SLLSF68 September 2019 THVD1505
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
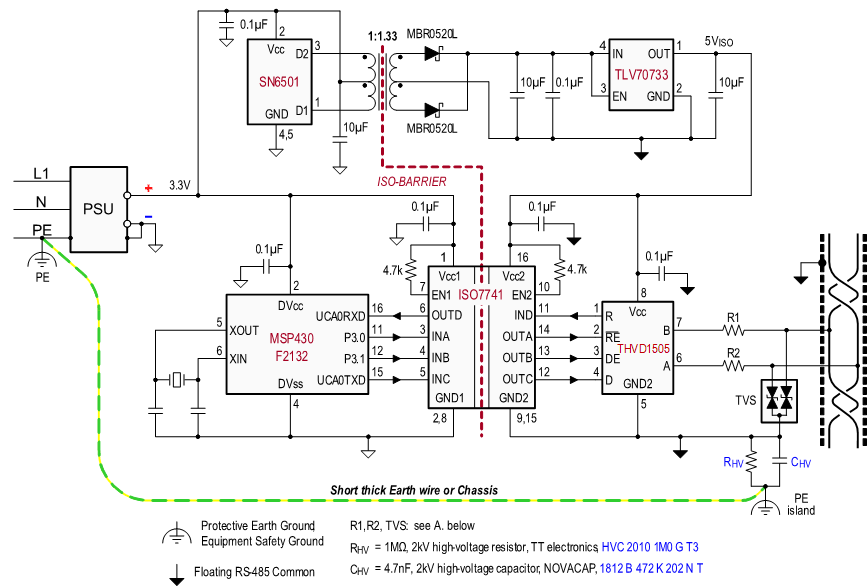
9.2 Typical Application
Many RS-485 networks use isolated bus nodes to prevent the creation of unintended ground loops and their disruptive impact on signal integrity. An isolated bus node typically includes a micro controller that connects to the bus transceiver through a multi-channel, digital isolator (Figure 29).