SPRS948 July 2016 SM320C6457-HIREL
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1Device Overview
- 2Revision History
- 3Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
4Specifications
- 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 4.2 ESD Ratings
- 4.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.4 Electrical Characteristics
- 4.5 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 4.6 Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 4.7
Peripherals
- 4.7.1 Enhanced Direct Memory Access (EDMA3) Controller
- 4.7.2 Interrupts
- 4.7.3 Reset Controller
- 4.7.4
PLL1 and PLL1 Controller
- 4.7.4.1 PLL1 Controller Device-Specific Information
- 4.7.4.2 PLL1 Controller Memory Map
- 4.7.4.3
PLL1 Controller Registers
- 4.7.4.3.1 PLL1 Control Register
- 4.7.4.3.2 PLL Multiplier Control Register
- 4.7.4.3.3 PLL Post-Divider Control Register
- 4.7.4.3.4 PLL Controller Divider 3 Register
- 4.7.4.3.5 PLL Controller Divider 6 Register
- 4.7.4.3.6 PLL Controller Divider 7 Register
- 4.7.4.3.7 PLL Controller Divider 8 Register
- 4.7.4.3.8 PLL Controller Command Register
- 4.7.4.3.9 PLL Controller Status Register
- 4.7.4.3.10 PLL Controller Clock Align Control Register
- 4.7.4.3.11 PLLDIV Ratio Change Status Register
- 4.7.4.3.12 SYSCLK Status Register
- 4.7.4.4 PLL1 Controller Input and Output Electrical Data/Timing
- 4.7.5 PLL2
- 4.7.6 DDR2 Memory Controller
- 4.7.7 External Memory Interface A (EMIFA)
- 4.7.8 I2C Peripheral
- 4.7.9 Host-Port Interface (HPI) Peripheral
- 4.7.10 Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP)
- 4.7.11 Ethernet MAC (EMAC)
- 4.7.12 Management Data Input/Output (MDIO)
- 4.7.13 Timers
- 4.7.14 Enhanced Viterbi-Decoder Coprocessor (VCP2)
- 4.7.15 Enhanced Turbo Decoder Coprocessor (TCP2)
- 4.7.16 UTOPIA
- 4.7.17 Serial RapidIO (SRIO) Port
- 4.7.18 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 4.7.19 Emulation Features and Capability
- 5Detailed Description
- 6Device and Documentation Support
- 7Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- GMH|688
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6 Device and Documentation Support
6.1 Device Nomenclature
To designate the stages in the product development cycle, TI assigns prefixes to the part numbers of all DSP devices and support tools. Each DSP commercial family member has one of three prefixes: TMX, TMP, or TMS (e.g., TMX320C6457GMH). Texas Instruments recommends two of three possible prefix designators for its support tools: TMDX and TMDS. These prefixes represent evolutionary stages of product development from engineering prototypes (TMX/TMDX) through fully qualified production devices/tools (TMS/TMDS).
Device development evolutionary flow:
- TMX: Experimental device that is not necessarily representative of the final device's electrical specifications
- TMP: Final silicon die that conforms to the device's electrical specifications but has not completed quality and reliability verification
- TMS: Fully qualified production device
Support tool development evolutionary flow:
- TMDX: Development-support product that has not yet completed Texas Instruments internal qualification testing.
- TMDS: Fully qualified development-support product
TMX and TMP devices and TMDX development-support tools are shipped with the following disclaimer:
- "Developmental product is intended for internal evaluation purposes."
TMS devices and TMDS development-support tools have been characterized fully, and the quality and reliability of the device have been demonstrated fully. TI's standard warranty applies.
Predictions show that prototype devices (TMX or TMP) have a greater failure rate than the standard production devices. Texas Instruments recommends that these devices not be used in any production system because their expected end-use failure rate still is undefined. Only qualified production devices are to be used.
TI device nomenclature also includes a suffix with the device family name. This suffix indicates the package type (for example, GMH), the temperature range (for example, blank is the default case temperature range), and the device speed range, in megahertz (for example, blank is 1000 MHz [1 GHz]).
Figure 6-1 provides a legend for reading the complete device name for any TMS320C64x+™ DSP generation member.
For device part numbers and further ordering information for C6457 in the GMH package type, see the TI website www.ti.com or contact your TI sales representative.
