SPRS948 July 2016 SM320C6457-HIREL
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1Device Overview
- 2Revision History
- 3Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
4Specifications
- 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 4.2 ESD Ratings
- 4.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.4 Electrical Characteristics
- 4.5 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 4.6 Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 4.7
Peripherals
- 4.7.1 Enhanced Direct Memory Access (EDMA3) Controller
- 4.7.2 Interrupts
- 4.7.3 Reset Controller
- 4.7.4
PLL1 and PLL1 Controller
- 4.7.4.1 PLL1 Controller Device-Specific Information
- 4.7.4.2 PLL1 Controller Memory Map
- 4.7.4.3
PLL1 Controller Registers
- 4.7.4.3.1 PLL1 Control Register
- 4.7.4.3.2 PLL Multiplier Control Register
- 4.7.4.3.3 PLL Post-Divider Control Register
- 4.7.4.3.4 PLL Controller Divider 3 Register
- 4.7.4.3.5 PLL Controller Divider 6 Register
- 4.7.4.3.6 PLL Controller Divider 7 Register
- 4.7.4.3.7 PLL Controller Divider 8 Register
- 4.7.4.3.8 PLL Controller Command Register
- 4.7.4.3.9 PLL Controller Status Register
- 4.7.4.3.10 PLL Controller Clock Align Control Register
- 4.7.4.3.11 PLLDIV Ratio Change Status Register
- 4.7.4.3.12 SYSCLK Status Register
- 4.7.4.4 PLL1 Controller Input and Output Electrical Data/Timing
- 4.7.5 PLL2
- 4.7.6 DDR2 Memory Controller
- 4.7.7 External Memory Interface A (EMIFA)
- 4.7.8 I2C Peripheral
- 4.7.9 Host-Port Interface (HPI) Peripheral
- 4.7.10 Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP)
- 4.7.11 Ethernet MAC (EMAC)
- 4.7.12 Management Data Input/Output (MDIO)
- 4.7.13 Timers
- 4.7.14 Enhanced Viterbi-Decoder Coprocessor (VCP2)
- 4.7.15 Enhanced Turbo Decoder Coprocessor (TCP2)
- 4.7.16 UTOPIA
- 4.7.17 Serial RapidIO (SRIO) Port
- 4.7.18 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 4.7.19 Emulation Features and Capability
- 5Detailed Description
- 6Device and Documentation Support
- 7Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- GMH|688
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
3 Terminal Configuration and Functions
3.1 Pin Diagram
Figure 3-1 shows the ball locations for the 688-pin GMH package and is used in conjunction with Table 4-1 through Table 4-27 to locate signal names and ball grid numbers.
_Package_sprs948.gif) Figure 3-1 GMH 688-Pin Ball Grid Array (BGA) Package
Figure 3-1 GMH 688-Pin Ball Grid Array (BGA) Package
3.2 Pin Attributes
Table 3-2 identifies the external signal names, the associated pin (ball) numbers along with the mechanical package designator, the pin type (I, O/Z, or I/O/Z), whether the pin has any internal pullup/pulldown resistors, and a functional pin description. For more detailed information on device configuration, peripheral selection, multiplexed/shared pins, and pullup/pulldown resistors, see Section 5.5.
Use the symbol definitions in Table 3-1 when reading Table 3-2.
Table 3-1 I/O Functional Symbol Definitions
| FUNCTIONAL SYMBOL | DEFINITION | Table 3-2
COLUMN HEADING |
|---|---|---|
| IPD or IPU | Internal 100-µA pulldown or pullup is provided for this terminal. In most systems, a 1-kΩ resistor can be used to oppose the IPD/IPU. For more detailed information on pulldown/pullup resistors and situations in which external pulldown/pullup resistors are required, see Section 5.5.6. | IPD/IPU |
| A | Analog signal | Type |
| GND | Ground | Type |
| I | Input terminal | Type |
| O | Output terminal | Type |
| S | Supply voltage | Type |
| Z | Three-state terminal or high impedance | Type |
Table 3-2 Pin Attributes
| SIGNAL NAME | BALL NO. | TYPE | IPD/IPU | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLOCK/PLL CONFIGURATIONS | ||||
| CORECLKN | AH7 | I | Clock Input for PLL1 (differential). | |
| CORECLKP | AH6 | I | Clock Input for PLL1 (differential). | |
| ALTCORECLK | AF6 | Alternate Core Clock (single-ended) input to main PLL [vs. CORECLK(N|P)]. | ||
| CORECLKSEL | AE6 | Core Clock Select. Selects between CORECLK(N|P) and ALTCORECLK to the Main PLL.
|
||
| SYSCLKOUT | AD7 | O/Z | IPD | SYSCLKOUT is the clock output at 1/10 (default rate) of the device speed. |
| DDRREFCLKN | E6 | I | DDR Reference Clock Input to DDR PLL (differential). | |
| DDRREFCLKP | D6 | I | DDR Reference Clock Input to DDR PLL (differential). | |
| ALTDDRCLK | C6 | I | Alternate DDR Clock (single-ended) input to DDR PLL [vs. DDRREFCLK(N|P)]. | |
| DDRCLKSEL | G6 | I | DDR Clock Select. Selects between DDRREFCLK(N|P) and ALTDDRCLK to the DDR PLL.
