SNVSB73 September 2018 LM2735-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1 LM2735X-Q1 SOT-23 Design Example 1
- 8.2.2 LM2735Y-Q1 SOT-23 Design Example 2
- 8.2.3 LM2735X-Q1 WSON Design Example 3
- 8.2.4 LM2735Y-Q1 WSON Design Example 4
- 8.2.5 LM2735X-Q1 SOT-23 Design Example 6
- 8.2.6 LM2735Y-Q1 SOT-23 Design Example 7
- 8.2.7 LM2735X-Q1 SOT-23 Design Example 8
- 8.2.8 LM2735Y-Q1 SOT-23 Design Example 9
- 8.2.9 LM2735X-Q1 WSON Design Example 10
- 8.2.10 LM2735Y-Q1 WSON Design Example 11
- 8.2.11 LM2735X-Q1 WSON SEPIC Design Example 12
- 8.2.12 LM2735X-Q1 SOT-23 LED Design Example 14
- 8.2.13 LM2735Y-Q1 WSON FlyBack Design Example 15
- 8.2.14 LM2735X-Q1 SOT-23 LED Design Example 16 VRAIL > 5.5 V Application
- 8.2.15 LM2735X-Q1 SOT-23 LED Design Example 17 Two-Input Voltage Rail Application
- 8.2.16 SEPIC Converter
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.1.2.4 Output Capacitor
The LM2735-Q1 operates at frequencies allowing the use of ceramic output capacitors without compromising transient response. Ceramic capacitors allow higher inductor ripple without significantly increasing output ripple. The output capacitor is selected based upon the desired output ripple and transient response. The initial current of a load transient is provided mainly by the output capacitor. The output impedance therefore determines the maximum voltage perturbation. The output ripple of the converter is a function of the reactance of the capacitor and its equivalent series resistance (ESR):
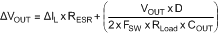
When using MLCCs, the ESR is typically so low that the capacitive ripple may dominate. When this occurs, the output ripple is approximately sinusoidal and 90° phase shifted from the switching action.
Given the availability and quality of MLCCs and the expected output voltage of designs using the LM2735-Q1, there is really no need to review any other capacitor technologies. Another benefit of ceramic capacitors is their ability to bypass high-frequency noise. A certain amount of switching edge noise couples through parasitic capacitances in the inductor to the output. A ceramic capacitor bypasses this noise while a tantalum does not. Since the output capacitor is one of the two external components that control the stability of the regulator control loop, most applications require a minimum at 4.7 µF of output capacitance. Like the input capacitor, recommended multilayer ceramic capacitors are X7R or X5R. Again, verify actual capacitance at the desired operating voltage and temperature.