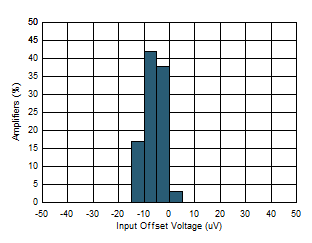
| Offset Voltage Distribution |
Figure 1 |
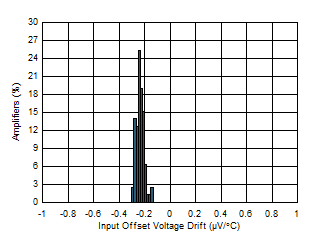
| Offset Voltage Drift (-40°C to +125C°C) |
Figure 2 |
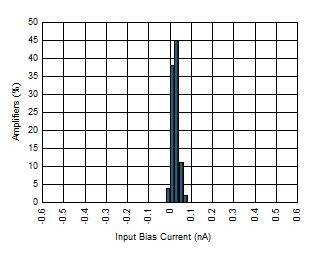
| Input Bias Current Distribution |
Figure 3 |
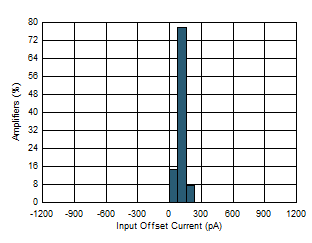
| Input Offset Current Distribution |
Figure 4 |
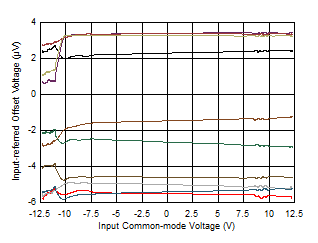
| Offset Voltage vs Common-Mode Voltage |
Figure 5 |
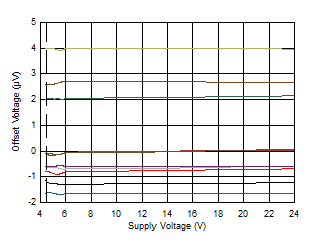
| Offset Voltage vs Supply Voltage |
Figure 6 |
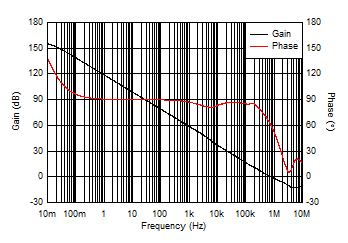
| Open-Loop Gain and Phase vs Frequency |
Figure 7 |
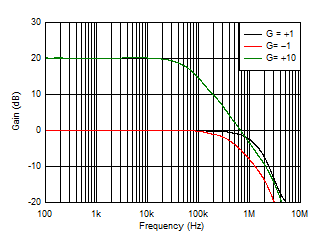
| Closed-Loop Gain vs Frequency |
Figure 8 |
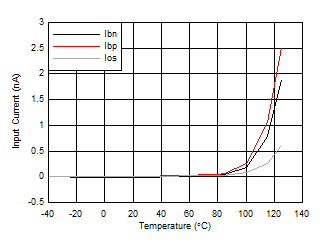
| Input Bias Current and Offset Current vs Temperature |
Figure 9 |
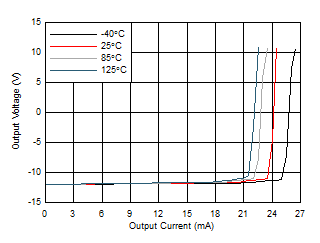
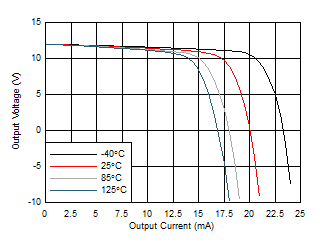
| Output Voltage Swing vs Output Current (Sourcing) |
Figure 10 |
| Output Voltage Swing vs Output Current (Sinking) |
Figure 11 |
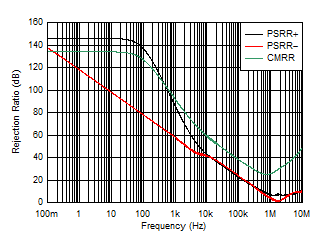
| CMRR and PSRR vs Frequency |
Figure 12 |
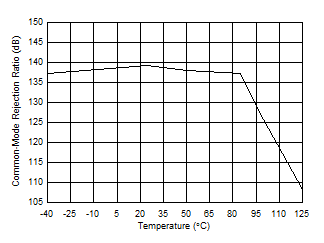
| CMRR vs Temperature |
