SLUSA12G December 2009 – November 2022 UCC28C40-Q1 , UCC28C41-Q1 , UCC28C42-Q1 , UCC28C43-Q1 , UCC28C44-Q1 , UCC28C45-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 9.2.2.2 Input Bulk Capacitor and Minimum Bulk Voltage
- 9.2.2.3 Transformer Turns Ratio and Maximum Duty CycleG
- 9.2.2.4 Transformer Inductance and Peak Currents
- 9.2.2.5 Output Capacitor
- 9.2.2.6 Current Sensing Network
- 9.2.2.7 Gate Drive Resistor
- 9.2.2.8 VREF Capacitor
- 9.2.2.9 RT/CT
- 9.2.2.10 Start-Up Circuit
- 9.2.2.11 Voltage Feedback Compensation
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 9.2.4 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9.2.5 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.3.8 Enable and Disable
There are a few ways to enable or disable the UCC28C4x-Q1 devices, depending on which type of restart is required. The two basic techniques use external transistors to either pull the error amplifier output low (< 2 VBE) or pull the current sense input high (> 1.1 V). Application of the disable signal causes the output of the PWM comparator to be high. The PWM latch is reset dominant so that the output remains low until the next clock cycle after the shutdown condition at the COMP or CS pin is removed. Another choice for restart without a soft start is to pull the current sense input above the cycle-by-cycle current limiting threshold. A logic level P-channel FET from the reference voltage to the current sense input can be used.
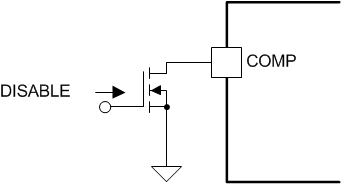 Figure 8-7 Disable Circuit
Figure 8-7 Disable Circuit