SLUSBD8E February 2013 – December 2014 UCC28251
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 VDD (5/12)
- 8.3.2 VREF (Reference Generator) (20/7)
- 8.3.3 EN (Enable Pin) (18/5)
- 8.3.4 RT (Oscillator Frequency Set and Synchronization) (15/2)
- 8.3.5 SP (Synchronous Rectifier Turn-Off to Primary Output Turn-On Dead Time Programming) (13/19)
- 8.3.6 PS (Primary Output Turn-Off to Synchronous Rectifier Turn-On Dead Time Programming) (11/18)
- 8.3.7 RAMP/CS (PWM Ramp Input or Current Sense Input) (16/3)
- 8.3.8 REF/EA+ (1/8)
- 8.3.9 FB/EA- (2/9)
- 8.3.10 COMP (3/10)
- 8.3.11 VSENSE (14/1)
- 8.3.12 SS (Soft Start Programming Pin) (13/20)
- 8.3.13 ILIM (Current Limit for Cycle-by-Cycle Over-Current Protection) (17/4)
- 8.3.14 HICC (10/17)
- 8.3.15 OVP/OTP (19/6)
- 8.3.16 OUTA (9/16) and OUTB (8/15)
- 8.3.17 SRA (7/14) and SRB (6/13)
- 8.3.18 GND (4/11)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1
Circuit Diagram in Design Example
- 9.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1.2.1 Step 1: Power Stage Design
- 9.2.1.2.2 Step 2: Feedback Loop Design
- 9.2.1.2.3 Step 3: Programming The Device
- 9.2.1.2.4 Step 3-3: Determine Soft-Start Capacitance
- 9.2.1.2.5 Step 3-4: Determine Dead-Time Resistance
- 9.2.1.2.6 Step 3-5: Determine OCP Hiccup Off-Time Capacitance
- 9.2.1.2.7 Step 3-6: Determine Primary-Side OVP Resistance
- 9.2.1.2.8 Step 3-7: Select Capacitance for VDD and VREF
- 9.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 9.2.2 Secondary-Side Half-Bridge Controller With Synchronous Rectification
- 9.2.1
Circuit Diagram in Design Example
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGP|20
Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
In order to increase the reliability and robustness of the design, it is recommended that the following layout guidelines be met.
- REF/EA+ The REF/EA+ pin is the non-inverting input of the error amplifier. For secondary side control, this pin is used to set the reference of voltage loop which decides the output voltage. So it is important to keep it clear from any of high voltage switching nodes. In addition, a decoupling capacitor located closely is recommended. For primary side control, this pin needs to be connected to opto-coupler. it is important minimize the loop area by running the EA+ signal and GND trace in parallel.
- FB/EA- Please minimize the loop between FB/EA- and COMP and keep it clear from any of high voltage switch nodes in order to avoid the noise injection into to the compensation loop.
- COMP Please minimize the loop between FB/EA- and COMP and keep it clear from any of high voltage switch nodes in order to avoid the noise injection into to the compensation loop.
- GND As with all PWM controllers, the effectiveness of the filter capacitors on the signal pins depends upon the integrity of the ground return. Place all decoupling and filter capacitors as close as possible to the device pins with short traces. The AGND pin is used as the return connection for the low-power signaling and sensitive signal so it should be separated from the power stage ground to avoid ground bouncing.
- VDD, VREF The VCC pin must be decoupled to GND by minimum 1-μF ceramic capacitors placed close to the pins.
- SRA, SRB, OUTA, OUTB The SRA and SRB gate drive pins can be used to drive the inputs of gate driver or to directly drive the primary winding of a gate-drive transformer or the to directly drive the input of isolator. The tracks connected to these pins carry high dv/dt signals. Minimize noise pickup by routing them as far away as possible from tracks connected to sensitive signal including EA+, EA-, COMP, VSENSE, RT, RAMP/CS, ILIM, PS, SP.
- HICC, SS, EN, OVP/OTP The connection track between the pin and external corresponding capacitor should be short.
- PS, SP, RT, VSENSE, RAMP/CS, ILIM These pins are noise sensitive so please allocate related resistor as close as possible with the good ground connection.
11.2 Layout Example
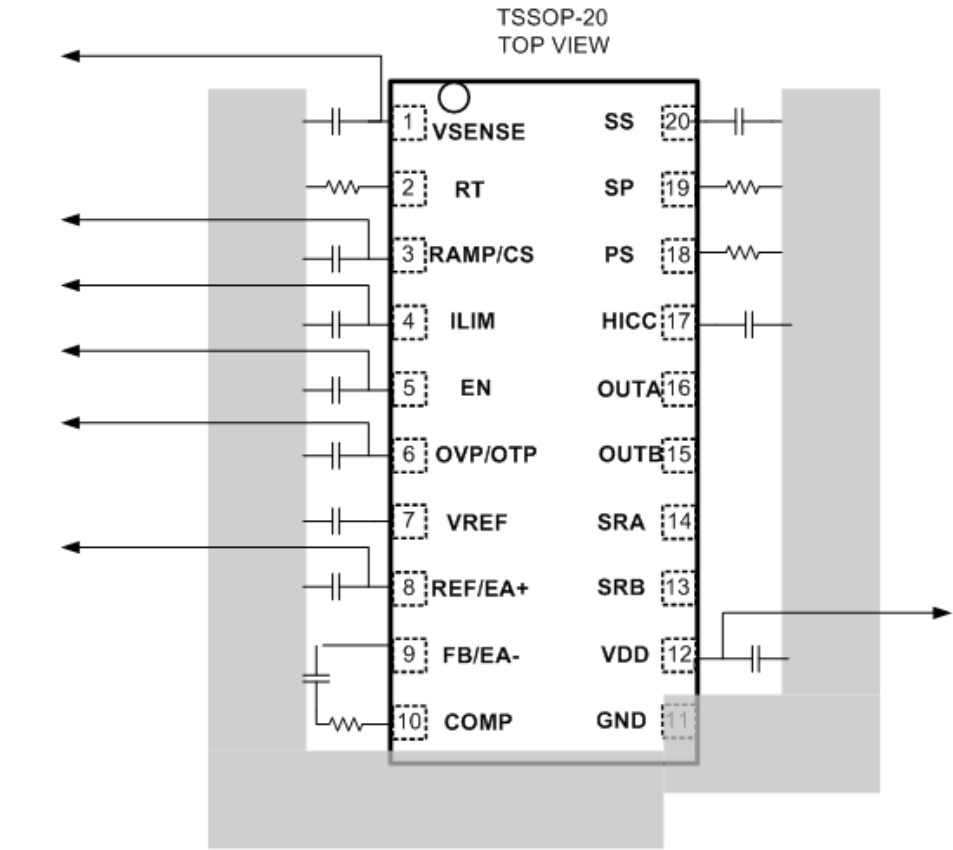 Figure 54. Layout Example
Figure 54. Layout Example
11.3 Thermal Protection
Internal thermal shutdown circuitry protects the UCC28251 in the event the maximum rated junction temperature is exceeded. When activated, typically at 160 °C, with the maximum threshold at 170°C and minimum threshold at 150 °C the controller is forced into a low power standby mode. The outputs (OUTA, OUTB, SRA, SRB) are disabled. This helps to prevent accidental device overheating. A 20 °C hysteresis is added to prevent comparator oscillation. During thermal shutdown, the UCC28251 follows a normal start up sequence after the junction temperature falls below 140 °C (typical value, with 130 °C minimum threshold and 150 °C maximum threshold).