SNVSAW9 June 2017 LM5122-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 7.3.2 High Voltage VCC Regulator
- 7.3.3 Oscillator
- 7.3.4 Slope Compensation
- 7.3.5 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.6 PWM Comparator
- 7.3.7 Soft-Start
- 7.3.8 HO and LO Drivers
- 7.3.9 Bypass Operation (VOUT = VIN)
- 7.3.10 Cycle-by-Cycle Current Limit
- 7.3.11 Clock Synchronization
- 7.3.12 Maximum Duty Cycle
- 7.3.13 Thermal Protection
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1
Application Information
- 8.1.1 Feedback Compensation
- 8.1.2 Sub-Harmonic Oscillation
- 8.1.3 Interleaved Boost Configuration
- 8.1.4 DCR Sensing
- 8.1.5 Output Overvoltage Protection
- 8.1.6 SEPIC Converter Simplified Schematic
- 8.1.7 Non-Isolated Synchronous Flyback Converter Simplified Schematic
- 8.1.8 Negative to Positive Conversion
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Timing Resistor RT
- 8.2.2.3 UVLO Divider RUV2, RUV1
- 8.2.2.4 Input Inductor LIN
- 8.2.2.5 Current Sense Resistor RS
- 8.2.2.6 Current Sense Filter RCSFP, RCSFN, CCS
- 8.2.2.7 Slope Compensation Resistor RSLOPE
- 8.2.2.8 Output Capacitor COUT
- 8.2.2.9 Input Capacitor CIN
- 8.2.2.10 VIN Filter RVIN, CVIN
- 8.2.2.11 Bootstrap Capacitor CBST and Boost Diode DBST
- 8.2.2.12 VCC Capacitor CVCC
- 8.2.2.13 Output Voltage Divider RFB1, RFB2
- 8.2.2.14 Soft-Start Capacitor CSS
- 8.2.2.15 Restart Capacitor CRES
- 8.2.2.16 Low-Side Power Switch QL
- 8.2.2.17 High-Side Power Switch QH and Additional Parallel Schottky Diode
- 8.2.2.18 Snubber Components
- 8.2.2.19 Loop Compensation Components CCOMP, RCOMP, CHF
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.1
Application Information
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | VIN, CSP, CSN | –0.3 | 75 | V |
| BST to SW, FB, MODE, UVLO, OPT, VCC(2) | –0.3 | 15 | V | |
| SW | –5 | 105 | V | |
| BST | –0.3 | 115 | V | |
| SS, SLOPE, SYNCIN/RT | –0.3 | 7 | V | |
| CSP to CSN, PGND | –0.3 | 0.3 | V | |
| Output(3) | HO to SW | –0.3 | BST to SW + 0.3 | V |
| LO | –0.3 | VCC + 0.3 | V | |
| COMP, RES, SYNCOUT | –0.3 | 7 | V | |
| Thermal | Junction temperature | –40 | 150 | °C |
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –55 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions are not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. Unless otherwise specified, all voltages are referenced to AGND pin.
(2) See Application and Implementation when input supply voltage is less than the VCC voltage.
(3) All output pins are not specified to have an external voltage applied.
6.2 ESD Ratings: LM5122-Q1
| VALUE | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per AEC Q100-002(1) | ±2000 | V | |
| Charged device model (CDM), per AEC Q100-011 | Corner pins (1, 10, 11, and 20) | ±1000 | |||
| Other pins | ±1000 | ||||
(1) AEC Q100-002 indicates HBM stressing is done in accordance with the ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001 specification.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input supply voltage(2) | VIN | 4.5 | 65 | V |
| Low-side driver bias voltage | VCC | 14 | V | |
| High-side driver bias voltage | BST to SW | 3.8 | 14 | V |
| Current sense common mode range(2) | CSP, CSN | 3 | 65 | V |
| Switch node voltage | SW | 100 | V | |
| Junction temperature, TJ | –40 | 125 | °C | |
(1) Recommended Operating Conditions are conditions under which operation of the device is intended to be functional, but do not ensure specific performance limits.
(2) Minimum VIN operating voltage is always 4.5 V. The minimum input power supply voltage can be 3 V after start-up, assuming VIN voltage is supplied from an available external source.