|
|
| RIOSGMIICLKN | AG6 | RapidIO/SGMII Reference Clock to drive the RapidIO and SGMII SerDes (differential). | ||
| RIOSGMIICLKP | AG7 | RapidIO/SGMII Reference Clock to drive the RapidIO and SGMII SerDes (differential). | ||
| JTAG EMULATION | ||||
| TMS | Y2 | I | IPU | JTAG test-port mode select |
| TDO | AF1 | O/Z | JTAG test-port data out | |
| TDI | AB1 | I | IPU | JTAG test-port data in |
| TCK | AH3 | I | IPU | JTAG test-port clock |
| TRST | AE2 | I | IPD | JTAG test-port reset. For IEEE 1149.1 JTAG compatibility, see Section 4.7.19.3.1. |
| EMU0(3) | AD5 | I/O/Z | IPU | Emulation pin 0 |
| EMU1(3) | AE5 | Emulation pin 1 | ||
| EMU2 | AH5 | Emulation pin 2 | ||
| EMU3 | AE4 | Emulation pin 3 | ||
| EMU4 | AH4 | Emulation pin 4 | ||
| EMU5 | AG4 | Emulation pin 5 | ||
| EMU6 | AF4 | Emulation pin 6 | ||
| EMU7 | AG2 | Emulation pin 7 | ||
| EMU8 | AG3 | Emulation pin 8 | ||
| EMU9 | AD4 | Emulation pin 9 | ||
| EMU10 | AE3 | Emulation pin 10 | ||
| EMU11 | AF2 | Emulation pin 11 | ||
| EMU12 | AE1 | Emulation pin 12 | ||
| EMU13 | AF3 | Emulation pin 13 | ||
| EMU14 | AC1 | Emulation pin 14 | ||
| EMU15 | AD1 | Emulation pin 15 | ||
| EMU16 | AD3 | Emulation pin 16 | ||
| EMU17 | AA1 | Emulation pin 17 | ||
| EMU18 | AC2 | Emulation pin 18 | ||
| RESETS, INTERRUPTS, AND GENERAL-PURPOSE INPUT/OUTPUTS | ||||
| RESET | AH23 | I | Device reset | |
| NMI | AE19 | I | IPD | Nonmaskable interrupt, edge-driven (rising edge). NOTE: Any noise on the NMI pin may trigger an NMI interrupt. Therefore, if the NMI pin is not used, it is recommended that the NMI pin be grounded instead of relying on the IPD. |
| RESETSTAT | AF23 | O | Reset Status pin. The RESETSTAT pin indicates when the device is in reset | |
| POR | AG22 | I | Power on reset. | |
| GP15 | F23 | I/O/Z | IPD | General-purpose input/output (GPIO) pins (I/O/Z). GPIO[15:0] pins are multiplexed at power-on reset for configuration latching:
|
| GP14 | D23 | |||
| GP13 | C23 | |||
| GP12 | D24 | |||
| GP11 | C25 | |||
| GP10 | A25 | |||
| GP09 | C24 | |||
| GP08 | B25 | |||
| GP07 | F5 | |||
| GP06 | C5 | |||
| GP05 | F6 | |||
| GP04 | B5 | |||
| GP03 | B4 | |||
| GP02 | D5 | |||
| GP01 | E5 | |||
| GP00 | A5 | |||
| HOST PORT INTERFACE (HPI) | ||||
| HINT | L4 | I/O/Z | Host interrupt from DSP to host (O/Z) | |
| HCNTL1 | M5 | I/O/Z | Host control -selects between control, address, or data registers (I) [default] | |
| HCNTL0 | L6 | I/O/Z | Host control -selects between control, address, or data registers (I) [default] | |
| HHWIL | L3 | I/O/Z | Host half-word select — first or second half-word (not necessarily high or low order). For HPI16 bus width selection only] (I) [default] |
|
| HR/W | K5 | I/O/Z | Host read or write select (I) [default] | |
| HAS | M4 | I/O/Z | Host address strobe (I) [default] | |
| HCS | M3 | I/O/Z | Host chip select (I) [default] | |
| HDS1 | L2 | I/O/Z | Host data strobe 1 (I) [default] | |
| HDS2 | L5 | I/O/Z | Host data strobe 2 (I) [default] | |
| HRDY | M6 | I/O/Z | Host ready from DSP to host (O/Z) [default] | |
| HD31 | P3 | I/O/Z | Host-port data [31:16] pin (I/O/Z) [default] | |
| HD30 | N6 | |||
| HD29 | T5 | |||
| HD28 | P6 | |||
| HD27 | U5 | |||
| HD26 | N1 | |||
| HD25 | V2 | |||
| HD24 | M1 | |||
| HD23 | U6 | |||
| HD22 | V1 | |||
| HD21 | U1 | |||
| HD20 | N2 | |||
| HD19 | T1 | |||
| HD18 | P2 | |||
| HD17 | R1 | |||
| HD16 | N3 | I/O/Z | Host-port data [15:0] pin (I/O/Z) [default] | |
| HD15 | T2 | |||
| HD14 | P4 | |||
| HD13 | U2 | |||
| HD12 | N4 | |||
| HD11 | W1 | |||
| HD10 | R5 | |||
| HD09 | T3 | |||
| HD08 | N5 | |||
| HD07 | R4 | |||
| HD06 | T6 | |||
| HD05 | U4 | |||
| HD04 | R6 | |||
| HD03 | T4 | |||
| HD02 | P5 | |||
| HD01 | K6 | |||
| HD00 | W2 | |||
| EMIFA (64-BIT) — CONTROL SIGNALS COMMON TO ALL TYPES OF MEMORY | ||||
| ABA1 | V24 | O/Z | IPD | EMIFA bank address control (ABA[1:0]). Active-low bank selects for the 64-bit EMIFA.
|
| ABA0 | V25 | |||
| ACE5 | V26 | O/Z | IPU | EMIFA memory space enables.
NOTE The SM320C6457-HIREL device does not have ACE0 and ACE1 pins. |
| ACE4 | U27 | |||
| ACE3 | W25 | |||
| ACE2 | W26 | |||
| ABE06 | L25 | O/Z | IPU | EMIFA byte-enable control.
