SBVS157E April 2011 – December 2020 TLV803 , TLV853
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBZ|3
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.1.2 Output Level Shifting
The RESET output of the TLV803 can be pulled to a maximum voltage of 6 V and can be pulled higher in voltage than VDD. It is useful to provide level shifting of the output for cases where the monitored voltage is less than the useful logic levels of the load. Figure 9-2 shows the TLV803Z used to monitor a 2.5-V power rail, with a logic RESET input to a microprocessor that is connected to 5.0 V and has 5.0-V logic levels.
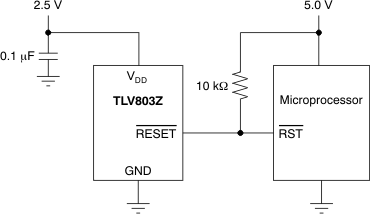 Figure 9-2 Output Voltage Level Shifting
Figure 9-2 Output Voltage Level Shifting