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | LM5122-Q1 | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PWP | ||||
| 20 PINS | ||||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 36 | °C/W | |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 20.1 | °C/W | |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 16.8 | °C/W | |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.4 | °C/W | |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 16.7 | °C/W | |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 1.7 | °C/W | |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified, these specifications apply for –40°C ≤ TJ ≤ +125°C, VVIN = 12 V, VVCC = 8.3 V, RT = 20 kΩ, no load on LO and HO. Typical values represent the most likely parametric norm at TJ = 25°C and are provided for reference purposes only.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN SUPPLY | ||||||
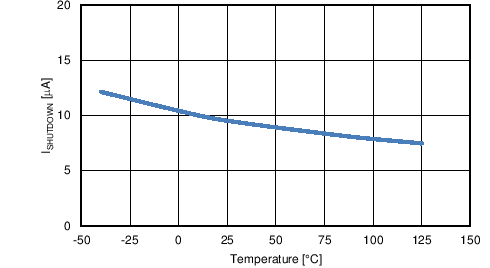
| ISHUTDOWN | VIN shutdown current | VUVLO = 0 V | 9 | 17 | µA | |
| IBIAS | VIN operating current (exclude the current into RT resistor) | VUVLO = 2 V, non-switching | 4 | 5 | mA | |
| VCC REGULATOR | ||||||
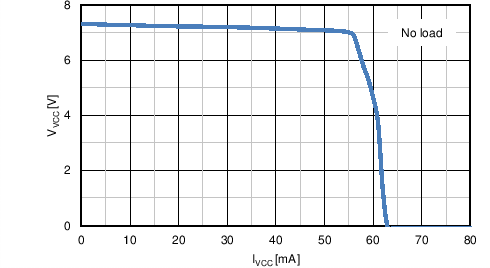
| VCC(REG) | VCC regulation | No load | 6.9 | 7.6 | 8.3 | V |
| VCC dropout (VIN to VCC) | VVIN = 4.5 V, no external load | 0.25 | V | |||
| VVIN = 4.5 V, IVCC = 25 mA | 0.28 | 0.5 | V | |||
| VCC sourcing current limit | VVCC = 0 V | 50 | 62 | mA | ||
| IVCC | VCC operating current (exclude the current into RT resistor) | VVCC = 8.3 V | 3.5 | 5 | mA | |
| VVCC = 12 V | 4.5 | 8 | mA | |||
| VCC undervoltage threshold | VCC rising, VVIN = 4.5 V | 3.9 | 4 | 4.1 | V | |
| VCC falling, VVIN = 4.5 V | 3.7 | V | ||||
| VCC undervoltage hysteresis | 0.385 | V | ||||
| UNDERVOLTAGE LOCKOUT | ||||||
| UVLO threshold | UVLO rising | 1.17 | 1.2 | 1.23 | V | |
| UVLO hysteresis current | VUVLO = 1.4 V | 7 | 10 | 13 | µA | |
| UVLO standby enable threshold | UVLO rising | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | V | |
