SNVSA50C August 2015 – May 2017 LP8861-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Internal LDO Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 Protection Electrical Characteristics
- 7.8 Power Line FET Control Electrical Characteristics
- 7.9 Current Sinks Electrical Characteristics
- 7.10 PWM Brightness Control Electrical Characteristics
- 7.11 Boost/SEPIC Converter Characteristics
- 7.12 Logic Interface Characteristics
- 7.13 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2 Typical Applications
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PWP|20
Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
Figure 35 is a layout recommendation for the LP8861-Q1 used to demonstrate the principles of good layout. This layout can be adapted to the actual application layout if or where possible. It is important that all boost components are close to the chip, and the high current traces must be wide enough. By placing boost components on one side of the chip it is easy to keep the ground plane intact below the high current paths. This way other chip pins can be routed more easily without splitting the ground plane. Bypass LDO capacitor must as close as possible to the device.
Here are some main points to help the PCB layout work:
- Current loops need to be minimized:
- For low frequency the minimal current loop can be achieved by placing the boost components as close as possible to the SW and PGND pins. Input and output capacitor grounds need to be close to each other to minimize current loop size
- Minimal current loops for high frequencies can be achieved by making sure that the ground plane is intact under the current traces. High-frequency return currents try to find route with minimum impedance, which is the route with minimum loop area, not necessarily the shortest path. Minimum loop area is formed when return current flows just under the positive current route in the ground plane, if the ground plane is intact under the route
- GND plane needs to be intact under the high current boost traces to provide shortest possible return path and smallest possible current loops for high frequencies.
- Current loops when the boost switch is conducting and not conducting need to be on the same direction in optimal case.
- Inductors must be placed so that the current flows in the same direction as in the current loops. Rotating inductor 180° changes current direction.
- Use separate power and noise-free grounds. Power ground is used for boost converter return current and noise-free ground for more sensitive signals, like LDO bypass capacitor grounding as well as grounding the GND pin of the device itself.
- Boost output feedback voltage to LEDs need to be taken out after the output capacitors, not straight from the diode cathode.
- Place LDO 1-µF bypass capacitor as close as possible to the LDO pin.
- Input and output capacitors need strong grounding (wide traces, many vias to GND plane).
- If two output capacitors are used they need symmetrical layout to get both capacitors working ideally.
- Output ceramic capacitors have DC-bias effect. If the output capacitance is too low, it can cause boost to become unstable on some loads; this increases EMI. DC bias characteristics need to be obtained from the component manufacturer; DC bias is not taken into account on component tolerance. X5R/X7R capacitors are recommended.
11.2 Layout Example
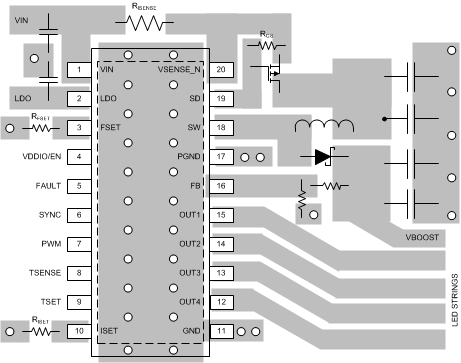 Figure 35. LP8861-Q1 Layout
Figure 35. LP8861-Q1 Layout