SNAS687C June 2016 – November 2017 LMK60A0-148351 , LMK60A0-148M , LMK60E0-156257 , LMK60E2-150M
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics - Power Supply
- 6.6 LVPECL Output Characteristics
- 6.7 LVDS Output Characteristics
- 6.8 HCSL Output Characteristics
- 6.9 OE Input Characteristics
- 6.10 Frequency Tolerance Characteristics
- 6.11 Power-On/Reset Characteristics (VDD)
- 6.12 PSRR Characteristics
- 6.13 PLL Clock Output Jitter Characteristics
- 6.14 Additional Reliability and Qualification
- 6.15 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- SIA|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9 Layout
9.1 Layout Guidelines
The following sections provides recommendations for board layout, solder reflow profile and power supply bypassing when using LMK60XX to ensure good thermal / electrical performance and overall signal integrity of entire system.
9.1.1 Ensuring Thermal Reliability
The LMK60XX is a high performance device. Therefore pay careful attention to device configuration and printed-circuit board (PCB) layout with respect to power consumption. The ground pin needs to be connected to the ground plane of the PCB through three vias or more, as shown in Figure 12, to maximize thermal dissipation out of the package.
Equation 1 describes the relationship between the PCB temperature around the LMK60XX and its junction temperature.
where
- TB: PCB temperature around the LMK60XX
- TJ: Junction temperature of LMK60XX
- ΨJB: Junction-to-board thermal resistance parameter of LMK60XX (37.7°C/W without airflow)
- P: On-chip power dissipation of LMK60XX
To ensure that the maximum junction temperature of LMK60XX is below 120°C, it can be calculated that the maximum PCB temperature without airflow should be at 90°C or below when the device is optimized for best performance resulting in maximum on-chip power dissipation of 0.68 W.
9.1.2 Best Practices for Signal Integrity
For best electrical performance and signal integrity of entire system with LMK60XX, TI recommends routing vias into decoupling capacitors and then into the LMK60XX. TI also recommends increasing the via count and width of the traces wherever possible. These steps ensure lowest impedance and shortest path for high-frequency current flow. Figure 12 shows the layout recommendation for LMK60XX.
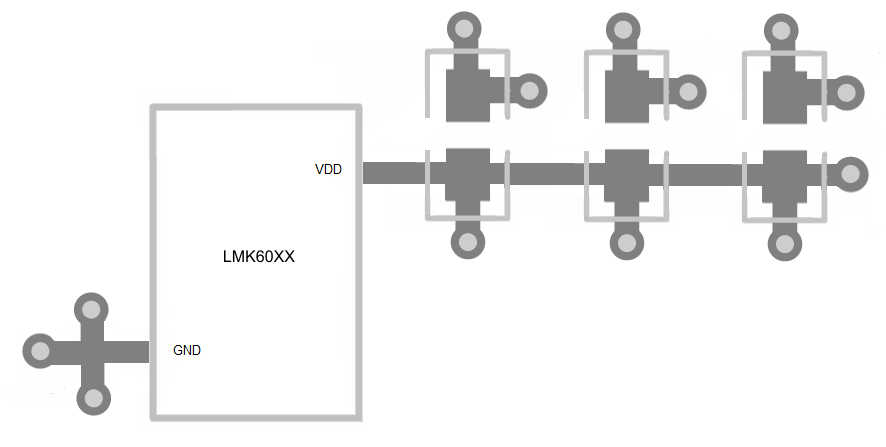 Figure 12. LMK60XX Layout Recommendation for Power Supply and Ground
Figure 12. LMK60XX Layout Recommendation for Power Supply and Ground
9.1.3 Recommended Solder Reflow Profile
TI recommends following the solder paste supplier's recommendations to optimize flux activity and to achieve proper melting temperatures of the alloy within the guidelines of J-STD-20. It is preferable for the LMK60XX to be processed with the lowest peak temperature possible while also remaining below the components peak temperature rating as listed on the MSL label. The exact temperature profile would depend on several factors including maximum peak temperature for the component as rated on the MSL label, Board thickness, PCB material type, PCB geometries, component locations, sizes, densities within PCB, as well solder manufactures recommended profile, and capability of the reflow equipment to as confirmed by the SMT assembly operation.