| UVLO standby enable hysteresis | 0.1 | 0.125 | V | |||
| MODE | ||||||
| Diode emulation mode threshold | MODE rising | 1.2 | 1.24 | 1.28 | V | |
| Diode emulation mode hysteresis | 0.1 | V | ||||
| Default MODE voltage | 145 | 155 | 170 | mV | ||
| Default skip cycle threshold | COMP rising, measured at COMP | 1.290 | V | |||
| COMP falling, measured at COMP | 1.245 | V | ||||
| Skip cycle hysteresis | Measured at COMP | 40 | mV | |||
| ERROR AMPLIFIER | ||||||
| VREF | FB reference voltage | Measured at FB, VFB = VCOMP | 1.188 | 1.2 | 1.212 | V |
| FB input bias current | VFB = VREF | 5 | nA | |||
| VOH | COMP output high voltage | ISOURCE = 2 mA, VVCC = 4.5 V | 2.75 | V | ||
| ISOURCE = 2 mA, VVCC = 12 V | 3.4 | V | ||||
| VOL | COMP output low voltage | ISINK = 2 mA | 0.25 | V | ||
| AOL | DC gain | 80 | dB | |||
| fBW | Unity gain bandwidth | 3 | MHz | |||
| Slave mode threshold | FB rising | 2.7 | 3.4 | V | ||
| OSCILLATOR | ||||||
| fSW1 | Switching frequency 1 | RT = 20 kΩ | 400 | 450 | 500 | kHz |
| fSW2 | Switching frequency 2 | RT = 10 kΩ | 775 | 875 | 975 | kHz |
| RT output voltage | 1.2 | V | ||||
| RT sync rising threshold | RT rising | 2.5 | 2.9 | V | ||
| RT sync falling threshold | RT falling | 1.6 | 2 | V | ||
| Minimum sync pulse width | 100 | ns | ||||
| SYNCOUT | ||||||
| SYNCOUT high-state voltage | ISYNCOUT = –1 mA | 3.3 | 4.3 | V | ||
| SYNCOUT low-state voltage | ISYNCOUT = 1 mA | 0.15 | 0.25 | V | ||
| OPT | ||||||
| Synchronization selection threshold | OPT rising | 2 | 3 | 4 | V | |
| SLOPE COMPENSATION | ||||||
| SLOPE output voltage | 1.17 | 1.2 | 1.23 | V | ||
| VSLOPE | Slope compensation amplitude | RSLOPE = 20 kΩ, fSW = 100 kHz, 50% duty cycle, TJ = –40°C to 125°C | 1.375 | 1.65 | 1.925 | V |
| RSLOPE= 20 kΩ, fSW= 100 kHz, 50% duty cycle, TJ = 25°C | 1.4 | 1.65 | 1.9 | V | ||
| SOFT START | ||||||
| ISS-SOURCE | SS current source | VSS = 0 V | 7.5 | 10 | 12 | µA |
| SS discharge switch RDS-ON | 13 | Ω | ||||
| PWM COMPARATOR | ||||||
| tLO-OFF | Forced LO off-time | VVCC = 5.5 V | 330 | 400 | ns | |
