SLUSBL7B December 2013 – October 2015 UCC28722
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Stand-by Power Estimate
- 8.2.2.2 Input Bulk Capacitance and Minimum Bulk Voltage
- 8.2.2.3 Transformer Turns Ratio, Inductance, Primary-Peak Current
- 8.2.2.4 Transformer Parameter Verification
- 8.2.2.5 Output Capacitance
- 8.2.2.6 VDD Capacitance, CDD
- 8.2.2.7 VS Resistor Divider, Line Compensation, and Cable Compensation
- 8.2.2.8 Startup Resistance and Startup Time
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
-
11Device and Documentation Support
- 11.1
Device Support
- 11.1.1
Device Nomenclature
- 11.1.1.1
Definition of Terms
- 11.1.1.1.1 Capacitance Terms in Farads
- 11.1.1.1.2 Duty Cycle Terms
- 11.1.1.1.3 Frequency Terms in Hertz
- 11.1.1.1.4 Current Terms in Amperes
- 11.1.1.1.5 Current and Voltage Scaling Terms
- 11.1.1.1.6 Transformer Terms
- 11.1.1.1.7 Power Terms in Watts
- 11.1.1.1.8 Resistance Terms in Ω
- 11.1.1.1.9 Timing Terms in Seconds
- 11.1.1.1.10 Voltage Terms in Volts
- 11.1.1.1.11 AC Voltage Terms in VRMS
- 11.1.1.1.12 Efficiency Terms
- 11.1.1.1
Definition of Terms
- 11.1.1
Device Nomenclature
- 11.2 Documentation Support
- 11.3 Community Resources
- 11.4 Trademarks
- 11.5 Electrostatic Discharge Caution
- 11.6 Glossary
- 11.1
Device Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DBV|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VVDD | Bias supply voltage, VDD | 38 | V | ||
| IDRV | Continuous base current sink | 50 | mA | ||
| IDRV | Continuous base current source | Self-limiting | mA | ||
| IVS | Peak current, VS | –1.2 | mA | ||
| VDRV | Base drive voltage at DRV | –0.5 | Self-limiting | V | |
| Voltage | VS | –0.75 | 7 | V | |
| CS, CBC | –0.5 | 5 | V | ||
| TJ | Operating junction temperature | –55 | 150 | °C | |
| Lead temperature 0.6 mm from case for 10 seconds | 260 | °C | |||
| Tstg | Storage temperature | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±500 | V | ||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VDD | Bias supply operating voltage | 9 | 35 | V | |
| CVDD | VDD bypass capacitor | 1.0 | 10 | µF | |
| RCBC | Cable-compensation resistance | 10 | kΩ | ||
| IVS | VS pin current | −1 | mA | ||
| TJ | Operating junction temperature | −40 | 125 | °C | |
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | UCC28722 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DBV (SOT-23) | |||
| 6 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 180.0 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 72.2 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 44.4 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 5.1 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 43.8 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | NA | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range, VVDD = 25 V, HV = open, RCBC = open, TA = -40°C to 125°C, TA = TJ(unless otherwise noted)
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIAS SUPPLY INPUT | |||||||
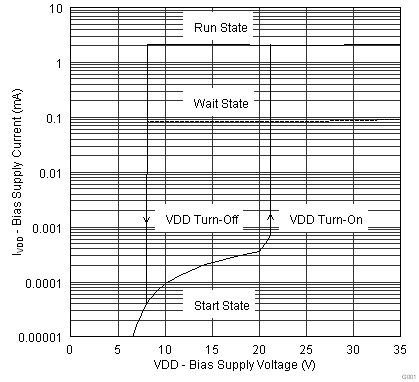
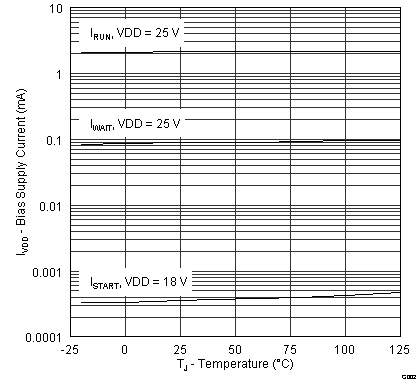
| IRUN | Supply current, run | IDRV = 0, run state | 2.00 | 2.65 | mA | ||
