SBAS670B July 2014 – April 2017 ADC3441 , ADC3442 , ADC3443 , ADC3444
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
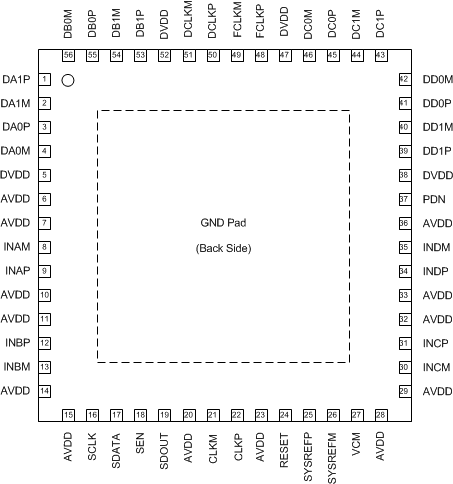
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics: General
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics: ADC3441, ADC3442
- 7.7 Electrical Characteristics: ADC3443, ADC3444
- 7.8 AC Performance: ADC3441
- 7.9 AC Performance: ADC3442
- 7.10 AC Performance: ADC3443
- 7.11 AC Performance: ADC3444
- 7.12 Digital Characteristics
- 7.13 Timing Requirements: General
- 7.14 Timing Requirements: LVDS Output
- 7.15 Typical Characteristics: ADC3441
- 7.16 Typical Characteristics: ADC3442
- 7.17 Typical Characteristics: ADC3443
- 7.18 Typical Characteristics: ADC3444
- 7.19 Typical Characteristics: Common
- 7.20 Typical Characteristics: Contour
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6
Register Maps
- 9.6.1
Serial Register Description
- 9.6.1.1 Register 01h (address = 01h)
- 9.6.1.2 Register 03h (address = 03h)
- 9.6.1.3 Register 04h (address = 04h)
- 9.6.1.4 Register 05h (address = 05h)
- 9.6.1.5 Register 06h (address = 06h)
- 9.6.1.6 Register 07h (address = 07h)
- 9.6.1.7 Register 09h (address = 09h)
- 9.6.1.8 Register 0Ah (address = 0Ah)
- 9.6.1.9 Register 0Bh (address = 0Bh)
- 9.6.1.10 Register 13h (address = 13h)
- 9.6.1.11 Register 0Eh (address = 0Eh)
- 9.6.1.12 Register 0Fh (address = 0Fh)
- 9.6.1.13 Register 15h (address = 15h)
- 9.6.1.14 Register 25h (address = 25h)
- 9.6.1.15 Register 27h (address = 27h)
- 9.6.1.16 Register 11Dh (address = 11Dh)
- 9.6.1.17 Register 122h (address = 122h)
- 9.6.1.18 Register 134h (address = 134h)
- 9.6.1.19 Register 139h (address = 139h)
- 9.6.1.20 Register 21Dh (address = 21Dh)
- 9.6.1.21 Register 222h (address = 222h)
- 9.6.1.22 Register 234h (address = 234h)
- 9.6.1.23 Register 239h (address = 239h)
- 9.6.1.24 Register 308h (address = 308h)
- 9.6.1.25 Register 41Dh (address = 41Dh)
- 9.6.1.26 Register 422h (address = 422h)
- 9.6.1.27 Register 434h (address = 434h)
- 9.6.1.28 Register 439h (address = 439h)
- 9.6.1.29 Register 51Dh (address = 51Dh)
- 9.6.1.30 Register 522h (address = 522h)
- 9.6.1.31 Register 534h (address = 534h)
- 9.6.1.32 Register 539h (address = 539h)
- 9.6.1.33 Register 608h (address = 608h)
- 9.6.1.34 Register 70Ah (address = 70Ah)
- 9.6.1
Serial Register Description
- 10Applications and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTQ|56
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTQ|56
Orderable Information
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
RTQ Package
56-Pin VQFN
Top View