SLVSBH4F June 2012 – July 2016 TPS22966
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DPU|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DPU|14
Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
For best performance, all traces must be as short as possible. To be most effective, the input and output capacitors must be placed close to the device to minimize the effects that parasitic trace inductances may have on normal operation. Using wide traces for VIN, VOUT, and GND helps minimize the parasitic electrical effects along with minimizing the case to ambient thermal impedance.
11.2 Layout Example
Notice the thermal vias located under the exposed thermal pad of the device. This allows for thermal diffusion away from the device.
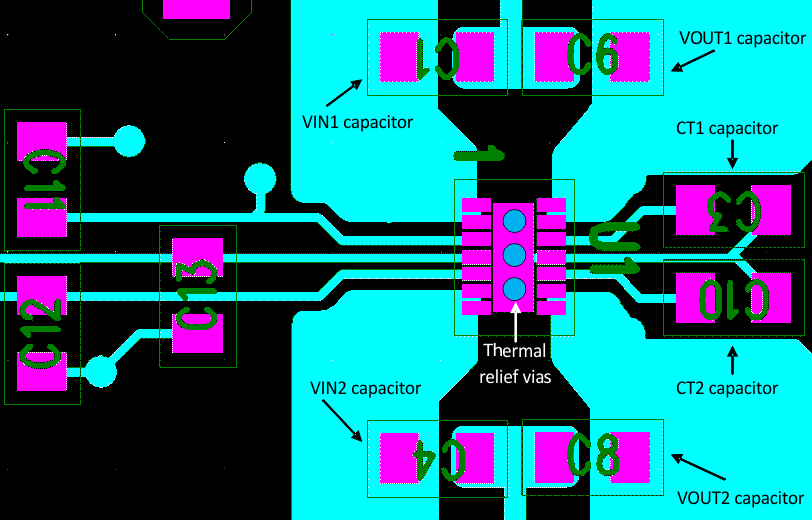 Figure 36. PCB Layout Example
Figure 36. PCB Layout Example
11.3 Thermal Considerations
The maximum IC junction temperature must be restricted to 125°C under normal operating conditions. To calculate the maximum allowable power dissipation, PD(max) for a given output current and ambient temperature, use Equation 5:
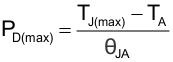
where
- PD(max) is the maximum allowable power dissipation
- TJ(max) is the maximum allowable junction temperature (125°C for the TPS22966)
- TA is the ambient temperature of the device
- θJA is the junction to air thermal impedance. See the Thermal Information section. This parameter is highly dependent upon board layout.