|
| ABE05 | L28 | |||
| ABE04 | L27 | |||
| ABE03 | Y28 | |||
| ABE02 | W27 | |||
| ABE01 | Y24 | |||
| ABE00 | Y25 | |||
| EMIFA (64-BIT) — BUS ARBITRATION | ||||
| AHOLDA | N25 | O | IPU | EMIFA hold-request-acknowledge to the host |
| AHOLD | R28 | I | IPU | EMIFA hold request from the host |
| ABUSREQ | L26 | O | IPU | EMIFA bus request output |
| EMIFA (64-BIT) — ASYNCHRONOUS/SYNCHRONOUS MEMORY CONTROL | ||||
| AECLKIN | N28 | I | IPD | EMIFA external input clock. The EMIFA input clock (AECLKIN or SYSCLK7 clock) is selected at reset via the pullup/pulldown resistor on the GPIO[15] pin. NOTE: AECLKIN is the default for the EMIFA input clock. |
| AECLKOUT | V28 | O/Z | IPD | EMIFA output clock [at EMIFA input clock (AECLKIN or SYSCLK7) frequency] |
| AAWE/ASWE | AA24 | O/Z | IPU | Asynchronous memory write-enable/Programmable synchronous interface write-enable |
| AARDY | K28 | I | IPU | Asynchronous memory ready input |
| AR/W | W24 | O/Z | IPU | Asynchronous memory read/write |
| AAOE/ASOE | AE25 | O/Z | IPU | Asynchronous/Programmable synchronous memory output-enable |
| ASADS/ASRE | R25 | O/Z | IPU | Programmable synchronous address strobe or read-enable
|
| EMIFA (64-BIT) — ADDRESS | ||||
| AEA19 | P24 | O/Z | IPD | EMIFA external address (word address) (O/Z) |
| AEA18 | M25 | |||
| AEA17 | M24 | |||
| AEA16 | P25 | |||
| AEA15 | P26 | |||
| AEA14 | T24 | |||
| AEA13 | R26 | O/Z | IPU | |
| AEA12 | N27 | O/Z | IPD | |
| AEA11 | T25 | |||
| AEA10 | N24 | O/Z | IPD | |
| AEA09 | M26 | |||
| AEA08 | R24 | |||
| AEA07 | N26 | |||
| AEA06 | T28 | |||
| AEA05 | U28 | |||
| AEA04 | R27 | |||
| AEA03 | T27 | |||
| AEA02 | T26 | |||
| AEA01 | U26 | |||
| AEA00 | U25 | |||
| EMIFA (64-BIT) — DATA | ||||
| AED63 | G24 | I/O/Z | IPU | EMIFA external data |
| AED62 | A26 | |||
| AED61 | C26 | |||
| AED60 | C27 | |||
| AED59 | E26 | |||
| AED58 | D27 | |||
| AED57 | D25 | |||
| AED56 | F26 | |||
| AED55 | H24 | |||
| AED54 | H25 | |||
| AED53 | D26 | |||
| AED52 | F27 | |||
| AED51 | B27 | |||
| AED50 | G26 | |||
| AED49 | B26 | |||
| AED48 | G27 | |||
| AED47 | J24 | |||
| AED46 | K25 | |||
| AED45 | J25 | |||
| AED44 | J26 | |||
| AED43 | H26 | |||
| AED42 | J27 | |||
| AED41 | C28 | |||
| AED40 | J28 | |||
| AED39 | D28 | |||
| AED38 | K24 | I/O/Z | IPU | EMIFA external data |
| AED37 | F28 | |||
| AED36 | G25 | |||
| AED35 | G28 | |||
| AED34 | K27 | |||
| AED33 | L24 | |||
| AED32 | K26 | |||
| AED31 | Y26 | |||
| AED30 | AF28 | |||
| AED29 | AA28 | |||
| AED28 | AB26 | |||
| AED27 | Y27 | |||
| AED26 | AB25 | |||
| AED25 | AA26 | I/O/Z | IPU | EMIFA external data |
| AED24 | AB24 | |||
| AED23 | AA25 | |||
| AED22 | AA27 | |||
| AED21 | AC28 | |||
| AED20 | AG27 | |||
| AED19 | AE28 | |||
| AED18 | AF27 | |||
| AED17 | AD28 | |||
| AED16 | AF26 | |||
| AED15 | AE27 | |||
| AED14 | AG25 | |||
| AED13 | AC27 | |||
| AED12 | AD26 | |||
| AED11 | AC25 | |||
| AED10 | AE26 | |||
| AED09 | AF25 | |||
| AED08 | AC26 | |||
| AED07 | AD25 | |||
| AED06 | AH26 | |||
| AED05 | AH25 | |||
| AED04 | AD27 | |||
| AED03 | AF24 | |||
| AED02 | AG26 | |||
| AED01 | AE24 | |||
| AED00 | AC24 | |||
| DDR2 MEMORY CONTROLLER | ||||
| DDRDQM0 | C10 | O/Z | DDR2 EMIF Data Masks | |
| DDRDQM1 | C7 | |||
| DDRDQM2 | C19 | |||
| DDRDQM3 | C22 | |||
| DDRBA0 | C14 | O/Z | DDR Bank Address | |
| DDRBA1 | D14 | |||
| DDRBA2 | E14 | |||
| DDRA00 | F17 | O/Z | DDR2 EMIF Address Bus | |
| DDRA01 | E17 | |||
| DDRA02 | D17 | |||
| DDRA03 | C17 | |||
| DDRA04 | E16 | |||
| DDRA05 | D16 | |||
| DDRA06 | C16 | |||
| DDRA07 | B16 | |||
| DDRA08 | D15 | |||
| DDRA09 | C15 | |||
| DDRA10 | B15 | |||
| DDRA11 | A15 | |||
| DDRA12 | A14 | |||
| DDRA13 | B14 | |||
| DDRCLKOUTP0 | A13 | O/Z | DDR2 EMIF Output Clocks to drive SDRAMs (one clock pair per SDRAM) | |
| DDRCLKOUTN0 | B13 | |||
| DDRCLKOUTP1 | A17 | |||
| DDRCLKOUTN1 | B17 | |||
| DDRD00 | A12 | O/Z | DDR2 EMIF Data Bus | |
| DDRD01 | B12 | |||
| DDRD02 | C11 | |||
| DDRD03 | D11 | |||
| DDRD04 | A10 | |||
| DDRD05 | B10 | |||
| DDRD06 | C9 | |||
| DDRD07 | D9 | |||
| DDRD08 | C8 | |||
| DDRD09 | D8 | |||
| DDRD10 | E8 | |||
| DDRD11 | F8 | |||
| DDRD12 | B7 | |||
| DDRD13 | A7 | |||
| DDRD14 | B6 | |||
| DDRD15 | A6 | |||
| DDRD16 | B18 | |||
| DDRD17 | A18 | |||
| DDRD18 | C18 | |||
| DDRD19 | D18 | |||
