SLVSC25B July 2013 – June 2017 TPS61197
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1
Protections
- 7.4.1.1 Switch Current Limit Protection Using the ISNS Pin
- 7.4.1.2 LED Open Protection
- 7.4.1.3 Schottky Diode Open Protection
- 7.4.1.4 Schottky Diode Short Protection
- 7.4.1.5 IFB Overvoltage Protection
- 7.4.1.6 Output Overvoltage Protection Using the OVP Pin
- 7.4.1.7 IFB Short-to-Ground Protection
- 7.4.1.8 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4.1
Protections
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7 Detailed Description
7.1 Overview
The TPS61197 provides a highly integrated solution for LCD TV backlight with high precision pulse width modulation (PWM) dimming resolution up to 5000:1. This device is a current-mode boost controller driving one WLED string with multiple LEDs in series. The input voltage range for the device is from 8 V to 30 V.
7.2 Functional Block Diagram
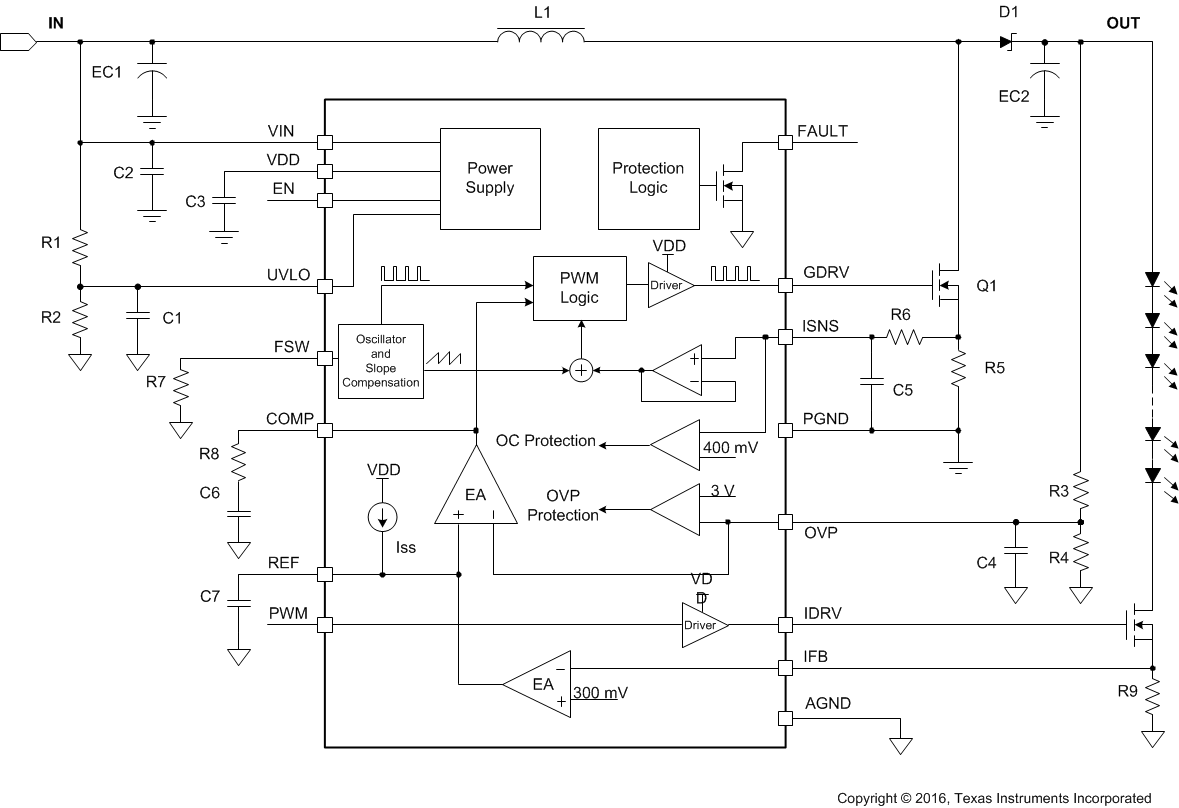
7.3 Feature Description
7.3.1 Supply Voltage
The TPS61197 has a built-in linear regulator to supply the device analog and logic circuits. The VDD pin (output of the regulator) must be connected to a bypass capacitor with more than 1-µF capacitance. VDD only has a current sourcing capability of 15 mA. VDD voltage is ready after the EN pin is pulled high.
7.3.2 Boost Controller
The TPS61197 regulates the output voltage with peak current mode PWM control. The control circuitry turns on an external switch FET at the beginning of each switching cycle. The input voltage is applied across the inductor and stores the energy as the inductor current ramps up. During this portion of the switching cycle, the load current is provided by the output capacitor. When the inductor current rises to the threshold set by the error amplifier (EA) output, the switch FET is turned off and the external Schottky diode is forward biased. The inductor transfers stored energy to replenish the output capacitor and supply the load current. This operation repeats each switching cycle. The switching frequency is programmed by an external resistor.
