SLVSA05B August 2009 – August 2015 TPS61086
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input voltage IN(2) | –0.3 | 7 | V |
| Voltage on pins EN, FB, SS, MODE, COMP | –0.3 | 7 | V |
| Voltage on pin SW | –0.3 | 20 | V |
| Operating junction temperature | –40 | 150 | °C |
| Storage temperature | –65 | 150 | °C |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability
(2) All voltage values are with respect to network ground terminal.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±500 | |||
| Machine Model | ±200 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process. Pins listed as ±2000 V may actually have higher performance.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process. Pins listed as ±500 V may actually have higher performance.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage | 2.3 | 6 | V | |
| VS | Boost output voltage | VIN + 0.5 | 18.5 | V | |
| TA | Operating free-air temperature | –40 | 85 | °C | |
| TJ | Operating junction temperature | –40 | 125 | °C | |
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TPS61086 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DRC (VSON) | |||
| 10 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 54.7 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 67.2 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 29.6 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 2.3 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 29.8 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 15.6 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
VIN = 3.3 V, EN = IN, VS = 12 V, TA = –40°C to 85°C, typical values are at TA = 25°C (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUPPLY | ||||||
| VIN | Input voltage range | 2.3 | 6 | V | ||
| IQ | Operating quiescent current into IN | Device not switching, VFB = 1.3 V | 75 | 100 | μA | |
| ISDVIN | Shutdown current into IN | EN = GND | 1 | μA | ||
| VUVLO | Undervoltage lockout threshold | VIN falling | 2.2 | V | ||
| VIN rising | 2.3 | V | ||||
| TSD | Thermal shutdown | Temperature rising | 150 | °C | ||
| TSDHYS | Thermal shutdown hysteresis | 14 | °C | |||
| LOGIC SIGNALS EN, FREQ | ||||||
| VIH | High level input voltage | VIN = 2.3 V to 6 V | 2 | V | ||
| VIL | Low level input voltage | VIN = 2.3 V to 6 V | 0.5 | V | ||
| IINLEAK | Input leakage current | EN = GND | 0.1 | μA | ||
| BOOST CONVERTER | ||||||
| VS | Boost output voltage | VIN + 0.5 | 18.5 | V | ||
| VFB | Feedback regulation voltage | 1.23 | 1.238 | 1.246 | V | |
| gm | Transconductance error amplifier | 107 | μA/V | |||
| IFB | Feedback input bias current | VFB = 1.238 V | 0.1 | μA | ||
| rDS(on) | N-channel MOSFET on-resistance | VIN = VGS = 5 V, ISW = current limit | 0.13 | 0.2 | Ω | |
| VIN = VGS = 3.3 V, ISW = current limit | 0.16 | 0.23 | ||||
| ISWLEAK | SW leakage current | EN = GND, VSW = 6 V | 10 | μA | ||
| ILIM | N-channel MOSFET current limit | 2 | 2.6 | 3.2 | A | |
| ISS | Soft-start current | VSS = 1.238 V | 7 | 10 | 13 | μA |
| fS | Oscillator frequency | 0.9 | 1.2 | 1.5 | MHz | |
| Line regulation | VIN = 2.3 V to 6 V, IOUT = 10 mA | 0.0002 | %/V | |||
| Load regulation | VIN = 3.3 V, IOUT = 1 mA to 400 mA | 0.11 | %/A | |||
6.6 Typical Characteristics
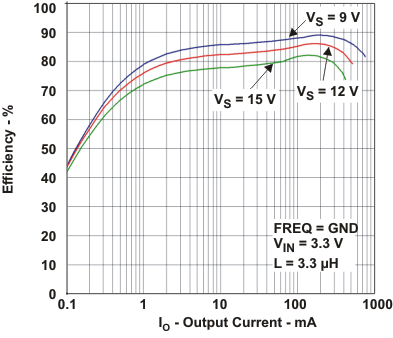
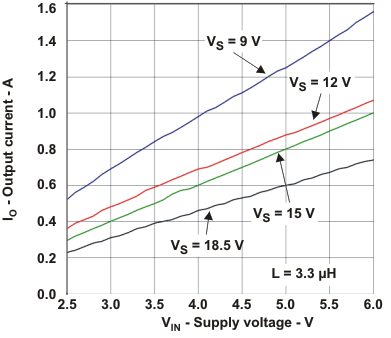
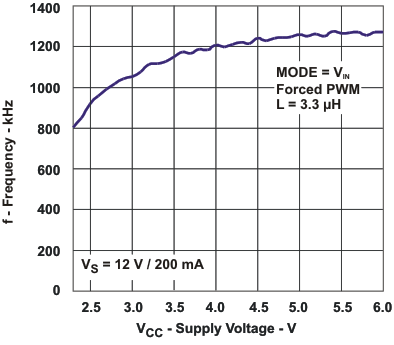
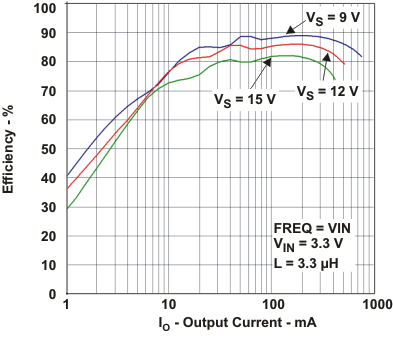
The typical characteristics are measured with the inductor CDRH6D12 3.3 µH from Sumida and the rectifier diode SL22.Table 1. Table of Graphs
| FIGURE | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| η | Efficiency vs Load current- PFM | VIN = 3.3 V, VS = 9 V, 12 V, 15 V | Figure 1 |
| η | Efficiencyvs Load current - Forced PWM | VIN = 3.3 V, VS = 9 V, 12 V, 15 V | Figure 2 |
| Iout(max) | Maximum output current | Figure 3 | |
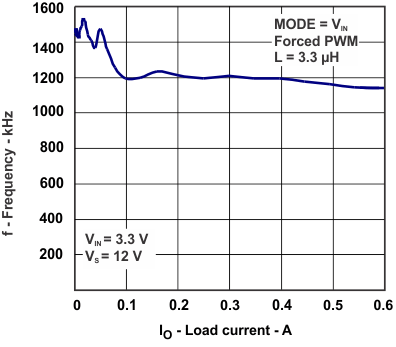
| fS | Switching frequency - Forced PWM | vs Load current, VIN = 3.3 V, VS = 12 V | Figure 4 |
| fS | Switching frequency - Forced PWM | vs Supply voltage, VS = 12 V, Iout = 200 mA | Figure 5 |
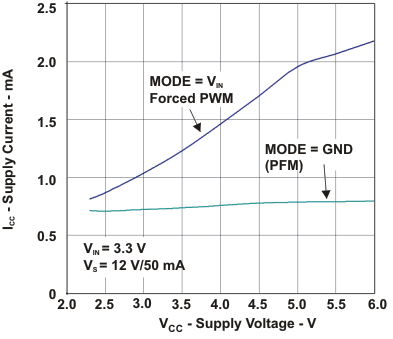
| Supply current | vs Supply voltage,VIN = 3.3 V, VS = 12 V | Figure 6 | |