SLVSFG3 April 2020 TPS92612
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBV|5
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
STEP 1: Determine the current setting resistor, R(SNS) value by using Equation 2.
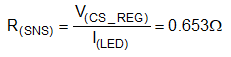
where
- V(CS_REG) = 98 mV (typical)
- I(LED) = 150 mA
STEP 2: Power consumption analysis for the worst application conditions.
Normally the thermal analysis is necessary for linear LED-driver applications to ensure that the operation junction temperature of TPS92612 is well managed. The total power consumption on the TPS92612 itself is one important factor determining operation junction temperature, and it can be calculated by using Equation 3. Based on the worst-case analysis for maximum power consumption on device, consider either optimizing PCB layout for better power dissipation as Layout describes or adding an extra heat-sharing resistor as described in Single-Channel LED Driver With Heat Sharing.
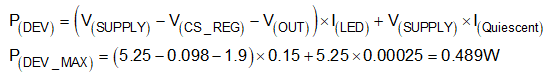
where
- V(CS_REG) = 98 mV (typical)
- I(Quiescent) = 250 µA (maximum)
In this application, the calculated result for maximum power consumption on the TPS92612 is 0.489 W at V(SUPPLY) = 5.25 V and I(LED) = 150 mA conditions.
TI recommends to add capacitors C(SUPPLY) at SUPPLY and C(OUT) at OUT. TI recommends one 1-μF capacitor plus one 100-nF decoupling ceramic capacitor close to the SUPPLY pin for C(SUPPLY) and a 10-nF ceramic capacitor close to the OUT pin for C(OUT). The larger capacitor for C(SUPPLY) or C(OUT) is helpful for EMI and ESD immunity; however, large C(OUT) takes a longer time to charge up the capacitor and may affect PWM dimming performance.