SLLS665M September 2005 – February 2023 SN65HVD30 , SN65HVD31 , SN65HVD32 , SN65HVD33 , SN65HVD34 , SN65HVD35
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics: Driver
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics: Receiver
- 7.7 Device Power Dissipation – PD
- 7.8 Supply Current Characteristics
- 7.9 Switching Characteristics: Driver
- 7.10 Switching Characteristics: Receiver
- 7.11 Dissipation Ratings
- 7.12 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- D|14
Orderable Information
9.2.1.1 Data Rate and Bus Length
There is an inverse relationship between data rate and bus length, meaning the higher the data rate, the shorter the cable length; and conversely, the lower the data rate, the longer the cable can be without introducing data errors. While most RS-485 systems use data rates between 10 kbps and 100 kbps, some applications require data rates up to 250 kbps at distances of 4000 feet and longer. Longer distances are possible by allowing for small signal jitter of up to 5 or 10%.
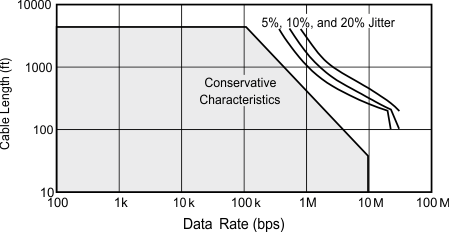 Figure 9-3 Cable Length vs Data Rate Characteristic
Figure 9-3 Cable Length vs Data Rate CharacteristicEven higher data rates are achievable (such as 26 Mbps for the SN65HVD30 and SN65HVD33 devices) in cases where the interconnect is short enough (or has suitably low attenuation at signal frequencies) to not degrade the data.