SLLS378E May 2000 – January 2023 SN65LBC180A , SN75LBC180A
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1Features
- 2Description
- 3Revision History
- 4Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5Reference
- 6Detailed Description
- 7Application Information
- 8Device and Documentation Support
- 9Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- N|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
Typical Characteristics
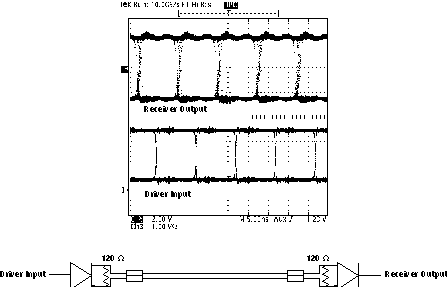 Figure 5-1 Typical Waveform of Nonreturn-to-Zero (NRZ), Pseudorandom Binary Sequence (PRBS) Data at 100 Mbps Through 15m, of CAT 5 Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable
Figure 5-1 Typical Waveform of Nonreturn-to-Zero (NRZ), Pseudorandom Binary Sequence (PRBS) Data at 100 Mbps Through 15m, of CAT 5 Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) CableTIA/EIA-485-A defines a maximum signaling rate as that in which the transition time of the voltage transition of a logic-state change remains less than or equal to 30% of the bit length. Transition times of greater length perform quite well even though they do not meet the standard by definition.
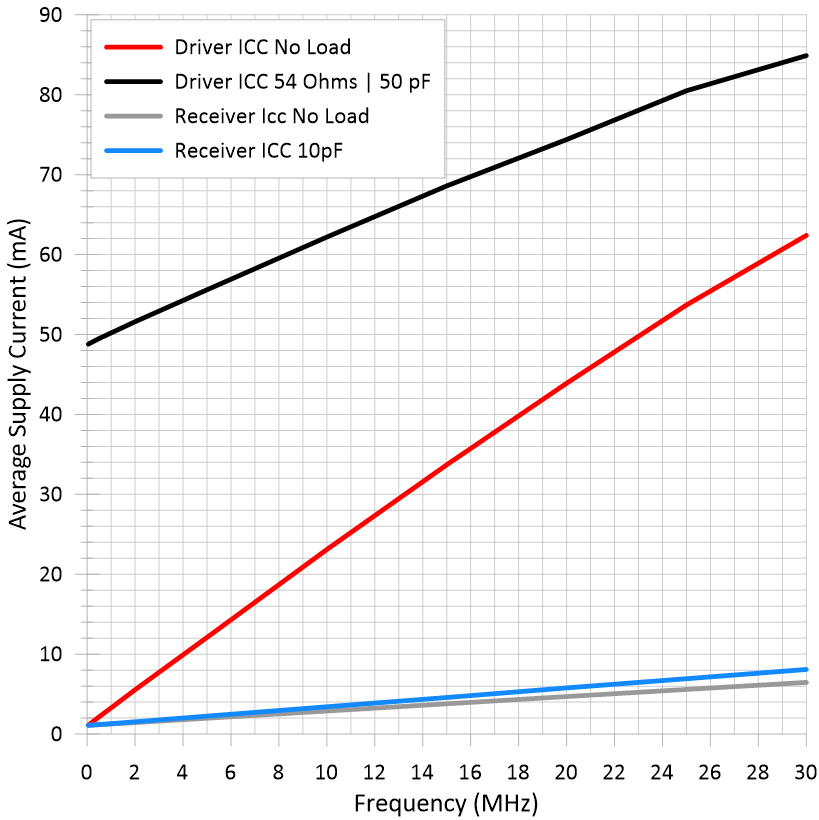 Figure 5-2 Average Supply Current vs
Frequency
Figure 5-2 Average Supply Current vs
Frequency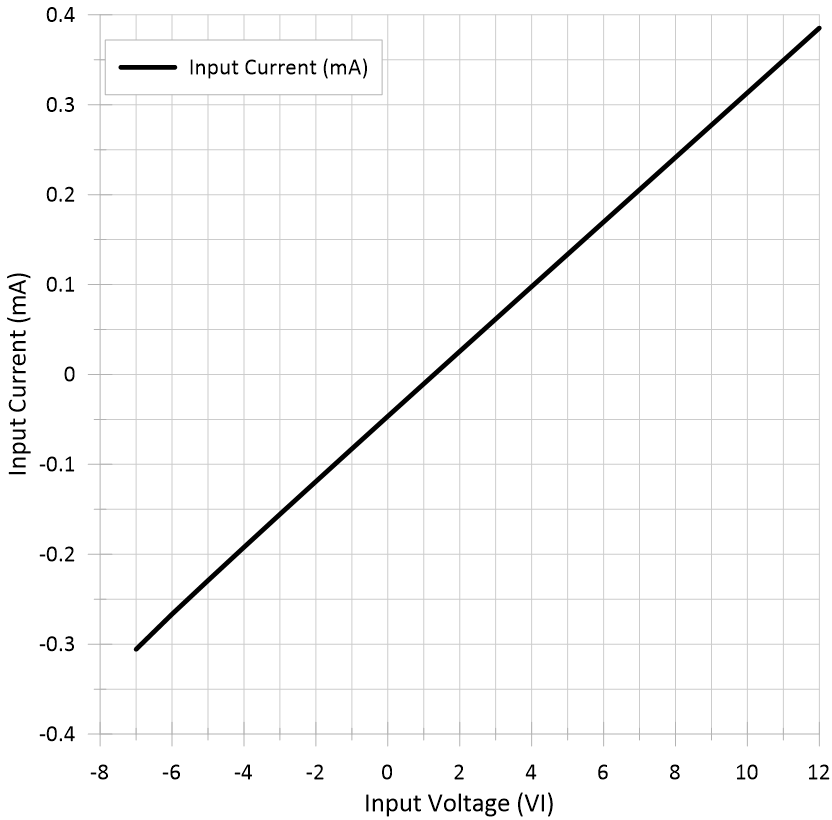 Figure 5-4 Bus Input Current vs Input
Voltage
Figure 5-4 Bus Input Current vs Input
Voltage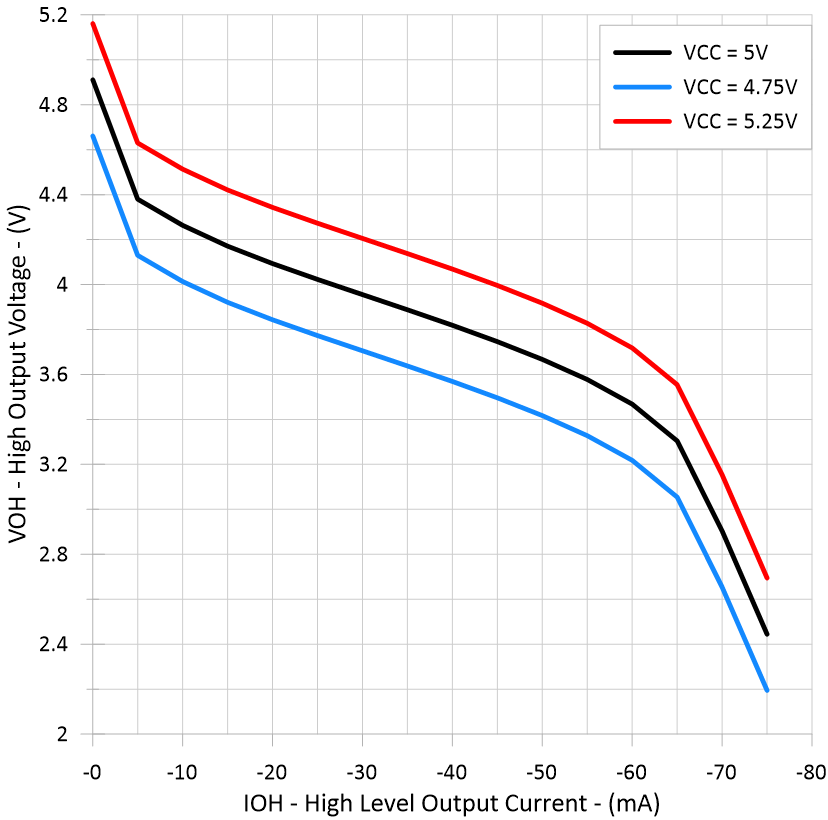 Figure 5-6 Driver High-Level Output
Voltage vs High-Level Output Current
