled interface between the PGA2500 preamplifier output and the inputs of common single-supply audio A/D converters.
A dedicated 0-dB input (pin 8) is provided so that the gain of the PGA2500 may be forced to unity. Check the Unity Gain checkbox in the GUI to activate this function.
The zero-crossing control input, named ZCEN (pin 9), is provided for enabling and disabling the internal zero-crossing detector function. Forcing the ZCEN input high enables the function, check the ZCEN checkbox in the GUI to activate this function. Zero-crossing detection is used to force gain changes on zero crossings of the analog input signal. This limits the glitch energy associated with the switched gain network, thereby minimizing audible artifacts at the preamplifier output. Since zero-crossing detection can add some delay when performing gain changes (up to 16 ms maximum for a detector timeout event), there may be cases where the user may wish to disable the function. Forcing the ZCEN input low (unchecking the checkbox in the GUI) disables zero-crossing detection, with gain changes occurring immediately when programmed.
An overflow indicator output, OVR, is provided at pin 5. The OVR pin is an active high, CMOS-logic-level output. The overflow output is forced high when the preamplifier output voltage exceeds one of two preset thresholds. The threshold is programmed through the graphical user interface using the Overload Indicator (RMS) drop-down menu. When this Overload Indicator option is set to "5.1V" RMS differential, that is approximately −1 dB below the specified output voltage range. When the Overload Indicator option is set to "4.0V" RMS differential, that is approximately −3 dB below the specified output voltage range.
The PGA2500 includes four general-purpose programmable digital outputs, named GPO1 through GPO4 (pins 1 through 4, respectively), which are controlled via the GUI as checkboxes. All four pins are CMOS-logic-level outputs. These pins may be used to control relay drivers or switches used for external preamplifier functions, including input pads, filtering, polarity reversal, or phantom power.