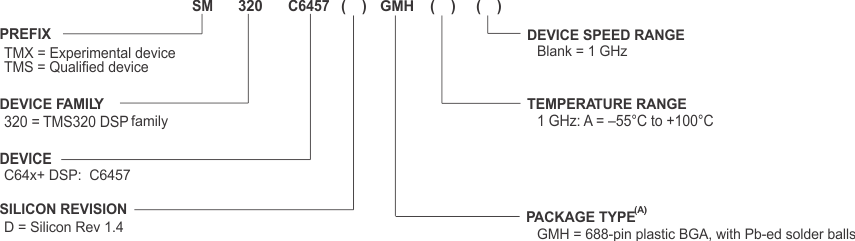 Figure 6-1 TMS320C64x+™ DSP Device Nomenclature (including the C6457 DSP)
Figure 6-1 TMS320C64x+™ DSP Device Nomenclature (including the C6457 DSP)
| (A) BGA = Ball Grid Array |
6.2 Tools and Software
In case the customer would like to develop their own features and software on the C6457 device, TI offers an extensive line of development tools for the TMS320C6000™ DSP platform, including tools to evaluate the performance of the processors, generate code, develop algorithm implementations, and fully integrate and debug software and hardware modules. The tool's support documentation is electronically available within the Code Composer Studio™ Integrated Development Environment (IDE).
The following products support development of C6000™ DSP-based applications:
-
Software Development Tools:
- Code Composer Studio™ Integrated Development Environment (IDE), including Editor C/C++/Assembly Code Generation, and Debug plus additional development tools
- Scalable, Real-Time Foundation Software (DSP/BIOS™), which provides the basic run-time target software needed to support any DSP application.
-
Hardware Development Tools:
- Extended Development System (XDS™) Emulator (supports C6000™ DSP multiprocessor system debug)
- EVM (Evaluation Module)
6.3 Documentation Support
The documents shown in Table 6-1 describe the C6457 Communications Infrastructure Digital Signal Processor. Copies of these documents are available on the Internet at www.ti.com. Tip: Enter the literature number in the search box provided at www.ti.com.
The current documentation that describes the C6457, related peripherals, and other technical collateral, is available in the C6000 DSP product folder at: www.ti.com/c6000.
Table 6-1 Relevant Documents
| TI LITERATURE NO. | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| SPRU732 | TMS320C64x/C64x+ DSP CPU and Instruction Set Reference Guide. Describes the CPU architecture, pipeline, instruction set, and interrupts for the TMS320C64x and TMS320C64x+ digital signal processors (DSPs) of the TMS320C6000 DSP family. The C64x/C64x+ DSP generation comprises fixed-point devices in the C6000 DSP platform. The C64x+ DSP is an enhancement of the C64x DSP with added functionality and an expanded instruction set. |
| SPRU871 | TMS320C64x+ Megamodule Reference Guide. Describes the TMS320C64x+ digital signal processor (DSP) megamodule. Included is a discussion on the internal direct memory access (IDMA) controller, the interrupt controller, the power-down controller, memory protection, bandwidth management, and the memory and cache. |
| SPRAA84 | TMS320C64x to TMS320C64x+ CPU Migration Guide. Describes migrating from the Texas Instruments TMS320C64x digital signal processor (DSP) to the TMS320C64x+ DSP. The objective of this document is to indicate differences between the two cores. Functionality in the devices that is identical is not included. |
| SPRU889 | High-Speed DSP Systems Design Reference Guide. Provides recommendations for meeting the many challenges of high-speed DSP system design. These recommendations include information about DSP audio, video, and communications systems for the C5000 and C6000 DSP platforms. |
| SPRU925 | TMS320TCI648x DSP External Memory Interface (EMIF) User's Guide. This document describes the operation of the external memory interface (EMIF) in the digital signal processors (DSPs) of the TMS320TCI648x DSP family. |
| SPRU725 | TMS320TCI648x DSP General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) User's Guide. This document describes the general-purpose input/output (GPIO) peripheral in the digital signal processors (DSPs) of the TMS320TCI648x DSP family. The GPIO peripheral provides dedicated general-purpose pins that can be configured as either inputs or outputs. When configured as an input, you can detect the state of the input by reading the state of an internal register. When configured as an output, you can write to an internal register to control the state driven on the output pin. |
| SPRU874 | TMS320TCI648x DSP Host Port Interface (HPI) User's Guide. This guide describes the host port interface (HPI) on the TMS320TCI648x digital signal processors (DSPs). The HPI enables an external host processor (host) to directly access DSP resources (including internal and external memory) using a 16-bit (HPI16) or 32-bit (HPI32) interface. |
| SPRUE11 | TMS320TCI648x DSP Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Module User's Guide. This document describes the inter-integrated circuit (I2C) module in the TMS320TCI648x Digital Signal Processor (DSP). The I2C provides an interface between the TMS320TCI648x device and other devices compliant with Philips Semiconductors Inter-IC bus (I2C-bus) specification version 2.1 and connected by way of an I2C-bus. This document assumes the reader is familiar with the I2C-bus specification. |
