SBOS751 December 2015 TLV2333 , TLV333 , TLV4333
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
11.1.1 General Layout Guidelines
Attention to good layout practice is always recommended. Keep traces short and, when possible, use a printed circuit board (PCB) ground plane with surface-mount components placed as close to the device pins as possible. Place a 0.1-μF capacitor closely across the supply pins. Apply these guidelines throughout the analog circuit to improve performance and to provide benefits such as reducing the electromagnetic interference (EMI) susceptibility.
For lowest offset voltage and precision performance, circuit layout and mechanical conditions must be optimized. Avoid temperature gradients that create thermoelectric (Seebeck) effects in the thermocouple junctions formed from connecting dissimilar conductors. These thermally-generated potentials can be made to cancel by assuring they are equal on both input terminals. Other layout and design considerations include:
- Use low thermoelectric-coefficient conditions (avoid dissimilar metals).
- Thermally isolate components from power supplies or other heat sources.
- Shield op amp and input circuitry from air currents, such as cooling fans.
Following these guidelines reduces the likelihood of junctions being at different temperatures, which can cause thermoelectric voltages of 0.1 μV/°C or higher, depending on materials used.
11.2 Layout Example
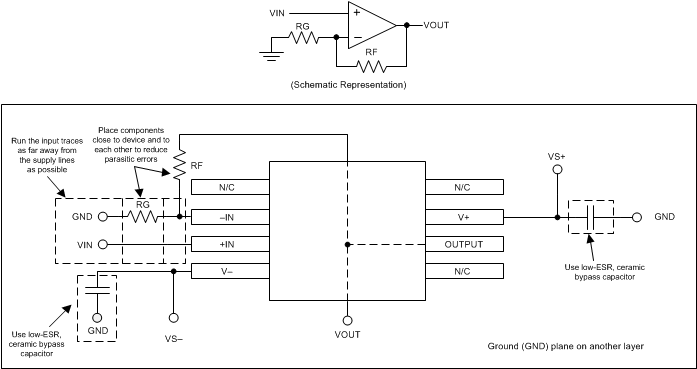 Figure 24. Layout Example
Figure 24. Layout Example