| VVCC = 4.5 V | 560 | 750 | ns | |||
| tON-MIN | Minimum LO on-time | RSLOPE = 20 kΩ | 150 | ns | ||
| RSLOPE = 200 kΩ | 300 | ns | ||||
| COMP to PWM voltage drop | TJ = –40°C to 125°C | 0.95 | 1.1 | 1.25 | V | |
| TJ = 25°C | 1 | 1.1 | 1.2 | V | ||
| CURRENT SENSE / CYCLE-BY-CYCLE CURRENT LIMIT | ||||||
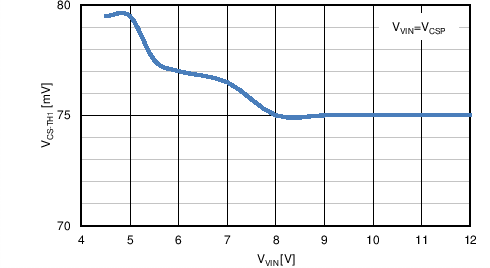
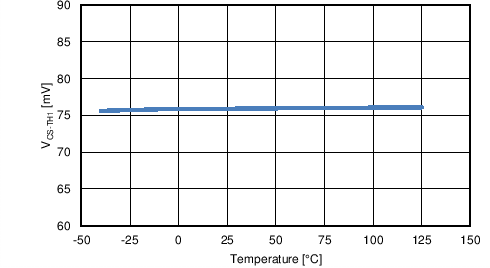
| VCS-TH1 | Cycle-by-cycle current limit threshold | CSP to CSN, TJ = –40°C to 125°C | 65.5 | 75 | 87.5 | mV |
| CSP to CSN, TJ = 25°C | 67 | 75 | 86 | mV | ||
| VCS-ZCD | Zero cross detection threshold | CSP to CSN, rising | 7 | mV | ||
| CSP to CSN, falling | 0.5 | 6 | 12 | mV | ||
| Current sense amplifier gain | 10 | V/V | ||||
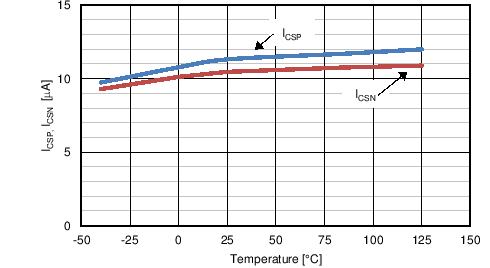
| ICSP | CSP input bias current | 12 | µA | |||
| ICSN | CSN input bias current | 11 | µA | |||
| Bias current matching | ICSP – ICSN | –1.75 | 1 | 3.75 | µA | |
| CS to LO delay | Current sense / current limit delay | 150 | ns | |||
| HICCUP-MODE RESTART | ||||||
| VRES | Restart threshold | RES rising | 1.15 | 1.2 | 1.25 | V |
| VHCP-UPPER | Hiccup counter upper threshold | RES rising | 4.2 | V | ||
| RES rising, VVIN = VVCC = 4.5 V |
3.6 | V | ||||
| VHCP-LOWER | Hiccup counter lower threshold | RES falling | 2.15 | V | ||
| RES falling, VVIN = VVCC = 4.5 V |
1.85 | V | ||||
| IRES-SOURCE1 | RES current source1 | Fault-state charging current | 20 | 30 | 40 | µA |
| IRES-SINK1 | RES current sink1 | Normal-state discharging current | 5 | µA | ||
| IRES-SOURCE2 | RES current source2 | Hiccup-mode off-time charging current | 10 | µA | ||
| IRES-SINK2 | RES current sink2 | Hiccup-mode off-time discharging current | 5 | µA | ||
| Hiccup cycle | 8 | Cycles | ||||
| RES discharge switch RDS-ON | 40 | Ω | ||||
| Ratio of hiccup mode off-time to restart delay time | 122 | |||||
| HO GATE DRIVER | ||||||
| VOHH | HO high-state voltage drop | IHO = –100 mA, VOHH = VBST –VHO | 0.15 | 0.24 | V | |
| VOLH | HO low-state voltage drop | IHO = 100 mA, VOLH = VHO –VSW | 0.1 | 0.18 | V | |