| IWAIT | Supply current, wait | IDRV = 0, wait state | 95 | 170 | µA | ||
| ISTART | Supply current, start | IDRV = 0, VVDD = 18 V, start state, IHV = 0 | 1.0 | 1.5 | µA | ||
| IFAULT | Supply current, fault | IDRV = 0, fault state | 2.00 | 2.65 | mA | ||
| UNDERVOLTAGE LOCKOUT | |||||||
| VVDD(on) | VDD turnon threshold | VVDD low to high | 19 | 21 | 23 | V | |
| VVDD(off) | VDD turnoff threshold | VVDD high to low | 7.2 | 7.7 | 8.3 | V | |
| VS INPUT | |||||||
| VVSR | Regulating level | Measured at no-load condition, TJ = 25°C(1) | 3.99 | 4.05 | 4.11 | V | |
| VVSNC | Negative clamp level | IVS = –300 µA, volts below ground | 190 | 250 | 325 | mV | |
| IVSB | Input bias current | VVS = 4 V | –0.25 | 0 | 0.25 | µA | |
| CS INPUT | |||||||
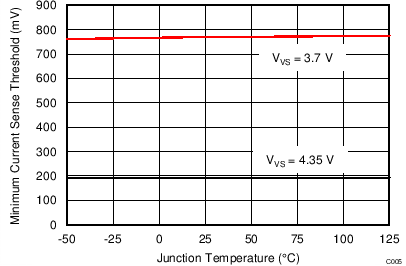
| VCST(max) | Max CS threshold voltage | VVS = 3.7 V | 730 | 780 | 820 | mV | |
| VCST(min) | Min CS threshold voltage | VVS = 4.35 V | 170 | 190 | 220 | mV | |
| KAM | AM control ratio | VCST(max) / VCST(min) | 3.6 | 4.0 | 4.4 | V/V | |
| VCCR | Constant current regulating level | CC regulation constant | 314 | 330 | 347 | mV | |
| KLC | Line compensation current ratio | IVSLS = –300 µA, IVSLS / current out of CS pin | 24.0 | 25.0 | 28.6 | A/A | |
| TCSLEB | Leading-edge blanking time | DRV output duration, V CS = 1 V | 230 | 290 | 355 | ns | |
| DRIVER | |||||||
| IDRS(max) | Maximum DRV source current | VDRV = 2 V, VVDD = 9 V, VVS = 3.85 V | 31 | 37 | 42 | mA | |
| IDRS(min) | Minimum DRV source current | VDRV = 2 V, VVDD = 9 V, VVS = 4.30 V | 15 | 19 | 23 | mA | |
| RDRVLS | DRV low-side drive resistance | IDRV = 10 mA | 1 | 2.4 | Ω | ||
| VDRCL | DRV clamp voltage | VVDD = 35 V | 5.9 | 7 | V | ||
| RDRVSS | DRV pulldown in start state | 20 | 25 | kΩ | |||
| TIMING | |||||||
| fSW(max) | Maximum switching frequency | VVS = 3.7 V | 72 | 80 | 89 | kHz | |
| fSW(min) | Minimum switching frequency | VVS = 4.35 V | 570 | 650 | 750 | Hz | |
| tZTO | Zero-crossing timeout delay | 2.4 | 3.1 | 3.7 | µs | ||
| PROTECTION | |||||||
| VOVP | Overvoltage threshold | At VS input, TJ = 25°C(1) | 4.49 | 4.60 | 4.75 | V | |
| VOCP | Overcurrent threshold | At CS input | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.6 | V | |
| IVSL(run) | VS line-sense run current | Current out of VS pin increasing | 188 | 225 | 277 | µA | |
| IVSL(stop) | VS line-sense stop current | Current out of VS pin decreasing | 70 | 80 | 100 | µA | |
| KVSL | VS line sense ratio | IVSL(run) / IVSL(stop) | 2.45 | 2.80 | 3.05 | A/A | |
| TJ(stop) | Thermal shutdown temperature | Internal junction temperature | 165 | °C | |||
| CABLE COMPENSATION | |||||||
| VCBC(max) | Cable compensation maximum voltage | Voltage at CBC at full load | 2.9 | 3.1 | 3.5 | V | |
| VCVS(min) | Minimum compensation at VS | VCBC = open, change in VS regulating level at full load | –55 | –15 | 25 | mV | |
| VCVS(max) | Maximum compensation at VS | VCBC = 0 V, change in VS regulating level at full load | 270 | 320 | 385 | mV | |
(1) The regulating level and over voltage at VS decreases with temperature by 0.8 mV/˚C. This compensation is included to reduce the power supply output voltage variance over temperature.
