SNVS053F June 2000 – September 2016 LM4140
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1 Precision DAC Reference
- 8.2.2 Boosted Output Current
- 8.2.3 Boosted Output Current With Current Limiter
- 8.2.4 Complimentary Outputs
- 8.2.5 Voltage Reference With Force and Sense Output
- 8.2.6 Precision Programmable Current Source
- 8.2.7 Strain Gauge Conditioner for 350-Ω Bridge
- 8.2.8 Bipolar Voltage References for Low Power ADC
- 8.2.9 Self-Biased Low Power ADC Reference With Trim Current Sources
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
The simplest ways to reduce the stress related shifts are:
- Mounting the device near the edges or the corners of the board where mechanical stress is at its minimum. The center of the board generally has the highest mechanical and thermal expansion stress.
- Mechanical isolation of the device by creating an island by cutting a U shape slot on the PCB for mounting the device. This approach would also provide some thermal isolation from the rest of the circuit.
Figure 39 is a recommended printed-circuit board layout with a slot cut on three sides of the circuit layout to serve as a strain relief.
10.2 Layout Example
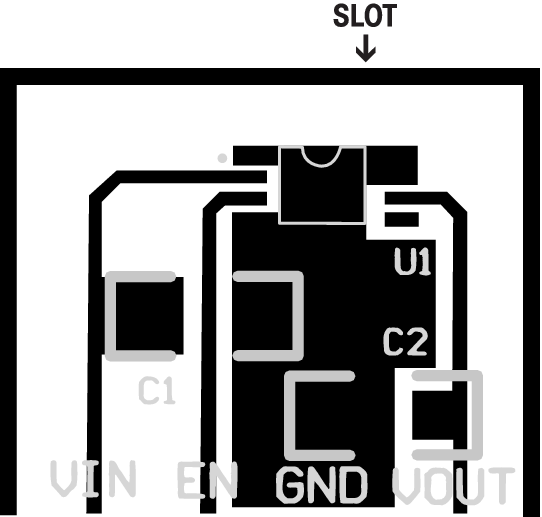 Figure 38. Suggested Schematic and External Components
Figure 38. Suggested Schematic and External Components
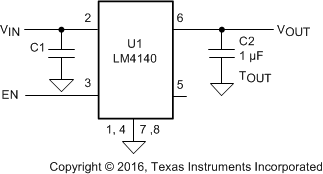 Figure 39. Suggested PCB Layout With Slot
Figure 39. Suggested PCB Layout With Slot