SBOS702E October 2014 – September 2021 TMP102-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Digital Temperature Output
- 7.3.2 Serial Interface
- 7.3.3 Bus Overview
- 7.3.4 Serial Bus Address
- 7.3.5 Writing and Reading Operation
- 7.3.6 Slave Mode Operations
- 7.3.7 SMBus Alert Function
- 7.3.8 General Call
- 7.3.9 High-Speed (Hs) Mode
- 7.3.10 Time-Out Function
- 7.3.11 Timing Diagrams
- 7.3.12 Two-Wire Timing Diagrams
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRL|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.5.1 Pointer Register
Figure 7-7 shows the internal register structure of the TMP102-Q1 device. The 8-bit pointer register of the device is used to address a given data register. The pointer register uses the two least-significant bytes (LSBs) (see Table 7-13) to identify which of the data registers must respond to a read or write command. The power-up reset value of P1 and P0 is 00. By default, the TMP102-Q1 device reads the temperature on power up.
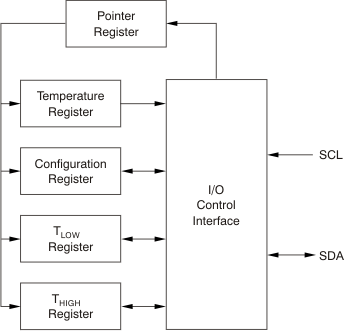 Figure 7-7 Internal Register Structure
Figure 7-7 Internal Register StructureTable 7-6 lists the pointer address of the registers available in the TMP102-Q1 device. Table 7-7 lists the bits of the pointer register byte. During a write command, P2 through P7 must always be 0.
Table 7-6 Pointer Addresses
| P1 | P0 | REGISTER |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | Temperature register (read only) |
| 0 | 1 | Configuration register (read and write) |
| 1 | 0 | TLOW register (read and write) |
| 1 | 1 | THIGH register (read and write) |
Table 7-7 Pointer Register Byte
| P7 | P6 | P5 | P4 | P3 | P2 | P1 | P0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Register bits | |