SLDS156B March 2009 – July 2015 TLC59108
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6
Register Maps
- 9.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 9.6.1.1 Mode Register 1 (MODE1)
- 9.6.1.2 Mode Register 2 (MODE2)
- 9.6.1.3 Brightness Control Registers 0 to 7 (PWM0 to PWM7)
- 9.6.1.4 Group Duty Cycle Control Register (GRPPWM)
- 9.6.1.5 Group Frequency Register (GRPFREQ)
- 9.6.1.6 LED Driver Output State Registers (LEDOUT0, LEDOUT1)
- 9.6.1.7 I2C Bus Subaddress Registers 1 to 3 (SUBADR1 to SUBADR3)
- 9.6.1.8 LED All Call I2C Bus Address Register (ALLCALLADR)
- 9.6.1.9 Output Gain Control Register (IREF)
- 9.6.1.10 Error Flags Registers (EFLAG)
- 9.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGY|20
Orderable Information
12 Layout
12.1 Layout Guidelines
The I2C signals (SDA / SCL) should be kept away from potential noise sources.
The traces carrying power through the LEDs should be wide enough to handle the necessary current.
All LED current passes through the device and into the ground node. There must be a strong connection between the device ground and the circuit board ground. For the RGY package, the thermal pad should be connected to the ground to help dissipate heat.
12.2 Layout Examples
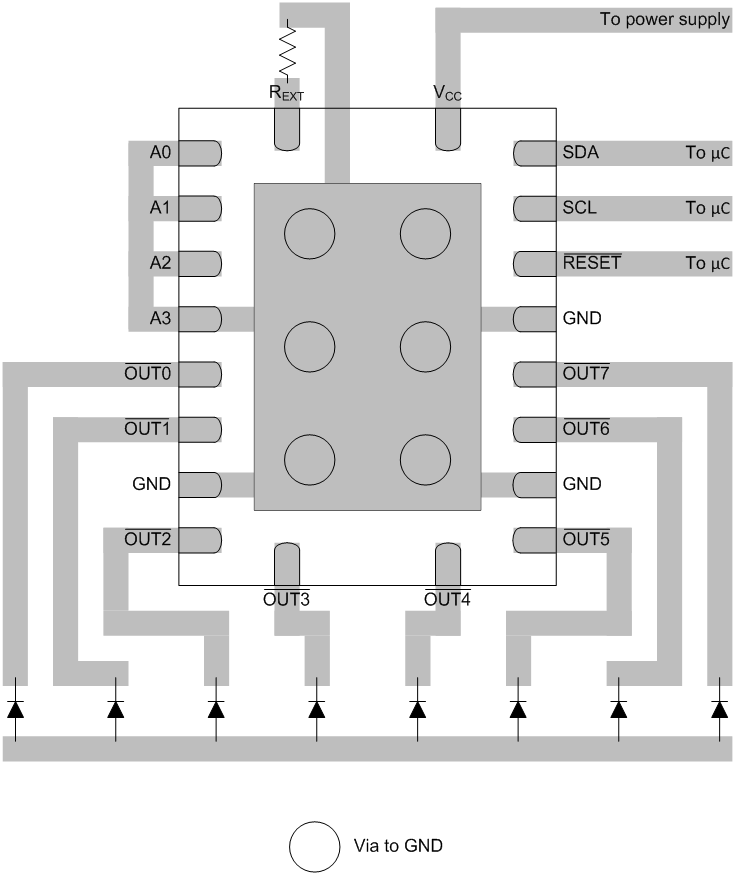 Figure 27. Layout Example for RGY Package
Figure 27. Layout Example for RGY Package
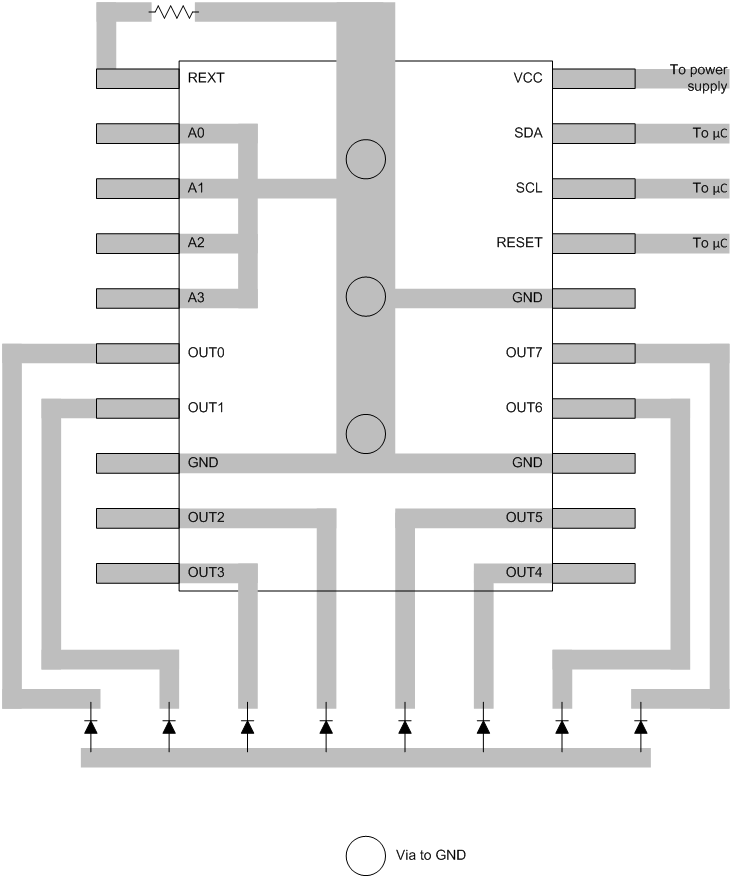 Figure 28. Layout Example for PW Package
Figure 28. Layout Example for PW Package