SBOS908A November 2017 – December 2017 OPA2333P
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DSG|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DSG|8
Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage, VS = (V+) - (V-) | Single-supply | 7 | V | ||
| Dual-supply | ±3.5 | ||||
| Signal input pins | Voltage | Common-mode(2) | (V–) – 0.3 | (V+) + 0.3 | |
| Differential(3) | ±0.5 | ||||
| Current | ±10 | mA | |||
| Output short current(4) | Continuous | ||||
| Temperature | Operating, TA | –55 | 150 | °C | |
| Junction, TJ | 150 | ||||
| Storage, Tstg | –65 | 150 | |||
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001, all pins(1) | ±4000 | V |
| Charged device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101, all pins(2) | ±1000 | |||
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VS | Supply voltage, [ (V+) – (V–) ] | Single supply | 1.8 | 5.5 | V | |
| Dual supply | ±0.9 | ±2.75 | ||||
| Specified temperature | –40 | 125 | °C | |||
6.4 Thermal Information: OPA2333P
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | OPA2333P | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DSG (WSON) | |||
| 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 74.5 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 93.5 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 41.1 | °C/W |
| ΨJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 4.3 | °C/W |
| ΨJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 41.2 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 15.7 | °C/W |
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
At TA = 25°C, RL= 10 kΩ connected to VS / 2, VCM = VS / 2, and VOUT = VS / 2 (unless otherwise noted)6.6 Typical Characteristics
Table 1. List of Typical Characteristics