A ramp signal from the oscillator is added to the current ramp to provide slope compensation, shown in the Functional Block Diagram. The duty cycle of the converter is then determined by the PWM logic block which compares the EA output and the slope compensated current ramp. The feedback loop regulates the OVP pin to a reference voltage generated by the current regulation control circuit which senses the LED current at the IFB pin. The output of the EA is connected to the COMP pin. An external RC compensation network must be connected to the COMP pin to optimize the feedback loop for stability and transient response.
The TPS61197 consistently adjusts the boost output voltage to account for any changes in LED forward voltages. In the event that the boost controller is not able to regulate the output voltage due to the minimum pulse width (ton(min), in the Electrical Characteristics table), the TPS61197 enters pulse skip mode. In this mode, the device keeps the power switch off for several switching cycles to prevent the output voltage from rising above the regulated voltage. This operation typically occurs in light load condition or when the input voltage is higher than the output voltage.
7.3.3 Switching Frequency
The switching frequency is programmed from 50 kHz to 800 kHz by an external resistor (R7 in Figure 18). To determine the resistance by a given frequency, use the curve in Figure 4 or calculate the resistance value by Equation 1. Table 2 shows the recommended resistance values for some switching frequencies.
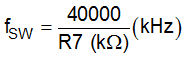
Table 2. Recommended Resistance Values For Switching Frequencies
| R7 (kΩ) | fSW (kHz) |
|---|---|
| 800 | 50 |
| 400 | 100 |
| 200 | 200 |
| 100 | 400 |
| 80 | 500 |
7.3.4 Enable and Undervoltage Lockout
The TPS61197 is enabled with soft start-up when the EN pin voltage is higher than 1.6 V. A voltage of less than 0.75 V disables the TPS61197. An undervoltage lockout (UVLO) protection feature is provided in the TPS61197. When the voltage at the VIN pin is less than 6.5 V, the TPS61197 is powered off. The TPS61197 resumes the operation once the voltage at the VIN pin recovers above the hysteresis (VVIN_HYS ) more than the UVLO falling threshold of input voltage. If a higher UVLO voltage is required, use the UVLO pin as shown in Figure 15 to adjust the input UVLO threshold by using an external resistor divider. Once the voltage at the UVLO pin exceeds the 1.229-V threshold, the TPS61197 is powered on and a hysteresis current source of 3.9 µA is added. When the voltage at the UVLO pin drops lower than 1.229 V, the current source is removed and the TPS61197 is powered off. The resistors of R1, R2 can be calculated by Equation 2 from required turnon voltage (VSTART) and turn-off voltage (VSTOP). To avoid noise coupling, the resistor divider R1 and R2 must be close to the UVLO pin. Placing a filter capacitor of more than 10nF as shown in Figure 15 can eliminate the impact of the switching ripple of the input voltage and improve the noise immunity.
If the UVLO function is not used, pull up the UVLO pin to the VDD pin.
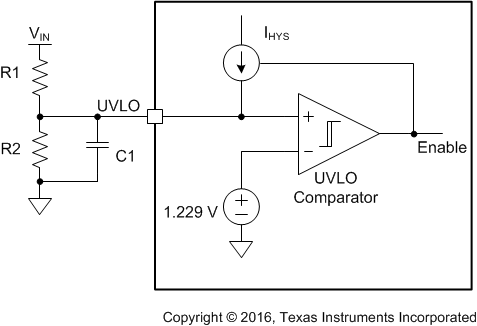 Figure 15. UVLO Circuit
Figure 15. UVLO Circuit

where
- IHYS is 3.9 µA sourcing current from the UVLO pin
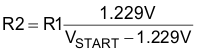
When the UVLO condition happens, the FAULT pin outputs high impedance. As long as the UVLO condition is removed, the FAULT pin outputs low impedance.
7.3.5 Power-Up Sequencing and Soft Start-up
The input voltage, UVLO pin voltage, EN input signal, and the input dimming PWM signal control the power up of the TPS61197. After the input voltage is above the required minimal input voltage of 7.5 V, the internal circuit is ready to be powered up. After the UVLO pin voltage is above the threshold of 1.229 V and the EN signal is high, the internal LDO and logic circuit are activated. When the PWM dimming signal is high, the soft start-up begins.