Figure 5-6 Driver High-Level Output
Voltage vs High-Level Output Current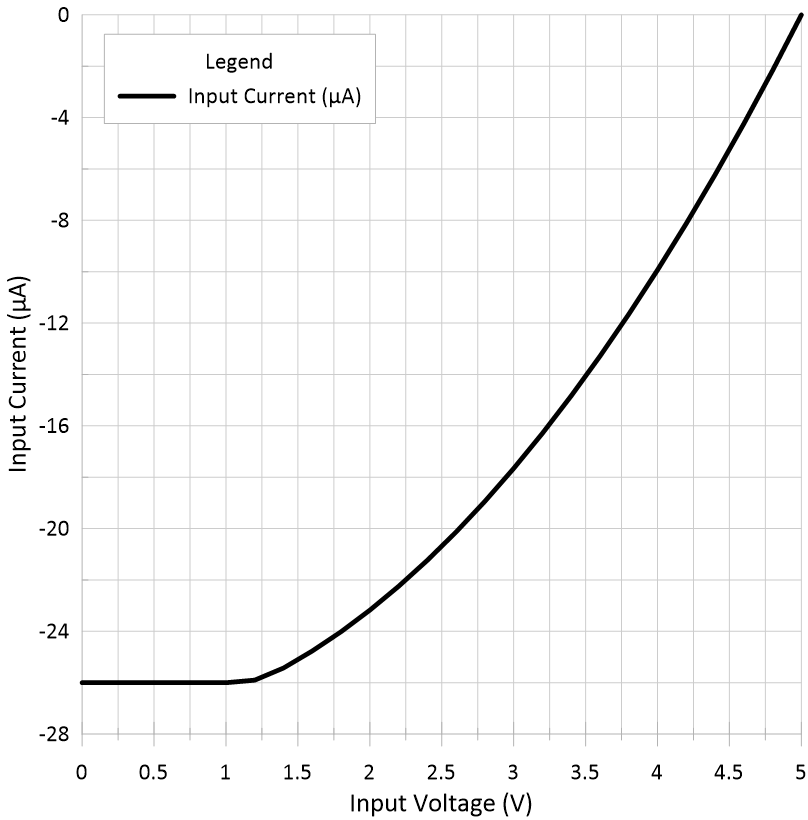 Figure 5-3 Logic Input Current vs
Input Voltage
Figure 5-3 Logic Input Current vs
Input Voltage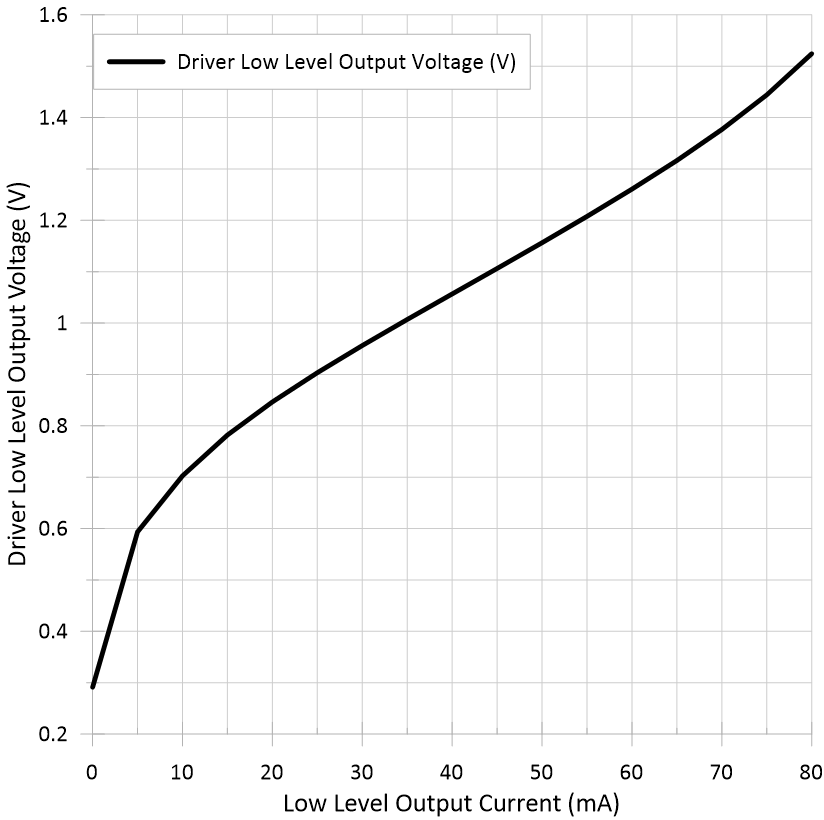 Figure 5-5 Driver Low-Level Output
Voltage vs Low-Level Output Current
Figure 5-5 Driver Low-Level Output
Voltage vs Low-Level Output Current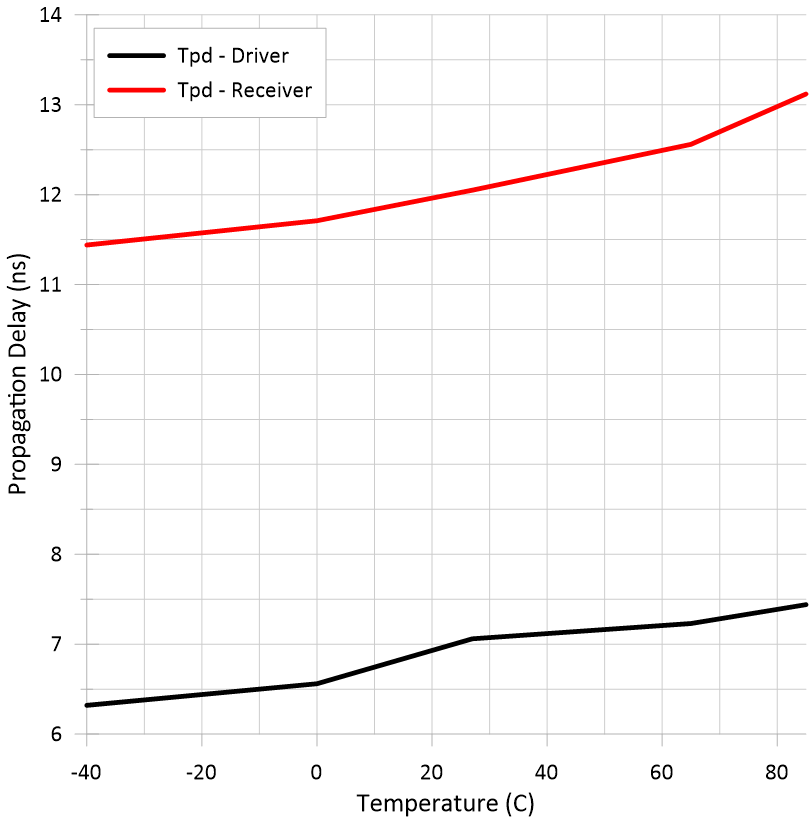 Figure 5-7 Propagation Delay Time vs
Case Temperature
Figure 5-7 Propagation Delay Time vs
Case Temperature