| TITLE | FIGURE |
|---|---|
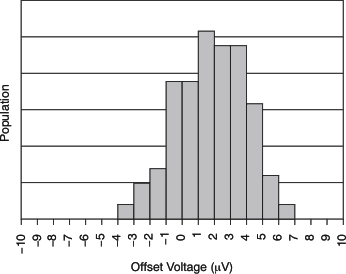
| Offset Voltage Production Distribution | Figure 1 |
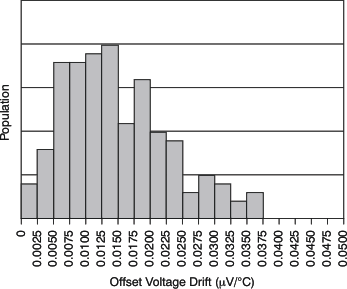
| Offset Voltage Drift Production Distribution | Figure 2 |
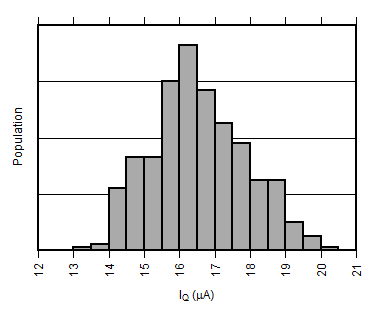
| Quiescent Current Production Distribution | Figure 3 |
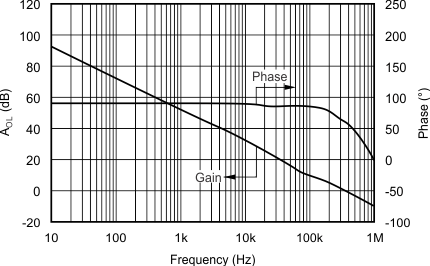
| Open-Loop Gain vs Frequency | Figure 4 |
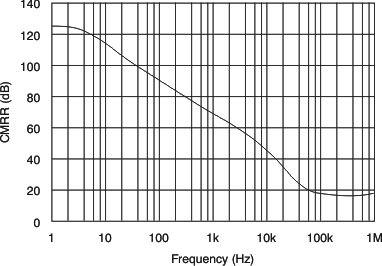
| Common-Mode Rejection Ratio vs Frequency | Figure 5 |
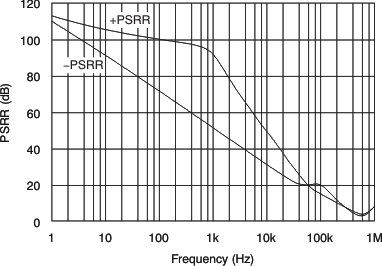
| Power-Supply Rejection Ratio vs Frequency | Figure 6 |
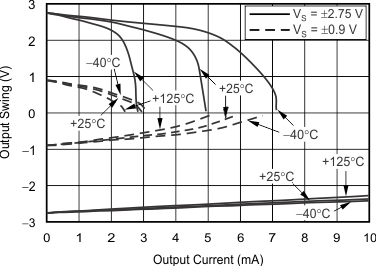
| Output Voltage Swing vs Output Current | Figure 7 |
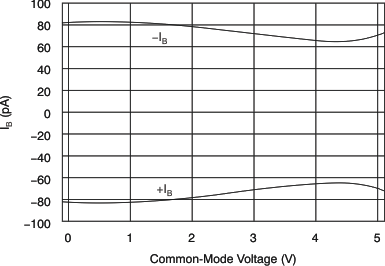
| Input Bias Current vs Common-Mode Voltage | Figure 8 |
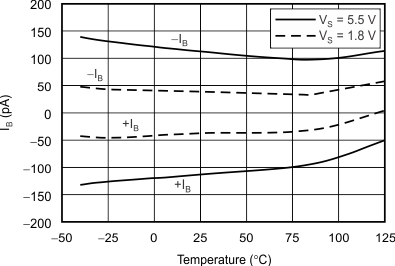
| Input Bias Current vs Temperature | Figure 9 |
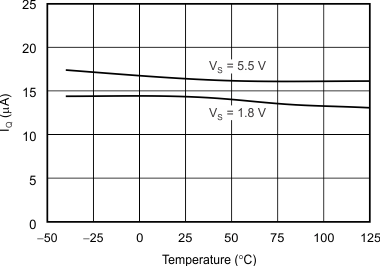
| Quiescent Current vs Temperature | Figure 10 |
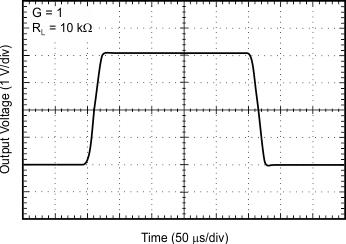
| Large-Signal Step Response | Figure 11 |
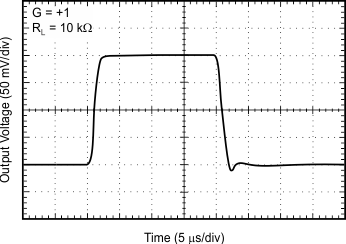
| Small-Signal Step Response | Figure 12 |
| Positive Overvoltage Recovery | Figure 13 |
| Negative Overvoltage Recovery | Figure 14 |
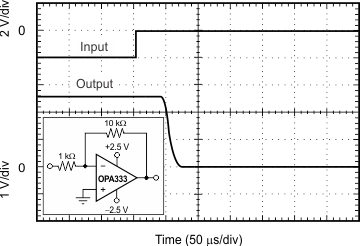
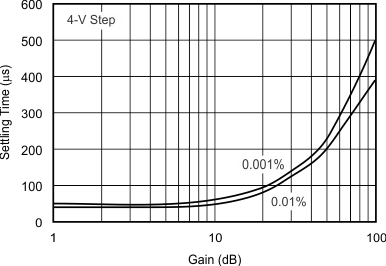
| Settling Time vs Closed-Loop Gain | Figure 15 |
| Small-Signal Overshoot vs Load Capacitance | Figure 16 |
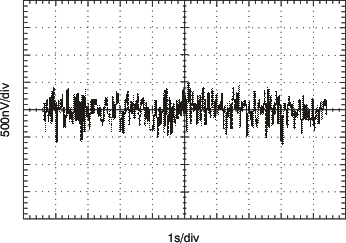
| 0.1-Hz to 10-Hz Noise | Figure 17 |
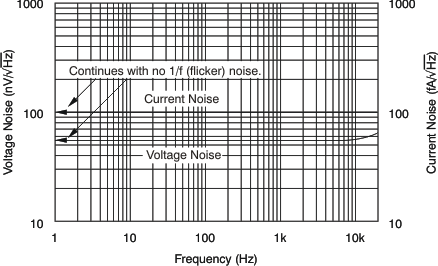
| Current and Voltage Noise Spectral Density vs Frequency | Figure 18 |
| VS = 5.5 V |
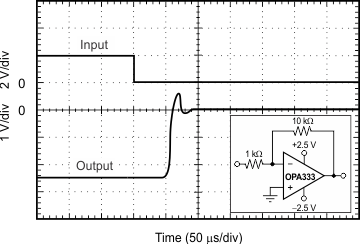
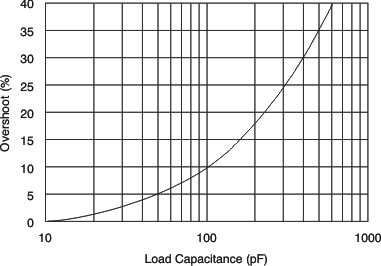
vs Load Capacitance