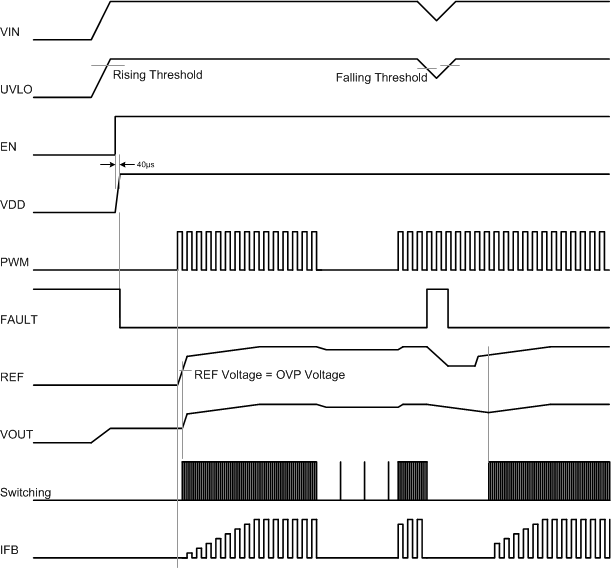 Figure 16. Power-Up Sequencing
Figure 16. Power-Up Sequencing
The TPS61197 has integrated the soft-start circuitry working with an external capacitor at the REF pin to avoid inrush current during start-up. During the start-up period, the capacitor at the REF pin is charged with a soft-start current source. When the REF pin voltage is higher than the output feedback voltage at the OVP pin, the boost controller starts switching, and the output voltage starts to ramp up. At the same time, the LED current regulation circuit starts to drive the LED string. At the beginning of the soft start, the charge current is 200 µA. Once the voltage of the REF pin exceeds 2 V, the charge current stops. The output voltage continues to ramp up until the IFB voltage is in regulation of 300 mV. The total soft-start time is determined by the external capacitance at the REF pin. The capacitance must be within 470 nF to 4.7 µF for different start-up time.
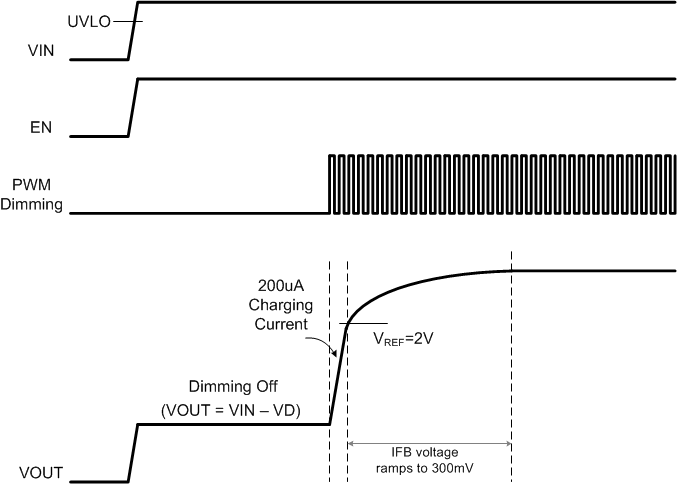 Figure 17. Soft-Start Waveforms
Figure 17. Soft-Start Waveforms
7.3.6 Current Regulation
The TPS61197 regulates the IFB voltage to 300 mV. Applying a current sense resistor (R9 in the Figure 18) at the IFB pin to set the required LED current.
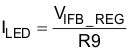
where
- VIFB_REG is the IFB pin regulation voltage of 300 mV
7.3.7 PWM Dimming
LED brightness dimming is set by applying an external PWM signal of 90 Hz to 22 kHz to the PWM pin. Varying the PWM duty cycle from 0% to 100% adjusts the LED from minimum to maximum brightness, respectively. The recommended minimum on-time of the LED string is 10 µs. Thus, the TPS61197 has a minimum dimming ratio of 5000:1 at 200 Hz.
When the PWM voltage is pulled low during dimming off, the TPS61197 turns off the LED string and keeps the boost converter running in pulse frequency modulation (PFM) mode. In PFM mode, the output voltage is kept at a level which is a little bit lower than that when the PWM voltage is high. Thus, the TPS61197 limits the output ripple due to the load transient that occurs during PWM dimming.
When the PWM voltages are pulled low for more than 20 ms, to avoid the REF pin voltage dropping due to the leakage current, the voltage of the REF pin is held by an internal reference voltage, which is a little bit lower than the REF pin voltage in normal dimming operation. Thus, the output voltage is kept unchanged during the long dimming off time.
Because the output voltage in long-time dimming off status is almost the same as the normal voltage for turning the LED on, the TPS61197 turns on the LED very fast without any flicker when recovering from long-time dimming off to normal dimming operation.
7.3.8 Indication for Fault Conditions
The TPS61197 has an open-drain fault indicator pin to indicate abnormal conditions. When the TPS61197 is operating normally, the voltage at the FAULT pin is low. When any fault condition happens, the FAULT pin is in high impedance, which can be pulled up to a high voltage level through an external resistor.