| DDRD20 | A20 | |||
| DDRD21 | B20 | O/Z | DDR2 EMIF Data Bus | |
| DDRD22 | C20 | |||
| DDRD23 | D20 | |||
| DDRD24 | A21 | |||
| DDRD25 | B21 | |||
| DDRD26 | C21 | |||
| DDRD27 | D21 | |||
| DDRD28 | A23 | |||
| DDRD29 | B23 | |||
| DDRD30 | A24 | |||
| DDRD31 | B24 | |||
| DDRCAS | E12 | O/Z | DDR2 EMIF Column Address Strobe | |
| DDRRAS | D12 | O/Z | DDR2 EMIF Row Address Strobe | |
| DDRCE | E13 | O/Z | DDR2 EMIF Chip Enable | |
| DDRWE | C12 | O/Z | DDR2 EMIF Write Enable | |
| DDRCKE | D13 | O/Z | DDR2 EMIF Clock Enable | |
| DDRDQS0P | E10 | I/O/Z | DDR2 EMIF Data Strobe | |
| DDRDQS0N | D10 | |||
| DDRDQS1P | E7 | |||
| DDRDQS1N | D7 | |||
| DDRDQS2P | E19 | |||
| DDRDQS2N | D19 | |||
| DDRDQS3P | E22 | |||
| DDRDQS3N | D22 | |||
| DDRRCVENIN0 | A9 | I | DDR2 EMIF Data Strobe Gate Input/Outputs to help meet DDR Timing | |
| DDRRCVENOUT0 | B9 | O/Z | ||
| DDRRCVENIN1 | E20 | I | ||
| DDRRCVENOUT1 | F20 | O/Z | ||
| DDRODT | E15 | O/Z | DDR2 EMIF On Die Termination Outputs used to set termination on the SDRAMs | |
| DDRSLRATE | A27 | I | DDR2 Slew rate control | |
| VREFSSTL | C13 | A | Reference Voltage Input for SSTL18 buffers used by DDR2 EMIF (VDDS18_2) | |
| TIMER 1 | ||||
| TOUT1L | AF19 | O/Z | IPD | Timer 1 output pin for lower 32-bit counter |
| TINP1L | AG19 | I | IPD | Timer 1 input pin for lower 32-bit counter |
| TIMER 0 | ||||
| TOUT0L | AG20 | O/Z | IPD | Timer 0 output pin for lower 32-bit counter |
| TINP0L | AH20 | I | IPD | Timer 0 input pin for lower 32-bit counter |
| INTER-INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (I2C) | ||||
| SCL | F24 | I/O/Z | I2C clock. When the I2C module is used, use an external pullup resistor. | |
| SDA | E24 | I/O/Z | I2C data. When I2C is used, ensure there is an external pullup resistor. | |
| MULTICHANNEL BUFFERED SERIAL PORT (McBSP) | ||||
| CLKS0 | AA4 | I | IPD | McBSP0 Module Clock |
| CLKR0 | Y5 | I/O/Z | IPD | McBSP0 Receive Clock |
| CLKX0 | AB3 | I/O/Z | IPD | McBSP0 Transmit Clock |
| DR0 | Y6 | I | IPD | McBSP0 Receive Data |
| DX0 | W6 | O/Z | IPD | McBSP0 Transmit Data |
| FSR0 | V4 | I/O/Z | IPD | McBSP0 Receive Frame Sync |
| FSX0 | W4 | I/O/Z | IPD | McBSP0 Transmit Frame Sync |
| CLKS1 | Y1 | I | IPD | McBSP1 Module Clock |
| CLKR1 | Y4 | I/O/Z | IPD | McBSP1 Receive Clock |
| CLKX1 | AA3 | I/O/Z | IPD | McBSP1 Transmit Clock |
| DR1 | W3 | I | IPD | McBSP1 Receive Data |
| DX1 | Y3 | O/Z | IPD | McBSP1 Transmit Data |
| FSR1 | V5 | I/O/Z | IPD | McBSP1 Receive Frame Sync |
| FSX1 | W5 | I/O/Z | IPD | McBSP1 Transmit Frame Sync |
| UNIVERSAL TEST AND OPERATIONS PHY INTERFACE for ASYNCHRONOUS TRANSFER MODE (ATM) [UTOPIA SLAVE] | ||||
| UTOPIA SLAVE (ATM CONTROLLER) — TRANSMIT INTERFACE | ||||
| UXCLK | A4 | I | Source clock for UTOPIA transmit driven by Master ATM Controller. | |
| UXCLAV | C3 | O/Z | Transmit cell available status output signal from UTOPIA Slave.
|
|
| UXENB | B3 | I | UTOPIA transmit interface enable input signal. Asserted by the Master ATM Controller to indicate that the UTOPIA Slave should put out on the Transmit Data Bus the first byte of valid data and the UXSOC signal in the next clock cycle. | |
| UXSOC | G4 | O/Z | Transmit Start-of-Cell signal. This signal is output by the UTOPIA Slave on the rising edge of the UXCLK, indicating that the first valid byte of the cell is available on the 8-bit Transmit Data Bus (UXDATA[7:0]). | |
| UXADDR4 | J4 | I | UTOPIA transmit address pins (UXADDR[4:0]) (I) 5-bit Slave transmit address input pins driven by the Master ATM Controller to identify and select one of the Slave devices (up to 31 possible) in the ATM System. | |
| UXADDR3 | H5 | |||
| UXADDR2 | K3 | |||
| UXADDR1 | J5 | |||
| UXADDR0 | H4 | |||
| UXDATA7 | F3 | O/Z | UTOPIA 8-bit transmit data bus (I/O/Z) Using the Transmit Data Bus, the UTOPIA Slave (on the rising edge of the UXCLK) transmits the 8-bit ATM cells to the Master ATM Controller. | |
| UXDATA6 | E4 | |||
| UXDATA5 | C4 | |||
| UXDATA4 | A3 | |||
| UXDATA3 | H3 | |||
| UXDATA2 | G3 | |||
| UXDATA1 | F4 | |||
| UXDATA0 | E3 | |||
| UTOPIA SLAVE (ATM CONTROLLER) — RECEIVE INTERFACE | ||||
| URCLK | C1 | I | Source clock for UTOPIA receive driven by Master ATM Controller. | |
| URCLAV | B2 | O/Z | Receive cell available status output signal from UTOPIA Slave.