| HO rise time (10% to 90%) | CLOAD = 4700 pF, VBST = 12 V | 25 | ns | |||
| HO fall time (90% to 10%) | CLOAD = 4700 pF, VBST = 12 V | 20 | ns | |||
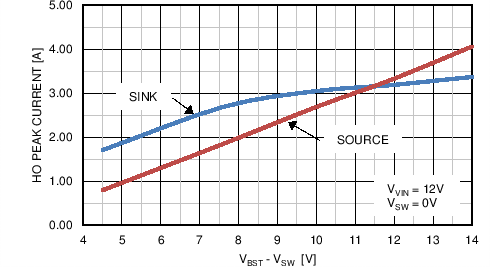
| IOHH | Peak HO source current | VHO = 0 V, VSW = 0 V, VBST = 4.5 V | 0.8 | A | ||
| VHO = 0 V, VSW = 0 V, VBST = 7.6 V | 1.9 | A | ||||
| IOLH | Peak HO sink current | VHO = VBST = 4.5 V | 1.9 | A | ||
| VHO = VBST= 7.6 V | 3.2 | A | ||||
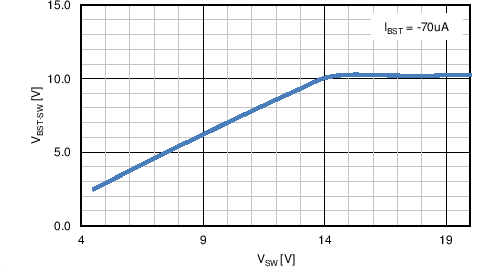
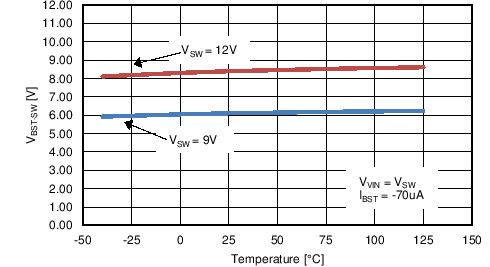
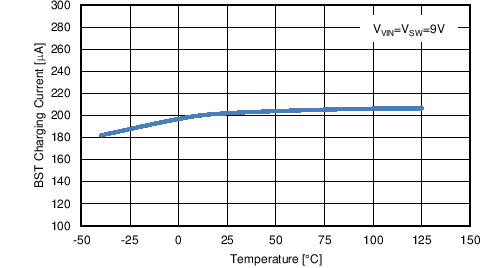
| IBST | BST charge pump sourcing current | VVIN = VSW = 9. V , VBST - VSW = 5 V | 100 | 200 | µA | |
| BST charge pump regulation | BST to SW, IBST= –70 μA, VVIN = VSW = 9 V |
5.3 | 6.2 | 6.75 | V | |
| BST to SW, IBST = –70 μA, VVIN = VSW = 12 V |
7 | 8.5 | 9 | V | ||
| BST to SW undervoltage | 2 | 3 | 3.5 | V | ||
| BST DC bias current | VBST – VSW = 12 V, VSW = 0 V | 30 | 45 | µA | ||
| LO GATE DRIVER | ||||||
| VOHL | LO high-state voltage drop | ILO = –100 mA, VOHL = VVCC –VLO | 0.15 | 0.25 | V | |
| VOLL | LO low-state voltage drop | ILO = 100 mA, VOLL = VLO | 0.1 | 0.17 | V | |
| LO rise time (10% to 90%) | CLOAD = 4700 pF | 25 | ns | |||
| LO fall time (90% to 10%) | CLOAD = 4700 pF | 20 | ns | |||
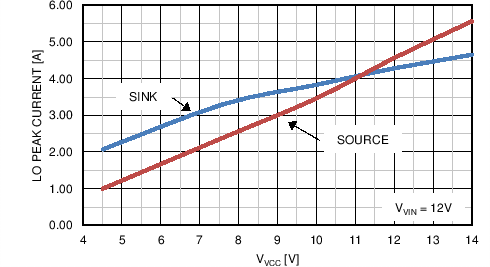
| IOHL | Peak LO source current | VLO = 0 V, VVCC = 4.5 V | 0.8 | A | ||
| VLO = 0 V | 2 | A | ||||
| IOLL | Peak LO sink current | VLO = VVCC = 4.5 V | 1.8 | A | ||
| VLO = VVCC | 3.2 | A | ||||
| SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
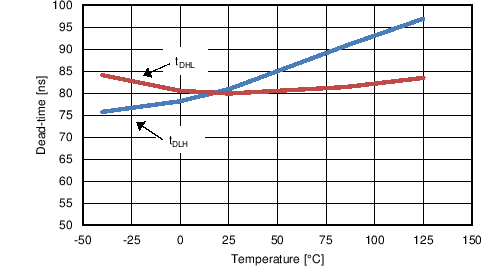
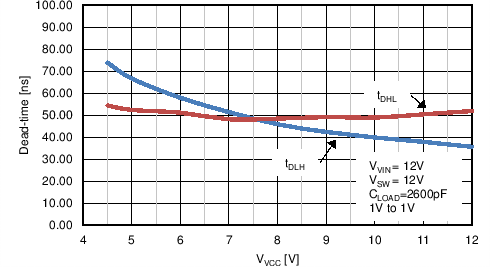
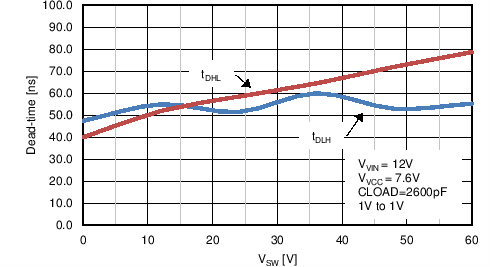
| tDLH | LO fall to HO rise delay | No load, 50% to 50% | 50 | 80 | 115 | ns |
| tDHL | HO fall to LO rise delay | No load, 50% to 50% | 60 | 80 | 105 | ns |
| THERMAL | ||||||
| TSD | Thermal shutdown | Temperature rising | 165 | °C | ||
| Thermal shutdown hysteresis | 25 | °C | ||||
6.6 Typical Characteristics
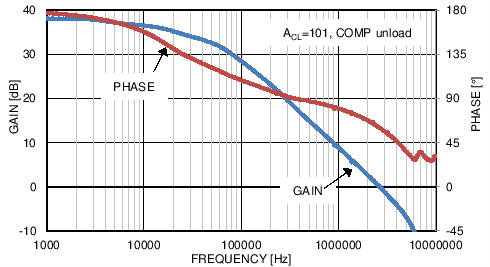
vs Frequency