SSZT645 august 2018 TS5USBC400 , TS5USBC402 , TS5USBC41
USB Type-C™ is changing how we connect and use our devices. With the availability of higher voltages at the USB Type-C connector through USB Power Delivery (USB PD), you need to include greater levels of protection in order to safeguard critical system components.
One element to consider is overvoltage protection (OVP), which protects against potential shorts that may occur in your system. The primary purpose of OVP is to protect from VBUS shorts across USB 2.0 data lines, configuration channel (CC) pins and sideband-use (SBU) lines in a USB Type-C connector.
The flip-ability of the connector has many advantages for end users, but the design of the connector brings new challenges, including higher pin counts and smaller sizes, with a reduced pin pitch that can bring new scenarios for damaging internal circuitry. This risk has particular significance in mobile applications such as smartphones and tablets. A USB Type-C connector or plug affected by moisture or debris caught in the pins could lead to a short from the VBUS pins across the USB 2.0 data lines.
Figure 1 shows a scenario where moisture accumulates in a USB Type-C connector. The moisture present will cause a short from the VBUS power pin and the USB 2.0 data lines. When the switch closes to begin data transmission, voltage from VBUS will only be applied to the USB 2.0 data lines. In this case, a solution without OVP will expose sensitive system components behind the switch to higher voltages on the data lines.
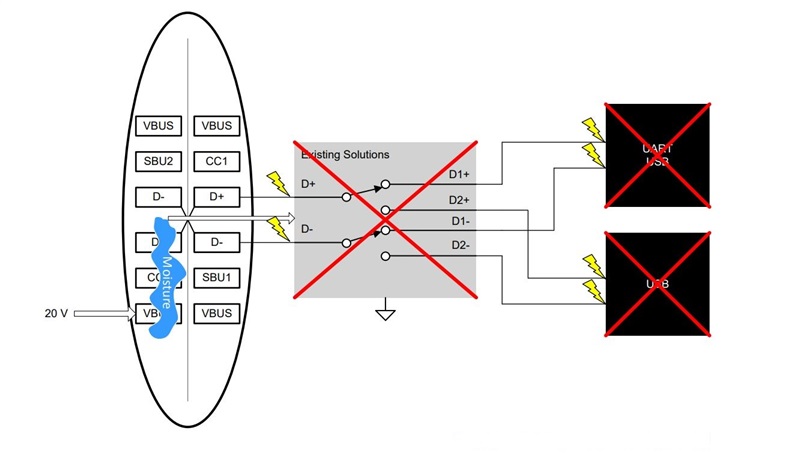 Figure 1 A Traditional USB Switch
without OVP
Figure 1 A Traditional USB Switch
without OVPHigher input voltages for fast-charging implementations in smartphones allow for a higher voltage presence on VBUS in the system for faster battery charging. A VBUS short across data lines when a higher charge voltage is present can damage critical components like processors that are not rated for higher charge voltages.
Noncompliant USB cables or power adapters may also cause concern for overvoltage events. Cables that aren’t rated to support a fast charge or non-USB charging implementation can be subject to overvoltage events, or adapters providing 20V before any USB PD negotiations begin.
With all of the potential scenarios that can damage a system, is there a solution available to thwart overvoltage events?
The TS5USBC41 2-to-1 USB 2.0 switch can support up to 24V OVP for USB Type-C ports (or traditional USB ports), protecting applications that require higher-voltage charging protection from fault conditions. The OVP feature is designed to protect sensitive system components behind the switch that would not survive a VBUS short across the D+ and D- pins on the connector.
Recalling the previous example where moisture was present on the USB Type-C connector, what happens if you include the TS5USBC41 between the connector and the rest of the system? If an overvoltage event were to occur, the TS5USBC41 would open all switches to block 20V from reaching the components, preventing damage to the system.
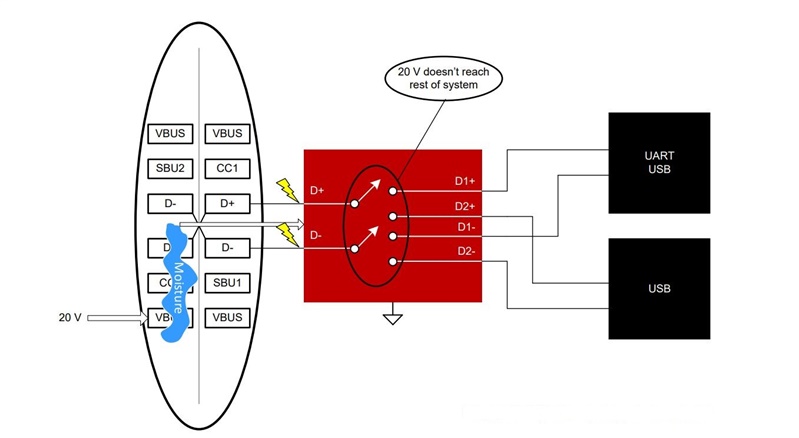 Figure 2 The TS5USBC41 Protecting the
System During an Overvoltage Event
Figure 2 The TS5USBC41 Protecting the
System During an Overvoltage EventThere are two versions of the TS5USBC41 available:
- TS5USBC412 (can suppor 24V OVP)
- TS5USBC410 (can support 20V OVP)
Both of these devices are pin-to-pin compatible in a small 1.62mm-by-1.24mm wafer chip-scale package (WCSP), perfect for mobile applications where small solution size is a critical factor.
The TS5USBC41 is also optimized for low power, and can achieve 10µA active current consumption to enable longer battery life in smartphone and tablet applications.
Another key feature included in the TS5USBC41 is powered-off protection. When the device has no power or when the supply voltage (VCC) is 0V, the input/outputs (I/Os) remain in a high-Z state, preventing errant voltages from reaching the system and maintaining isolation when the system powers up. This is an additional benefit of protection, since the TS5USBC41 is always adding a level of protection to critical system components connected to the device when active or in shutdown mode.
The two versions of the TS5USBC41 are not the only OVP USB switches available from TI. Pin-to-pin variants, the TS5USBC400 and TS5USBC402, share the same architecture as the TS5USBC41, but will provide up to 16V and 20V of OVP, respectively. The TS5USBC400 is good for cost-sensitive projects or implementations that do not require full 20V protection.
Overvoltage events can damage critical system components if there is no protection between the USB connector and the rest of the system. This is particularly critical in smartphones, where fast charging implementations could have a higher voltage present on VBUS. TI has solutions available today to protect USB Type-C ports, as well as traditional USB or Micro-B ports.
Additional Resources
- Watch an overview video about the TS5USBC41