SLUSBB3E December 2013 – January 2016
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configurations and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Supply Current
- 7.6 Digital Input and Output DC Characteristics
- 7.7 LDO Regulator, Wake-up, and Auto-Shutdown DC Characteristics
- 7.8 ADC (Temperature and Cell Measurement) Characteristics
- 7.9 I2C-Compatible Interface Communication Timing Characteristics
- 7.10 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YZF|9
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
- A capacitor, of value at least 0.47 µF, is connected between the VDD pin and VSS. The capacitor should be placed close to the gauge IC and have short traces to both the VDD pin and VSS.
- It is required to have a capacitor, at least 1.0 µF, connected between the BAT pin and VSS if the connection between the battery pack and the gauge BAT pin has the potential to pick up noise. The capacitor should be placed close to the gauge IC and have short traces to both the VDD pin and VSS.
- If the external pullup resistors on the SCL and SDA lines will be disconnected from the host during low-power operation, it is recommend to use external 1-MΩ pulldown resistors to VSS to avoid floating inputs to the I2C engine.
- The value of the SCL and SDA pullup resistors should take into consideration the pullup voltage and the bus capacitance. Some recommended values, assuming a bus capacitance of 10 pF, can be seen in Table 3.
- If the GPOUT pin is not used by the host, the pin should still be pulled up to VDD with a 4.7-kΩ or 10-kΩ resistor.
- If the battery pack thermistor is not connected to the BIN pin, the BIN pin should be pulled down to VSS with a 10-kΩ resistor.
- The BIN pin should not be shorted directly to VDD or VSS.
- The actual device ground is the center pin (B2). The C1 pin is floating internally and can be used as a bridge to connect the board ground plane to the device ground (B2).
Table 3. Recommended Values for SCL and SDA Pullup Resistors
| VPU | 1.8 V | 3.3 V | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPU | Range | Typical | Range | Typical |
| 400 Ω ≤ RPU ≤ 37.6 kΩ | 10 kΩ | 900 Ω ≤ RPU ≤ 29.2 kΩ | 5.1 kΩ | |
11.2 Layout Example
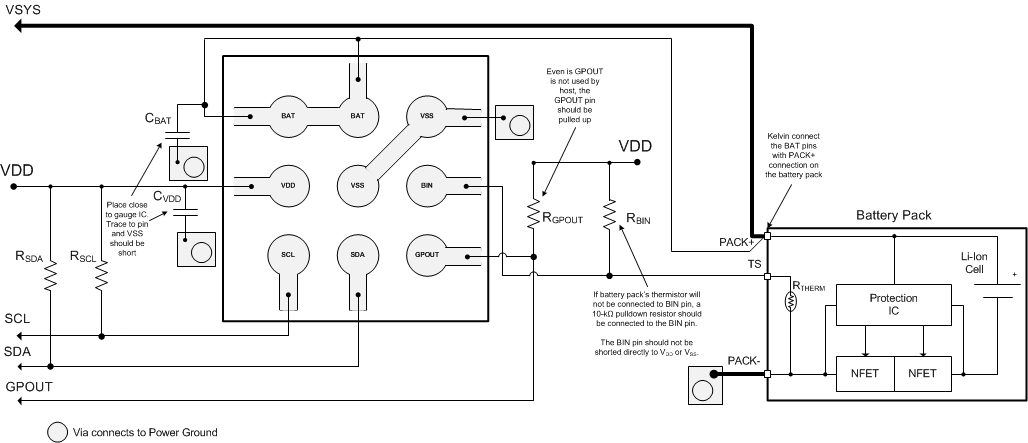 Figure 13. Layout Example
Figure 13. Layout Example