6.6 Typical Characteristics
VDD = 25 V, unless otherwise noted.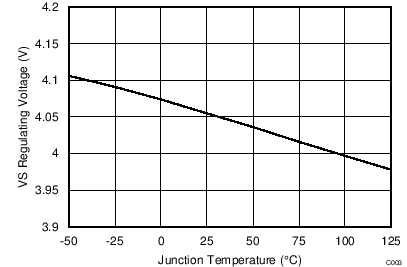
vs Junction Temperature
vs Temperature
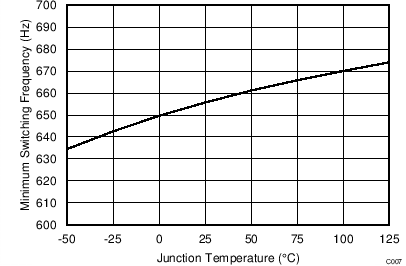
vs Junction Temperature
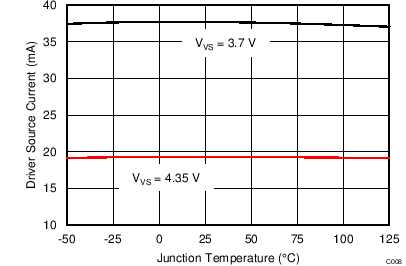
vs Junction Temperature
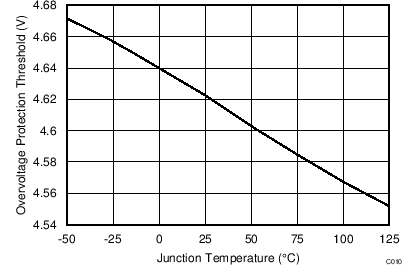
vs Junction Temperature
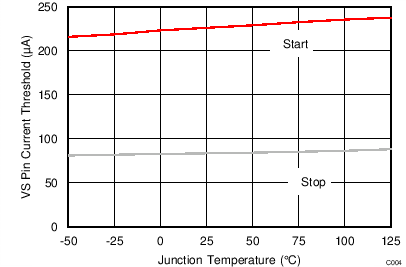
vs Junction Temperature
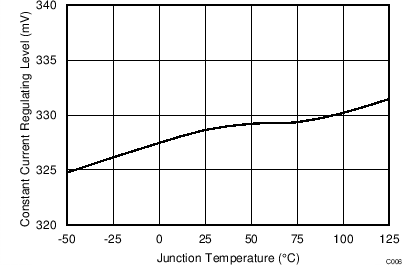
vs Junction Temperature
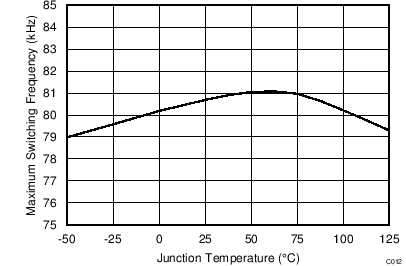
vs Junction Temperature
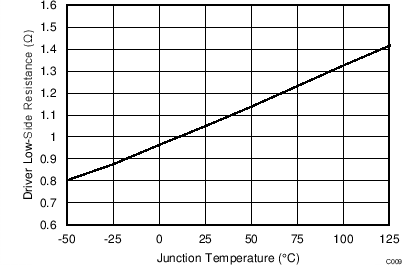
vs Junction Temperature