|
|
| URENB | K4 | I | UTOPIA receive interface enable input signal. Asserted by the Master ATM Controller to indicate to the UTOPIA Slave to sample the Receive Data Bus (URDATA[7:0]) and URSOC signal in the next clock cycle or thereafter. | |
| URSOC | G2 | I | Receive Start-of-Cell signal. This signal is output by the Master ATM Controller to indicate to the UTOPIA Slave that the first valid byte of the cell is available to sample on the 8-bit Receive Data Bus (URDATA[7:0]). | |
| URADDR4 | K1 | I | UTOPIA receive address pins [URADDR[4:0] (I)]: 5-bit Slave receive address input pins driven by the Master ATM Controller to identify and select one of the Slave devices (up to 31 possible) in the ATM System. | |
| URADDR3 | K2 | |||
| URADDR2 | J1 | |||
| URADDR1 | J3 | |||
| URADDR0 | H2 | |||
| URDATA7 | G1 | I | UTOPIA 8-bit Receive Data Bus (I/O/Z). Using the Receive Data Bus, the UTOPIA Slave (on the rising edge of the URCLK) can receive the 8-bit ATM cell data from the Master ATM Controller. | |
| URDATA6 | F2 | |||
| URDATA5 | F1 | |||
| URDATA4 | E2 | |||
| URDATA3 | E1 | |||
| URDATA2 | D2 | |||
| URDATA1 | D1 | |||
| URDATA0 | C2 | |||
| SERIAL RAPIDIO (SRIO) | ||||
| RIORXN0 | AG8 | I | Serial RapidIO Receive Data (4 links) | |
| RIORXP0 | AG9 | |||
| RIORXN1 | AF11 | |||
| RIORXP1 | AF10 | |||
| RIORXN2 | AH13 | |||
| RIORXP2 | AH12 | |||
| RIORXN3 | AE13 | |||
| RIORXP3 | AE12 | |||
| RIOTXN0 | AE9 | O | Serial RapidIO Transmit data (4 links) | |
| RIOTXP0 | AE8 | |||
| RIOTXN1 | AH9 | |||
| RIOTXP1 | AH10 | |||
| RIOTXN2 | AF13 | |||
| RIOTXP2 | AF14 | |||
| RIOTXN3 | AG13 | |||
| RIOTXP3 | AG14 | |||
| ETHERNET MAC (EMAC) AND SGMII | ||||
| SGMIIRXN | AF16 | I | Ethernet MAC SGMII Receive Data | |
| SGMIIRXP | AF17 | |||
| SGMIITXN | AH15 | O | Ethernet MAC SGMII Transmit Data | |
| SGMIITXP | AH14 | |||
| MANAGEMENT DATA INPUT/OUTPUT (MDIO) | ||||
| MDIO | AH19 | I/O/Z | IPU | MDIO Data |
| MDCLK | AH18 | O | IPD | MDIO Clock |
| VOLTAGE CONTROL TERMINALS | ||||
| PTV18 | A16 | A | PTV Compensation NMOS Reference Input. Install with 47-Ω, 5% resistor to GND | |
| SUPPLY VOLTAGE MONITOR TERMINALS | ||||
| CVDDMON | U19 | A | 1.1-V CVDD Supply Monitor | |
| DVDD33MON | U22 | A | 3.3-V DVDD Supply Monitor | |
| DVDD18MON | G23 | A | 1.8-V DVDD Supply Monitor | |
| SUPPLY VOLTAGE TERMINALS | ||||
| VDDR18 | AE10 | S | 1.8-V I/O supply voltage (SRIO/SGMII SerDes regulator supply). | |
| AE16 | ||||
| VDDA11 | AC10 | S | SRIO/SGMII analog supply: 1.1-V I/O supply voltage Do not use core supply. |
|
| AC12 | ||||
| AC14 | ||||
| AC16 | ||||
| VDDD11 | U13 | S | SRIO/SGMII SerDes digital supply: 1.1-V I/O supply voltage Do not use core supply. |
|
| V12 | ||||
| V14 | ||||
| W11 | ||||
| W13 | ||||
| W15 | ||||
| VDDT11 | AD9 | S | SRIO/SGMII SerDes termination supply: 1.1-V I/O supply voltage Do not use core supply. |
|
| AD11 | ||||
| AD13 | ||||
| AD15 | ||||
| AD17 | ||||
| AF9 | ||||
| AF15 | ||||
| AG11 | ||||
| AH17 | ||||
| DVDD18 | AA6 | S | 1.8-V I/O supply voltage | |
| AB18 | ||||
| AB20 | ||||
| AB7 | ||||
| AC19 | ||||
| AC21 | ||||
| AC3 | ||||
| AC8 | ||||
| AD18 | ||||
| AD22 | ||||
| AF18 | ||||
| AG5 | ||||
| AH1 | ||||
| B11 | ||||
| B19 | ||||
| B22 | ||||
| DVDD18 | B8 | S | 1.8-V I/O supply voltage | |
| E11 | ||||
| E21 | ||||
| E23 | ||||
| E9 | ||||
| F10 | ||||
| F12 | ||||
| F14 | ||||
| F16 | ||||
| F18 | ||||
| G11 | ||||
| G13 | ||||
| G15 | ||||
| G17 | ||||
| G19 | ||||
| G21 | ||||
| G7 | ||||
| G9 | ||||
| J7 | ||||
| V6 | ||||
| Y7 | ||||
| DVDD33 | A1 | S | 3.3-V I/O supply voltage | |
| A28 | ||||
| AA23 | ||||
| AB22 | ||||
| AB28 | ||||
| AC23 | ||||
| AD24 | ||||
| AH24 | ||||
| AH28 | ||||
| D3 | ||||
| E25 | ||||
| E27 | ||||
| H1 | ||||
| H22 | ||||
| H27 | ||||
| J23 | ||||
| K22 | ||||
| L1 | ||||
| L23 | ||||
| L7 | ||||
| M22 | ||||
| M27 | ||||
| N23 | ||||
| N7 | ||||
| P1 | ||||
| P22 | ||||
| DVDD33 | P27 | S | 3.3-V I/O supply voltage | |
| R23 | ||||
| R3 | ||||
| R7 | ||||
| T22 | ||||
| U7 | ||||
| V22 | ||||
| V3 | ||||
| W23 | ||||
| Y22 | ||||
| CVDD | K10 | S | 1.1-V core supply voltage | |
| K12 | ||||
| K14 | ||||
| K16 | ||||
| K18 | ||||
| L11 | ||||
| L13 | ||||
| L15 | ||||
| L17 | ||||
| L19 | ||||
| M10 | ||||
| M12 | ||||
| M14 | ||||
| M16 | ||||
| M18 | ||||
| N11 | ||||
