SLUSBL7B December 2013 – October 2015 UCC28722
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Stand-by Power Estimate
- 8.2.2.2 Input Bulk Capacitance and Minimum Bulk Voltage
- 8.2.2.3 Transformer Turns Ratio, Inductance, Primary-Peak Current
- 8.2.2.4 Transformer Parameter Verification
- 8.2.2.5 Output Capacitance
- 8.2.2.6 VDD Capacitance, CDD
- 8.2.2.7 VS Resistor Divider, Line Compensation, and Cable Compensation
- 8.2.2.8 Startup Resistance and Startup Time
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
-
11Device and Documentation Support
- 11.1
Device Support
- 11.1.1
Device Nomenclature
- 11.1.1.1
Definition of Terms
- 11.1.1.1.1 Capacitance Terms in Farads
- 11.1.1.1.2 Duty Cycle Terms
- 11.1.1.1.3 Frequency Terms in Hertz
- 11.1.1.1.4 Current Terms in Amperes
- 11.1.1.1.5 Current and Voltage Scaling Terms
- 11.1.1.1.6 Transformer Terms
- 11.1.1.1.7 Power Terms in Watts
- 11.1.1.1.8 Resistance Terms in Ω
- 11.1.1.1.9 Timing Terms in Seconds
- 11.1.1.1.10 Voltage Terms in Volts
- 11.1.1.1.11 AC Voltage Terms in VRMS
- 11.1.1.1.12 Efficiency Terms
- 11.1.1.1
Definition of Terms
- 11.1.1
Device Nomenclature
- 11.2 Documentation Support
- 11.3 Community Resources
- 11.4 Trademarks
- 11.5 Electrostatic Discharge Caution
- 11.6 Glossary
- 11.1
Device Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBV|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
- High frequency bypass Capacitor C7 should be placed arcoss Pin 2 and 5 as close as you can get it to the pins.
- Resistor R15 and C7 form a low pass filter and the connection of R15 and C7 should be as close to the VDD pin as possible.
- C9 should be put as close to CS pin and R10 as possible. This forms a low pass filter with R10.
- The connection for C9 and R10 should be as close to the CS pin as possible.
- C9 may not be required in all designs. However, it is wise to put a place holder for it in your design.
- The VS pin controls the output voltage through the transformer turns ratio and the voltage divider of R7 and R9. The trace with between the R7, R9 and VS pin should be as short as possible to reduce and eliminate possible EMI coupling.
- The IC ground and power ground should meet at the return of the bulk capacitors (C4 and C5). Ensure that high frequency and high current from the power stage does not go through the signal ground
- The high frequency and high current path that you need to be cautious of on the primary is C4, C5 +, T1(P1,P2), Q1e, Q1c, R13 to the return of C4 and C5.
- Keep all high current loops as short as possible.
- Keep all high current and high frequency traces away from or perpendicular to other traces in the design.
- Traces on the voltage clamp formed by D1, R1, D4 and C4 as short as possible.
- C4 return needs to be as close to the bulk capacitor supply as possible. This reduces the magnitude of dv/dt caused by large di/dt.
- Avoid mounting semiconductors under magnetics.
10.2 Layout Example
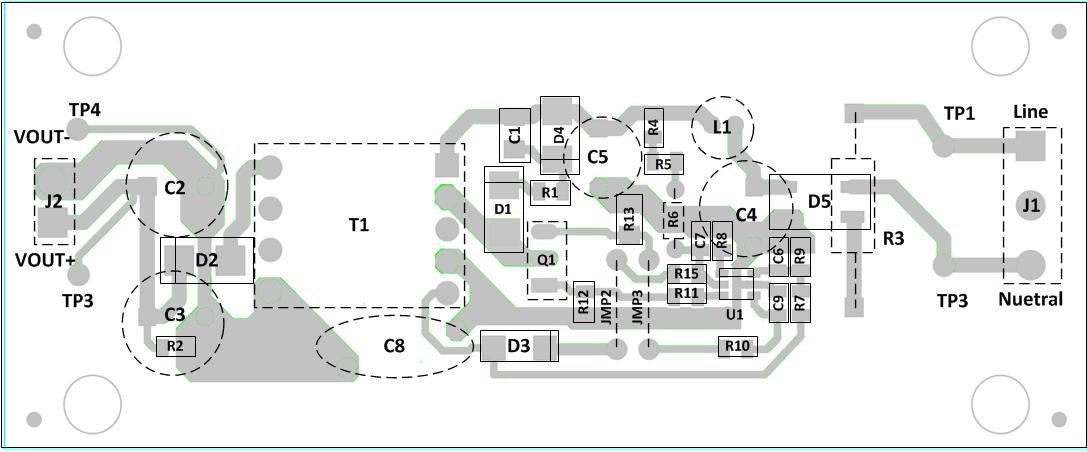 Figure 28. PCB Layout Example
Figure 28. PCB Layout Example
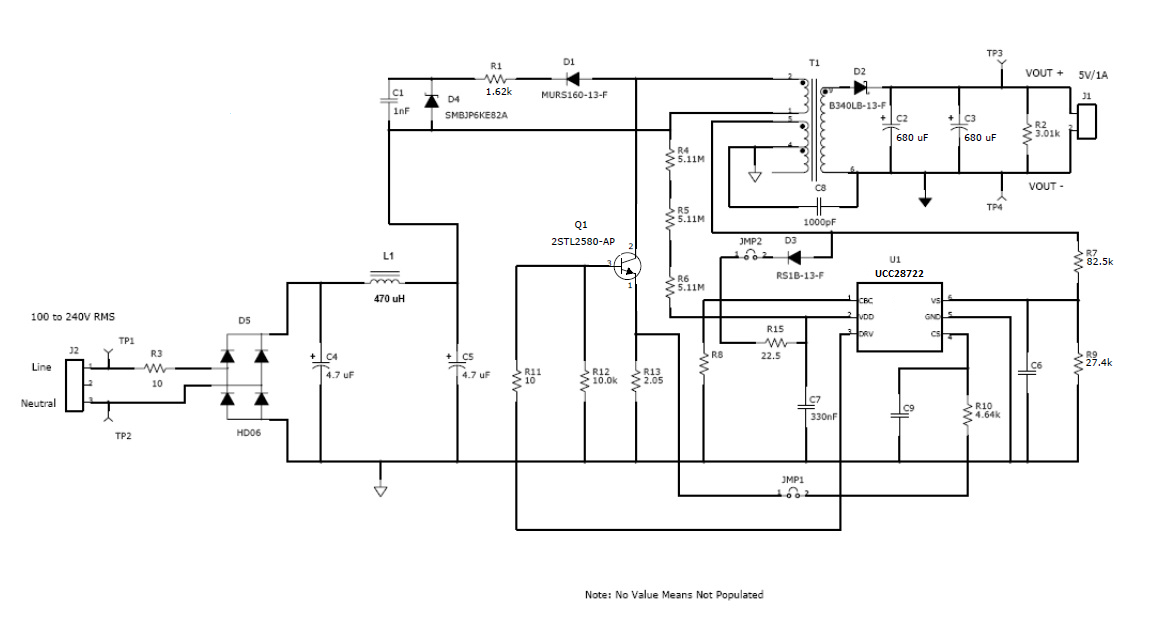 Figure 29. 5-W USB Adapter Schematic
Figure 29. 5-W USB Adapter Schematic