Figure 13 |
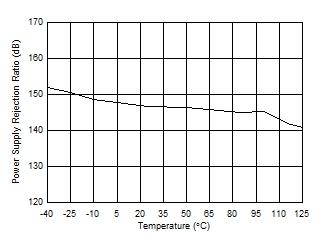
| PSRR vs Temperature |
Figure 14 |
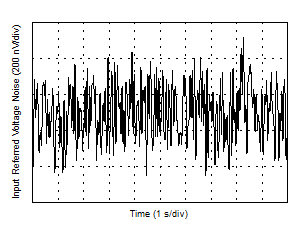
| 0.1-Hz to 10-Hz Voltage Noise |
Figure 15 |
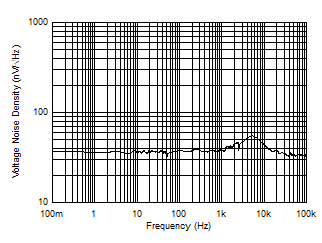
| Input Voltage Noise Spectral Density vs Frequency |
Figure 16 |
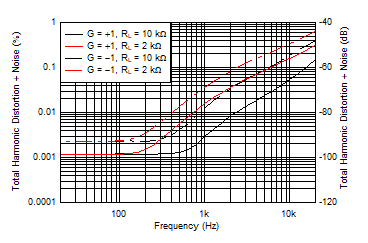
| THD+N vs Frequency |
Figure 17 |
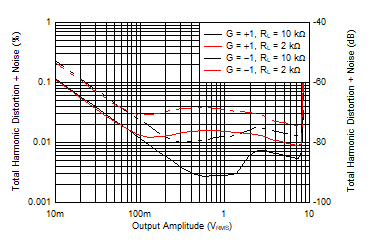
| THD+N vs Output Amplitude |
Figure 18 |
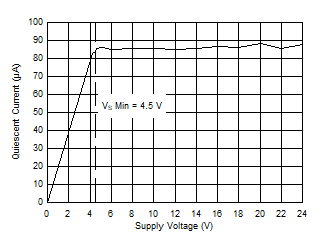
| Quiescent Current vs Supply Voltage |
Figure 19 |
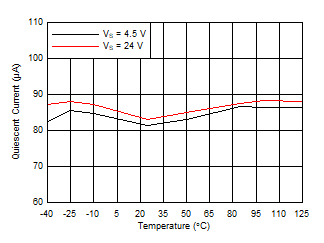
| Quiescent Current vs Temperature |
Figure 20 |
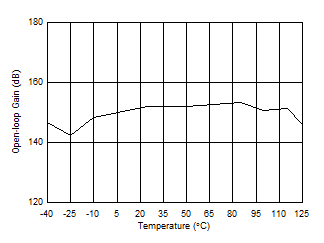
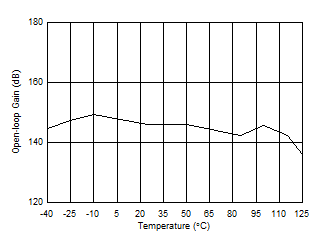
| Open-Loop Gain vs Temperature (10 kΩ) |
Figure 21 |
| Open-Loop Gain vs Temperature (2 kΩ) |
Figure 22 |
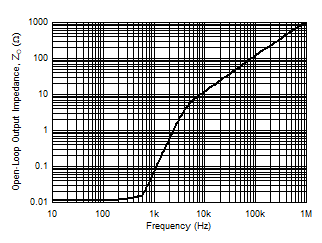
| Open-Loop Output Impedance vs Frequency |
Figure 23 |
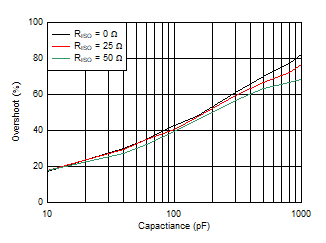
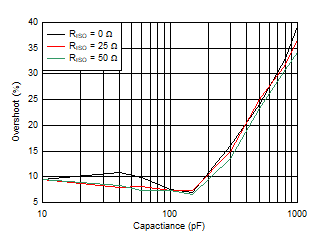
| Small-Signal Overshoot vs Capacitive Load (Gain = –1, 10-mV step) |
Figure 24 |
| Small-Signal Overshoot vs Capacitive Load (Gain = 1, 10-mV step) |
Figure 25 |