| N13 | ||||
| N15 | ||||
| N17 | ||||
| CVDD | N19 | S | 1.1-V core supply voltage | |
| P10 | ||||
| P12 | ||||
| P14 | ||||
| P16 | ||||
| P18 | ||||
| R11 | ||||
| R13 | ||||
| R15 | ||||
| R17 | ||||
| R19 | ||||
| T12 | ||||
| T14 | ||||
| T16 | ||||
| T18 | ||||
| U11 | ||||
| U15 | ||||
| U17 | ||||
| V10 | ||||
| V16 | ||||
| V18 | ||||
| W17 | ||||
| W19 | ||||
| PLLV1 | AC5 | S | 1.8-V PLL Supply | |
| PLLV2 | F7 | S | 1.8-V PLL Supply | |
| GROUND PINS | ||||
| VSS | A11 | GND | Ground pins | |
| A19 | ||||
| A2 | ||||
| A22 | ||||
| A8 | ||||
| AA2 | ||||
| AA22 | ||||
| AA7 | ||||
| AB10 | ||||
| AB11 | ||||
| AB12 | ||||
| AB13 | ||||
| AB14 | ||||
| AB15 | ||||
| AB16 | ||||
| AB17 | ||||
| AB19 | ||||
| AB21 | ||||
| AB23 | ||||
| AB27 | ||||
| AB6 | ||||
| AB8 | ||||
| AB9 | ||||
| AC11 | ||||
| AC13 | ||||
| AC15 | ||||
| AC17 | ||||
| AC18 | ||||
| AC20 | ||||
| AC22 | ||||
| AC9 | ||||
| AD10 | ||||
| AD12 | ||||
| AD14 | ||||
| AD16 | ||||
| AD19 | ||||
| AD2 | ||||
| VSS | AD23 | GND | Ground pins | |
| AD8 | ||||
| AE11 | ||||
| AE14 | ||||
| AE15 | ||||
| AE17 | ||||
| AE18 | ||||
| AF5 | ||||
| AF8 | ||||
| AG1 | ||||
| AG10 | ||||
| AG12 | ||||
| AG15 | ||||
| AG17 | ||||
| AG18 | ||||
| AG24 | ||||
| AG28 | ||||
| AH11 | ||||
| AH16 | ||||
| AH2 | ||||
| AH27 | ||||
| AH8 | ||||
| B1 | ||||
| B28 | ||||
| D4 | ||||
| E18 | ||||
| E28 | ||||
| F11 | ||||
| F13 | ||||
| F15 | ||||
| F19 | ||||
| F21 | ||||
| F22 | ||||
| F25 | ||||
| F9 | ||||
| G10 | ||||
| G12 | ||||
| G14 | ||||
| VSS | G16 | GND | Ground pins | |
| G18 | ||||
| G20 | ||||
| G22 | ||||
| G8 | ||||
| H23 | ||||
| H28 | ||||
| H7 | ||||
| J2 | ||||
| J22 | ||||
| K11 | ||||
| K13 | ||||
| K15 | ||||
| K17 | ||||
| K19 | ||||
| K23 | ||||
| K7 | ||||
| L10 | ||||
| L12 | ||||
| L14 | ||||
| L16 | ||||
| L18 | ||||
| L22 | ||||
| M11 | ||||
| M13 | ||||
| M15 | ||||
| M17 | ||||
| M19 | ||||
| M2 | ||||
| M23 | ||||
| M28 | ||||
| M7 | ||||
| N10 | ||||
| N12 | ||||
| N14 | ||||
| N16 | ||||
| N18 | ||||
| N22 | ||||
| VSS | P11 | GND | Ground pins | |
| P13 | ||||
| P15 | ||||
| P17 | ||||
| P19 | ||||
| P23 | ||||
| P28 | ||||
| P7 | ||||
| R12 | ||||
| R14 | ||||
| R16 | ||||
| R18 | ||||
| R2 | ||||
| R22 | ||||
| T11 | ||||
| T13 | ||||
| T15 | ||||
| T17 | ||||
| T19 | ||||
| T23 | ||||
| T7 | ||||
| U10 | ||||
| U12 | ||||
| U14 | ||||
| U16 | ||||
| U18 | ||||
| U23 | ||||
| U24 | ||||
| U3 | ||||
| V11 | ||||
| V13 | ||||
| V15 | ||||
| V17 | ||||
| V19 | ||||
| V23 | ||||
| V27 | ||||
| V7 | ||||
| W10 | ||||
| W12 | ||||
| W14 | ||||
| W16 | ||||
| VSS | W18 | GND | Ground pins | |
| W22 | ||||
| W7 | ||||
| Y23 | ||||
| RESERVED PINS | ||||
| RSV01 | AC4 | I/O/Z | IPU | Reserved - Unconnected |
| RSV02 | AB2 | I/O/Z | IPU | Reserved - Unconnected |
| RSV03 | AB4 | I/O/Z | IPU | Reserved - Unconnected |
| RSV04 | AD20 | O/Z | IPD | Reserved - Unconnected |
| RSV05 | AD21 | O/Z | IPD | Reserved - Unconnected |
| RSV06 | AE20 | A | Reserved - Unconnected | |
| RSV07 | AE21 | A | Reserved - Unconnected | |
| RSV08 | AE7 | O | Reserved - Unconnected | |
| RSV09 | AF7 | O | Reserved - Unconnected | |
| RSV10 | H6 | O | Reserved - Unconnected | |
| RSV11 | J6 | O | Reserved - Unconnected | |
| RSV12 | AB5 | A | Reserved - Connect to GND | |
| RSV13 | AA5 | A | Reserved - Unconnected | |
| RSV14 | AF20 | I/O/Z | IPU | Reserved - Unconnected |
| RSV15 | AF21 | I/O/Z | IPU | Reserved - Unconnected |
| RSV16 | AF12 | A | Reserved - Unconnected | |
| RSV17 | AG16 | A | Reserved - Unconnected | |
| RSV18 | AH21 | A | Reserved - Unconnected | |
| RSV19 | AG21 | A | Reserved - Unconnected | |
| RSV20 | AC6 | A | Reserved - Unconnected | |
| RSV21 | AC7 | A | Reserved - Unconnected | |
| RSV22 | AE23 | I | IPU | Reserved - Pullup to DVDD18 with 10-kΩ resistor. |
| RSV23 | R10 | S | Reserved - Connected to CVDD | |
| RSV23 | T10 | S | Reserved - Connected to CVDD | |
| RSV24 | AD6 | O/Z | IPD | Reserved - Unconnected |
| RSV25 | G5 | O/Z | IPD | Reserved - Unconnected |
| RSV26 | AE22 | Reserved - Unconnected | ||
| RSV27 | AF22 | Reserved - Unconnected | ||
| RSV28 | AG23 | Reserved - Unconnected | ||
| RSV29 | AH22 | Reserved - Unconnected | ||
3.2.1 Pin Map
Figure 3-2 through Figure 3-5 show the SM320C6457-HIREL pin assignments in four quadrants (A, B, C, and D).