| SPRU806 | TMS320TCI648x DSP Software-Programmable Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) Controller UG. This document describes the operation of the software-programmable phase-locked loop (PLL) controller in the TMS320TCI648x digital signal processors (DSPs). The PLL controller offers flexibility and convenience by way of software-configurable multipliers and dividers to modify the input signal internally. The resulting clock outputs are passed to the TMS320TCI648x DSP core, peripherals, and other modules inside the TMS320TCI648x DSP. |
| SPRU818 | TMS320TCI648x DSP 64-Bit Timer User's Guide. This document provides an overview of the 64-bit timer in the TMS320TCI648x DSP. The timer can be configured as a general-purpose 64-bit timer, dual general-purpose 32-bit timers, or a watchdog timer. When configured as a dual 32-bit timers, each half can operate in conjunction (chain mode) or independently (unchained mode) of each other. |
| SPRUE10 | TMS320TCI648x DSP Turbo-Decoder Coprocessor 2 (TCP2) Reference Guide. Channel decoding of high bit-rate data channels found in third generation (3G) cellular standards requires decoding of turbo-encoded data. The turbo-decoder coprocessor (TCP) in some of the digital signal processor (DSPs) of the TMS320C6000™ DSP family has been designed to perform this operation for IS2000 and 3GPP wireless standards. This document describes the operation and programming of the TCP. |
| SPRUE09 | TMS320TCI648x DSP Viterbi-Decoder Coprocessor 2 (VCP2) Reference Guide. Channel decoding of voice and low bit-rate data channels found in third generation (3G) cellular standards requires decoding of convolutional encoded data. The Viterbi-decoder coprocessor 2 (VCP2) provided in TMS320TCI648x devices has been designed to perform Viterbi-Decoding for IS2000 and 3GPP wireless standards. The VCP2 coprocessor has been designed to perform forward error correction for 2G and 3G wireless systems. The VCP2 coprocessor offers a very cost effective and synergistic solution when combined with Texas Instruments (TI) DSPs. The VCP2 can support 1941 12.2 Kbps class A 3G voice channels running at 333 MHz. This document describes the operation and programming of the VCP2. |
| SPRUFC4 | TMS320TCI6484 DSP Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC) / Management Data Input Output (MDIO) User’s Guide. This document provides a functional description of the Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC) and Physical layer (PHY) device Management Data Input/Output (MDIO) module integrated with TMS320TCI6487/8 devices. Included are the features of the EMAC and MDIO modules, a discussion of their architecture and operation, how these modules connect to the outside world, and the registers description for each module. |
| SPRUGK5 | TMS320C6457 DSP DDR2 Memory Controller User's Guide. This document describes the DDR2 memory controller in the TMS320C6457 digital-signal processors (DSPs). |
| SPRUGK6 | TMS320C6457 DSP Enhanced DMA (EDMA3) Controller User's Guide. This document describes the Enhanced DMA (EDMA3) Controller on the TMS320C6457 device. |
| SPRUGK2 | TMS320C6457 DSP External Memory Interface (EMIF) User's Guide. This document describes the operation of the external memory interface (EMIF) in the digital signal processors (DSPs) of the TMS320C6457 DSP family. |
| SPRUGL2 | TMS320C6457 DSP General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) User's Guide. This document describes the general-purpose input/output (GPIO) peripheral in the digital signal processors (DSPs) of the TMS320C6457 DSP family. The GPIO peripheral provides dedicated general-purpose pins that can be configured as either inputs or outputs. When configured as an input, you can detect the state of the input by reading the state of an internal register. When configured as an output, you can write to an internal register to control the state driven on the output pin. |
| SPRUGK7 | TMS320C6457 DSP Host Port Interface (HPI) User's Guide. This guide describes the host port interface (HPI) on the TMS320C6457 digital signal processors (DSPs). The HPI enables an external host processor (host) to directly access DSP resources (including internal and external memory) using a 16-bit (HPI16) or 32-bit (HPI32) interface. |
| SPRUGK3 | TMS320C6457 DSP Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Module User's Guide. This document describes the inter-integrated circuit (I2C) module in the TMS320C6457 Digital Signal Processor (DSP). The I2C provides an interface between the TMS320C6457 device and other devices compliant with Philips Semiconductors Inter-IC bus (I2C-bus) specification version 2.1 and connected by way of an I2C-bus. This document assumes the reader is familiar with the I2C-bus specification. |
| SPRUGK4 | TMS320C6457 Serial RapidIO (SRIO) User's Guide. This document describes the Serial RapidIO (SRIO) on the TMS320C6457 devices. |
| SPRUGL3 | TMS320C6457 DSP Software-Programmable Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) Controller UG. This document describes the operation of the software-programmable phase-locked loop (PLL) controller in the TMS320C6457 digital signal processors (DSPs). The PLL controller offers flexibility and convenience by way of software-configurable multipliers and dividers to modify the input signal internally. The resulting clock outputs are passed to the TMS320C6457 DSP core, peripherals, and other modules inside the TMS320C6457 DSP. |
