SLVSBF8C March 2013 – May 2015 TPS82692 , TPS82693 , TPS826951 , TPS82697 , TPS82698
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- SIP|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.3.1 Power-Save Mode
If the load current decreases, the converter will enter power save mode operation automatically. During power-save mode the converter operates in discontinuous current (DCM) with a minimum of one pulse, which produces low output ripple compared with other PFM architectures.
When in power-save mode, the converter resumes its operation when the output voltage trips below the nominal voltage. It ramps up the output voltage with a minimum of one pulse and goes into power-save mode when the output voltage is within its regulation limits again.
PFM mode is left and PWM operation is entered as the output current can no longer be supported in PFM mode. As a consequence, the DC output voltage is typically positioned ca. 1.5% above the nominal output voltage and the transition between PFM and PWM is seamless.
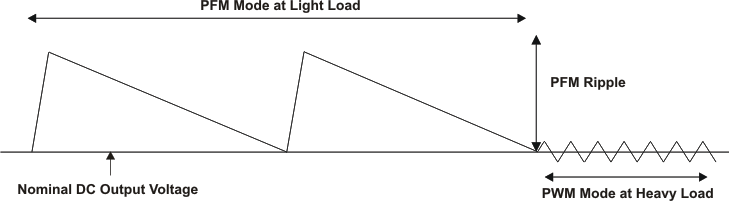 Figure 44. Operation In PFM Mode And Transfer To PWM Mode
Figure 44. Operation In PFM Mode And Transfer To PWM Mode