![SM320C6457-HIREL SM320C6457-HIREL Pin Map (Bottom View) [Quadrant A] SM320C6457-HIREL Pin_Map_Quad_A_6484.gif](/ods/images/SPRS948/Pin_Map_Quad_A_6484.gif) Figure 3-2 SM320C6457-HIREL Pin Map (Bottom View) [Quadrant A]
Figure 3-2 SM320C6457-HIREL Pin Map (Bottom View) [Quadrant A]
![SM320C6457-HIREL TCI648F Pin Map (Bottom View)
[Quadrant B] SM320C6457-HIREL Pin_Map_Quad_B_6484.gif](/ods/images/SPRS948/Pin_Map_Quad_B_6484.gif) Figure 3-3 TCI648F Pin Map (Bottom View) [Quadrant B]
Figure 3-3 TCI648F Pin Map (Bottom View) [Quadrant B]
![SM320C6457-HIREL TCI648F Pin Map (Bottom View)
[Quadrant C] SM320C6457-HIREL Pin_Map_Quad_C_6484.gif](/ods/images/SPRS948/Pin_Map_Quad_C_6484.gif) Figure 3-4 TCI648F Pin Map (Bottom View) [Quadrant C]
Figure 3-4 TCI648F Pin Map (Bottom View) [Quadrant C]
![SM320C6457-HIREL TCI648F Pin Map (Bottom View)
[Quadrant D] SM320C6457-HIREL Pin_Map_Quad_D_6484.gif](/ods/images/SPRS948/Pin_Map_Quad_D_6484.gif) Figure 3-5 TCI648F Pin Map (Bottom View) [Quadrant D]
Figure 3-5 TCI648F Pin Map (Bottom View) [Quadrant D]
3.3 Signal Descriptions
Figure 3-6 shows the CPU and core peripheral signal groups.
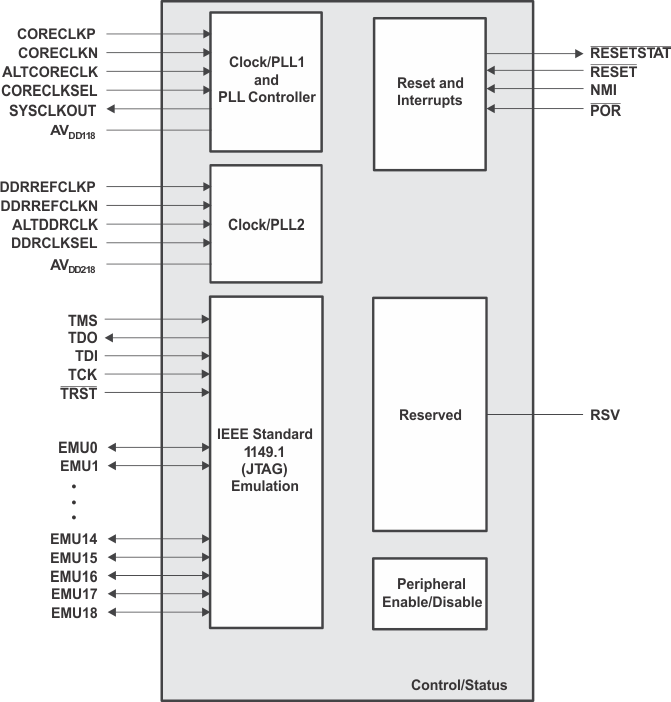 Figure 3-6 CPU and Peripheral Signals
Figure 3-6 CPU and Peripheral Signals
Figure 3-7 shows the timer peripheral I/O, the general purpose I/O, the Serial RapidIO, and the general purpose I/O reference clock, transmit, and receive signals.
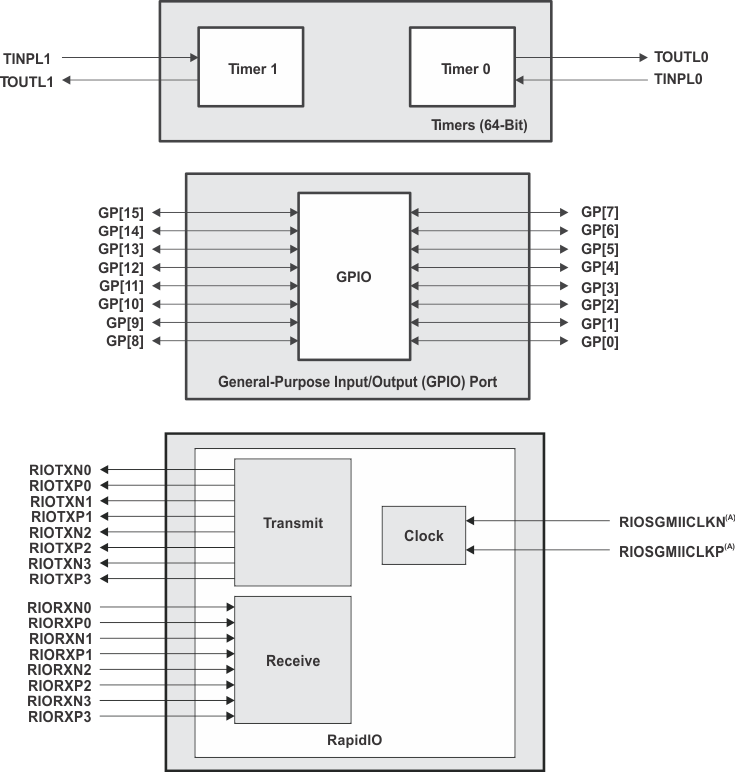 Figure 3-7 Timers/GPIO/RapidIO Peripheral Signals
Figure 3-7 Timers/GPIO/RapidIO Peripheral Signals
| (A) Reference clock to drive RapidIO and SGMII. |
Figure 3-8 shows the EMIFA and DDR2 peripheral interfaces.