| SPRUGL0 | TMS320C6457 DSP 64-Bit Timer User's Guide. This document provides an overview of the 64-bit timer in the TMS320C6457 DSP. The timer can be configured as a general-purpose 64-bit timer, dual general-purpose 32-bit timers, or a watchdog timer. When configured as a dual 32-bit timers, each half can operate in conjunction (chain mode) or independently (unchained mode) of each other. |
| SPRUGK1 | TMS320C6457 DSP Turbo-Decoder Coprocessor 2 (TCP2) Reference Guide. Channel decoding of high bit-rate data channels found in third generation (3G) cellular standards requires decoding of turbo-encoded data. The turbo-decoder coprocessor (TCP) in some of the digital signal processor (DSPs) of the TMS320C6000™ DSP family has been designed to perform this operation for IS2000 and 3GPP wireless standards. This document describes the operation and programming of the TCP. |
| SPRUGL1 | TMS320C6457 DSP Universal Test & Operations PHY Interface for ATM 2 (UTOPIA2) User's Guide. This document describes the universal test and operations PHY interface for asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) 2 (UTOPIA2) in the TMS320C6457 digital signal processors (DSPs) of the TMS320C6000™ DSP family. |
| SPRUGK0 | TMS320C6457 DSP Viterbi-Decoder Coprocessor 2 (VCP2) Reference Guide. Channel decoding of voice and low bit-rate data channels found in third generation (3G) cellular standards requires decoding of convolutional encoded data. The Viterbi-decoder coprocessor 2 (VCP2) provided in TMS320C6457 devices has been designed to perform Viterbi-Decoding for IS2000 and 3GPP wireless standards. The VCP2 coprocessor has been designed to perform forward error correction for 2G and 3G wireless systems. The VCP2 coprocessor offers a very cost effective and synergistic solution when combined with Texas Instruments (TI) DSPs. The VCP2 can support 1941 12.2 Kbps class A 3G voice channels running at 333 MHz. This document describes the operation and programming of the VCP2. |
| SPRUGK9 | TMS320C6457 DSP Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC) / Management Data Input Output (MDIO) User’s Guide. This document provides a functional description of the Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC) and Physical layer (PHY) device Management Data Input/Output (MDIO) module integrated with TMS320C6457 devices. Included are the features of the EMAC and MDIO modules, a discussion of their architecture and operation, how these modules connect to the outside world, and the registers description for each module. |
| SPRUGK8 | TMS320C6457 DSP Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP) Reference Guide. This document describes the operation of the multichannel buffered serial port (McBSP) in the digital signal processors (DSPs) of the TMS320C6000™ DSP family. |
| SPRUGL4 | TMS320C6457 DSP Power/Sleep Controller (PSC) User’s Guide. This document covers the usage of the Power/Sleep Controller (PSC) in the TMS320C6457 device. |
| SPRUGL5 | TMS320C6457 DSP Bootloader User’s Guide. This document describes the features of the on-chip bootloader provided with the TMS320C6457 Digital Signal Processor (DSP). |
6.3.1 Receiving Notification of Documentation Updates
To receive notification of documentation updates, navigate to the device product folder on ti.com. In the upper right corner, click on Alert me to register and receive a weekly digest of any product information that has changed. For change details, review the revision history included in any revised document.
6.4 Community Resources
The following links connect to TI community resources. Linked contents are provided "AS IS" by the respective contributors. They do not constitute TI specifications and do not necessarily reflect TI's views; see TI's Terms of Use.
-
TI E2E™ Online Community TI's Engineer-to-Engineer (E2E) Community. Created to foster collaboration among engineers. At e2e.ti.com, you can ask questions, share knowledge, explore ideas and help solve problems with fellow engineers.
-
TI Embedded Processors Wiki Texas Instruments Embedded Processors Wiki. Established to help developers get started with Embedded Processors from Texas Instruments and to foster innovation and growth of general knowledge about the hardware and software surrounding these devices.
6.5 Trademarks
TMS320C64x+, TMS320C6000, VelociTI, Code Composer Studio, E2E are trademarks of Texas Instruments.
Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
6.6 Electrostatic Discharge Caution

This integrated circuit can be damaged by ESD. Texas Instruments recommends that all integrated circuits be handled with appropriate precautions. Failure to observe proper handling and installation procedures can cause damage.
ESD damage can range from subtle performance degradation to complete device failure. Precision integrated circuits may be more susceptible to damage because very small parametric changes could cause the device not to meet its published specifications.
6.7 Glossary
-
TI Glossary This glossary lists and explains terms, acronyms, and definitions.