7.4 Device Functional Modes
7.4.1 Protections
The TPS61197 has full set of protections making the system safe to any abnormal conditions. Some protections latch the TPS61197 in off state until its power supply is recycled or it is disabled and then enabled again. In the latch-off state, the REF pin voltage is discharged to 0 V.
7.4.1.1 Switch Current Limit Protection Using the ISNS Pin
The TPS61197 monitors the inductor current through the voltage across a sense resistor (R5 in Figure 18) in order to provide current-limit protection. During the switch FET on period, when the voltage at the ISNS pin rises above the overcurrent protection threshold (VPWM_OCP or VPFM_OCP in Electrical Characteristics), the device turns off the FET immediately and does not turn it back on until the next switching cycle. The switch current limit is equal to VPWM_OCP / R5 (or VPFM_OCP / R5). The current limit is different for PWM mode and PFM mode. In the PWM mode, the current limit threshold voltage is 400 mV typically. In the PFM mode, it is 180 mV typically.
7.4.1.2 LED Open Protection
When the LED string is open, the IFB pin voltage drops to zero volt during dimming on-time. The TPS61197 keeps increasing the output voltage until it touches the output over-voltage protection threshold. The TPS61197 is then latched off.
7.4.1.3 Schottky Diode Open Protection
When the TPS61197 is enabled, it checks the topology connection first. The TPS61197 detects the voltage at the OVP pin to check if the Schottky diode is not connected or the boost output is hard-shorted to ground. If the voltage at the OVP pin is lower than 70 mV for 80 ms, the TPS61197 is locked in off state until the input power is recycled or the TPS61197 is enabled again.
7.4.1.4 Schottky Diode Short Protection
If the rectifier Schottky diode is shorted, the reverse current from output capacitor to ground is very large when the switch MOSFET is turned on. The TPS61197 uses a secondary current limit threshold of 800 mV across the current sense resistor to permanently disable the switching if the threshold is touched.
7.4.1.5 IFB Overvoltage Protection
When the IFB pin reaches the threshold (VIFB_OVP in the Electrical Characteristics table) of 1.1V during startup or normal operation, the device stops switching and stays in the latch-off state immediately to protect from damage. This function protects the external dimming MOSFET from damage when the LED string is shorted from the anode (connecting to output of the boost converter) to its cathode.
7.4.1.6 Output Overvoltage Protection Using the OVP Pin
Use a resistor divider to program the maximum output voltage of the boost converter. To ensure the LED string can be turned on with setting current, the maximum output voltage must be higher than the forward voltage drop of the LED string. The maximum required voltage can be calculated by multiplying the maximum LED forward voltage (VFWD(max) ) and number (n) of series LEDs , and adding extra 2 V to account for regulation and resistor tolerances and load transients.
The recommended bottom feedback resistor of the resistor divider (R4 in Figure 18) is 20 kΩ. Calculate the top feedback resistor (R3 in the Figure 18) using Equation 5, where VOUT_OVP is the output overvoltage protection threshold of the boost converter.

When the device detects that the OVP pin voltage exceeds the overvoltage protection threshold of 3.04 V, indicating that the output voltage has exceeded the over-voltage proteciton threshold, the TPS61197 clamps the output voltage to prevent it going up any more. If the OVP pin voltage does not drop below the OVP threshold for more than 640 ms, the TPS61197 is latched off until the input power or the EN pin is re-cycled.
7.4.1.7 IFB Short-to-Ground Protection
The TPS61197 monitors the IFB pin voltage when the device is enabled. If the IFB pin voltage is less than 200 mV, the TPS61197 keeps increasing the output voltage until the over-voltage protection or the switch overcurrent protection happens. If the IFB pin voltage is still under 200 mV for 60 ms in these protection conditions, the TPS61197 is latched off.
7.4.1.8 Thermal Shutdown
When the internal junction temperature of the TPS61197 is over 150°C, the thermal protection circuit is triggered and shuts down the device immediately. The device automatically restarts when the junction temperature falls back to less than 150°C, with approximate 15°C hysteresis.
Table 3. Protection List
| PROTECTION ITEM | FAULT CONDITIONS | FAULT | RESULT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diode open | VOVP < 70 mV for more than 80 ms | Y | Latch off |
| Diode short | VISNS > 800 mV for three switching cycles | Y | Latch off |
| Output overvoltage | VOVP > 3.04 V for more than 640 ms | Y | Latch off |
| LED string open | (VIFB < 200 mV and VOVP > 3.04 V) for more than 60 ms | Y | Latch off |
| LED string short | VIFB > 1.1 V | Y | Latch off |
| IFB short to ground | (VIFB < 200 mV and VOVP > 3.04 V) or (VIFB < 200 mV and VISNS > 400 mV) for more than 60 ms | Y | Latch off |
| Input voltage under UVLO threshold | VUVLO < 1.229 V | Y | Retry |
| Thermal shutdown | TJ > 150°C | Y | Retry |