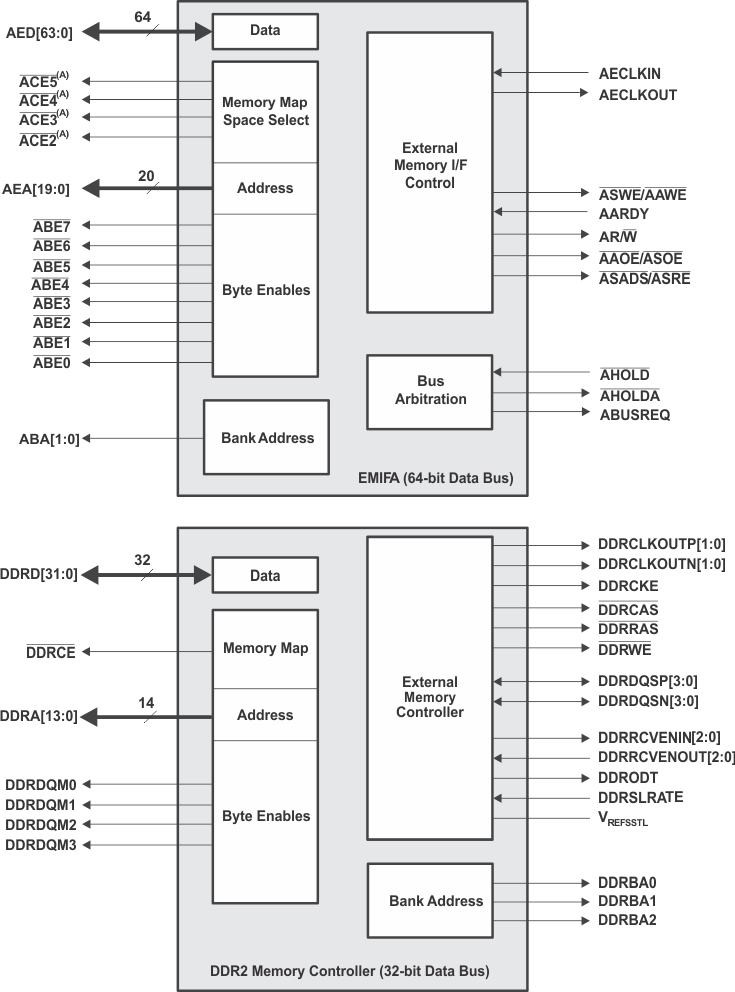 Figure 3-8 EMIFA and DDR2 Memory Controller Peripheral Signals
Figure 3-8 EMIFA and DDR2 Memory Controller Peripheral Signals
| (A) The EMIFA ACE0 and ACE1 are not functionally supported on SM320C6457-HIREL devices. |
Figure 3-9 shows the HPI, McBSP, and I2C peripheral signals.
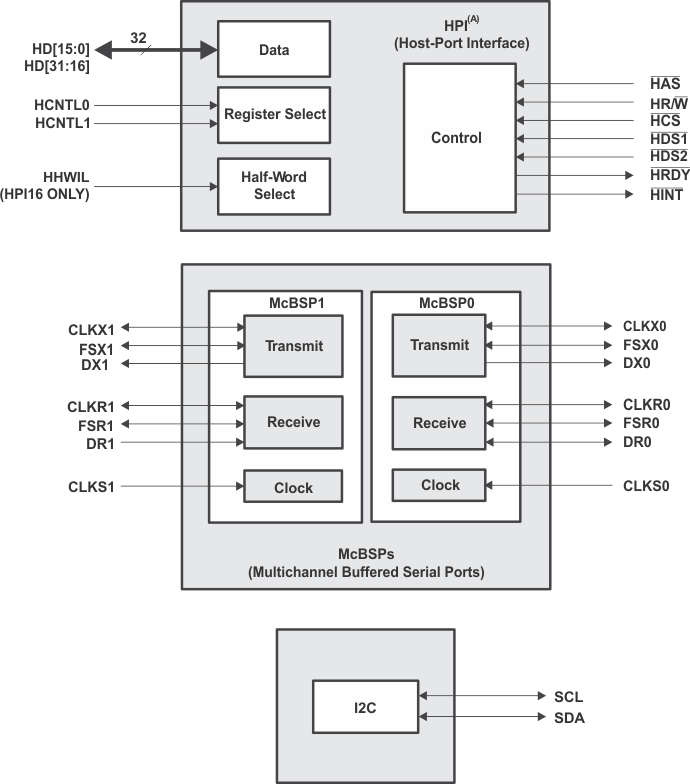 Figure 3-9 HPI/McBSP/I2C Peripheral Signals
Figure 3-9 HPI/McBSP/I2C Peripheral Signals
| (A) When the HPI is enabled, the number of HPI pins used depends on the HPI configuration (HPI16 or HPI32). |
Figure 3-10 shows the EMAC/MDIO (SGMII) peripheral signals.
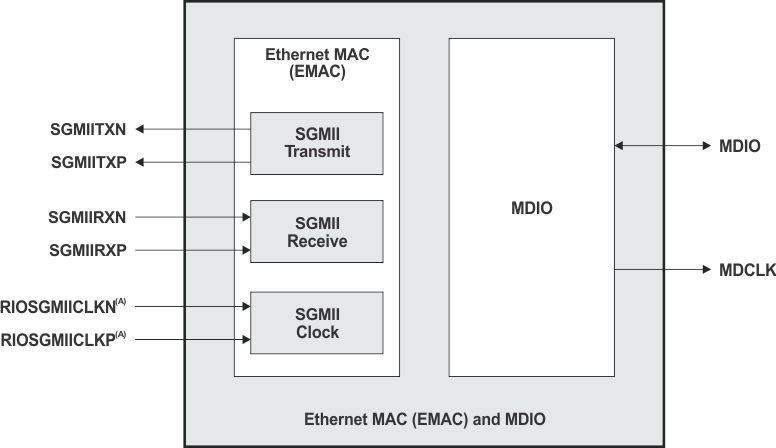 Figure 3-10 EMAC/MDIO (SGMII) Peripheral Signals
Figure 3-10 EMAC/MDIO (SGMII) Peripheral Signals
| (A) Reference clock to drive RapidIO and SGMII. |
Figure 3-11 shows the UTOPIA peripheral signals.
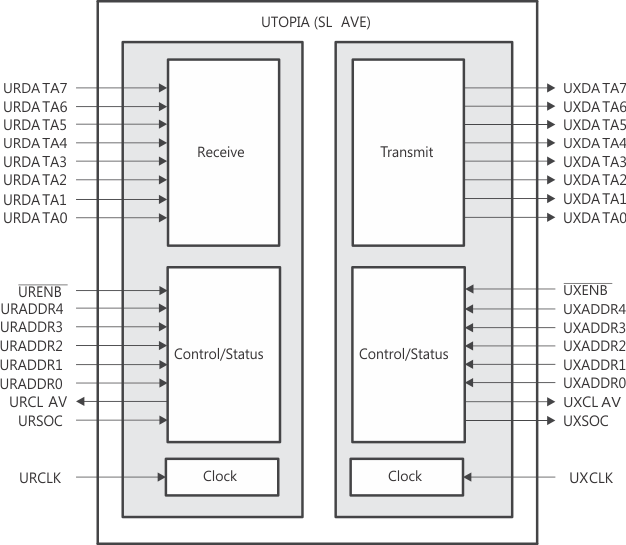 Figure 3-11 UTOPIA Peripheral Signals
Figure 3-11 UTOPIA Peripheral Signals