SLVSB70C October 2013 – January 2021 TPS62085 , TPS62086 , TPS62087
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Options
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
8.3.1 Power Save Mode
As the load current decreases, the TPS62085, TPS62086, and TPS62087 enter Power Save Mode (PSM) operation. During Power Save Mode, the converter operates with reduced switching frequency and with a minimum quiescent current maintaining high efficiency. The power save mode occurs when the inductor current becomes discontinuous. Power Save Mode is based on a fixed on-time architecture, as related in Equation 1. The switching frequency over the whole load current range is also shown in Figure 7-1 for a typical application.
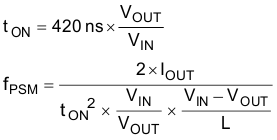
In Power Save Mode, the output voltage rises slightly above the nominal output voltage, as shown in Figure 9-7. This effect is minimized by increasing the output capacitor or inductor value. The output voltage accuracy in PSM operation is reflected in the electrical specification table and given for a 22-μF output capacitor.
During PAUSE period in PSM (shown in Figure 8-1 ), the device does not change the PG pin state nor does it detect an UVLO event, in order to achieve a minimum quiescent current and maintain high efficiency at light loads.
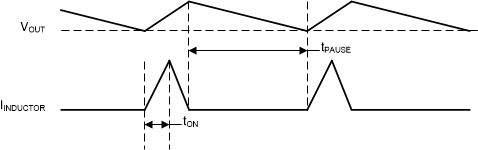 Figure 8-1 Power Save Mode Waveform Diagram
Figure 8-1 Power Save Mode Waveform Diagram