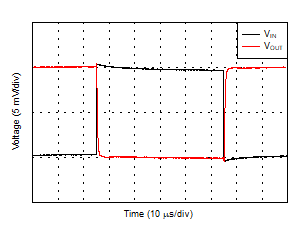
| No Phase Reversal |
Figure 26 |
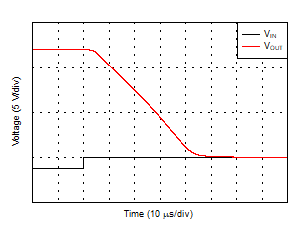
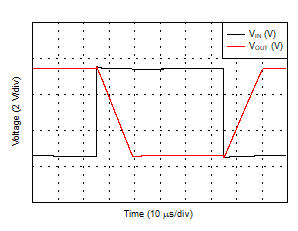
| Positive Overload Recovery |
Figure 27 |
| Negative Overload Recovery |
Figure 28 |
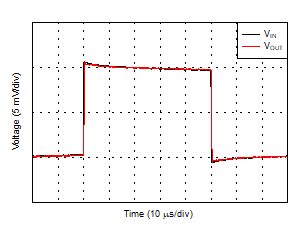
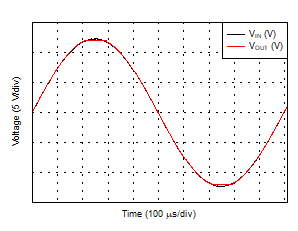
| Small-Signal Step Response (Gain = 1, 10-mV step) |
Figure 29 |
| Small-Signal Step Response (Gain = –1, 10-mV step) |
Figure 30 |
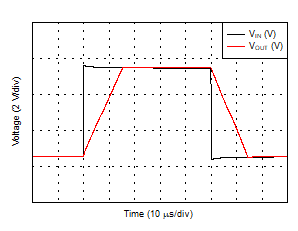
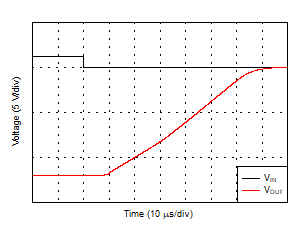
| Large-Signal Step Response (Gain = 1, 10-V step) |
Figure 31 |
| Large-Signal Step Response (Gain = –1, 10-V step) |
Figure 32 |
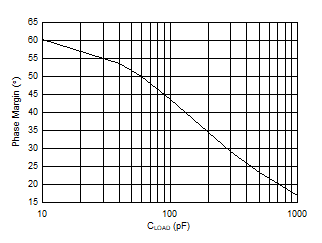
| Phase Margin vs Capacitive Load |
Figure 33 |
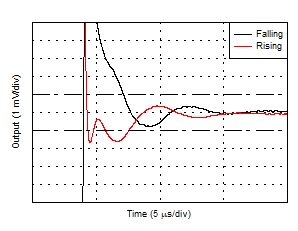
| Settling Time (1-V Step, 0.1% Settling) |
Figure 34 |
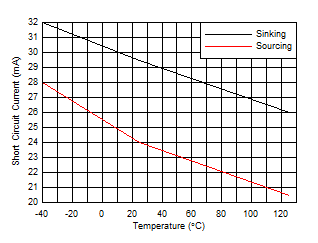
| Short Circuit Current vs Temperature |
Figure 35 |
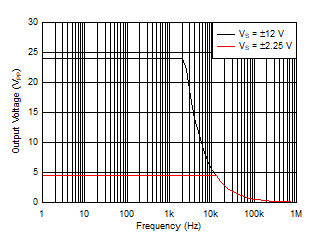
| Maximum Output Voltage vs Frequency |
Figure 36 |
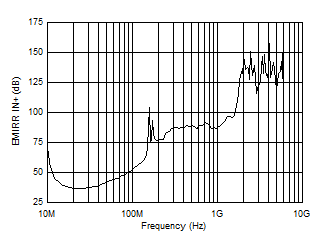
| EMIRR vs Frequency |
Figure 37 |
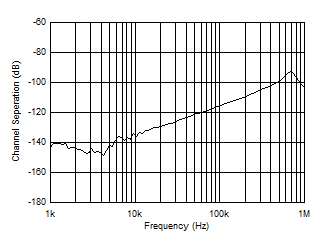
| Channel Separation |
Figure 38 |