SBVS012I December 2000 – September 2020 DCP010505B , DCP010505DB , DCP010507DB , DCP010512B , DCP010512DB , DCP010515B , DCP010515DB , DCP011512DB , DCP011515DB , DCP012405B , DCP012415DB
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2 Typical Application
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.4.2.2 Connecting the DCP01B in Series
Multiple DCP01B isolated 1-W DC/DC converters can be connected in series to provide non-standard voltage rails. This configuration is possible by using the floating outputs provided by the galvanic isolation of the DCP01.
Connect the +VOUT from one DCP01B to the –VOUT of another (see Figure 7-6). If the SYNCIN pins are tied together, the self-synchronization feature of the DCP01B prevents beat frequencies on the voltage rails. The synchronization feature of the DCP01B allows easy series connection without external filtering, thus minimizing cost.
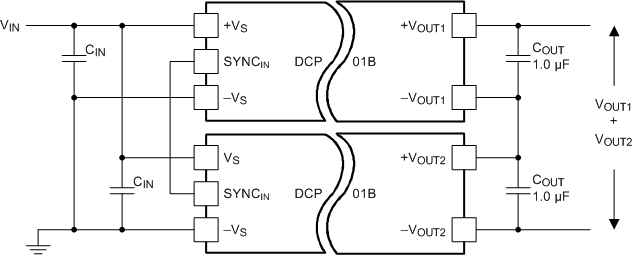 Figure 7-6 Multiple DCP01B Devices Connected in Series
Figure 7-6 Multiple DCP01B Devices Connected in SeriesThe outputs of a dual-output DCP01B can also be connected in series to provide two times the magnitude of +VOUT, as shown in Figure 7-7. For example, connect a dual-output, 15-V, DCP012415DB device to provide a 30-V rail.
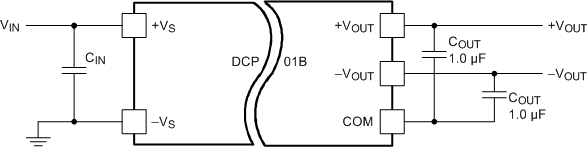 Figure 7-7 Dual Output Devices Connected in Series
Figure 7-7 Dual Output Devices Connected in Series