SLVSEW4 April 2019 TPS650002-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTE|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTE|16
Orderable Information
8.2.2.1.2 Output Capacitor Selection
The advanced fast response voltage mode control scheme of the converter allows the use of small ceramic capacitors with a typical value of 22 μF, without having large output voltage under and overshoots during heavy load transients. TI recommends ceramic capacitors with low ESR values because they result in lowest output voltage ripple. See for the TI-recommended components.
If ceramic output capacitors are used, the capacitor RMS ripple current rating always meets the application requirements. The RMS ripple current is calculated as in Equation 4:
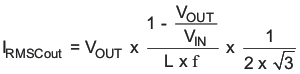
At nominal load current, the device operates in PWM mode and the overall output voltage ripple is the sum of the voltage spike caused by the output capacitor ESR plus the voltage ripple caused by charging and discharging the output capacitor as calculated in Equation 5:
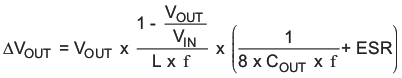
Where the highest output voltage ripple occurs at the highest input voltage VIN.
At light load currents, the converter operates in power save mode and the output voltage ripple is dependent on the output capacitor value. The output voltage ripple is set by the internal comparator delay and the external capacitor. The typical output voltage ripple is less than 1% of the nominal output voltage.