SLUS492K June 2001 – November 2023 UCC27323 , UCC27324 , UCC27325 , UCC37323 , UCC37324 , UCC37325
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Revision History
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DGN|8
Orderable Information
8.2.2.1 Source/Sink Capabilities During Miller Plateau
Large power MOSFETs present a large load to the control circuitry. Proper drive is required for efficient, reliable operation. The UCCx732x drivers have been optimized to provide maximum drive to a power MOSFET during the Miller plateau region of the switching transition. This interval occurs while the drain voltage is swinging between the voltage levels dictated by the power topology, requiring the charging/discharging of the drain-gate capacitance with current supplied or removed by the driver device [1].
Two circuits are used to test the current capabilities of the UCCx732x driver. In each case external circuitry is added to clamp the output near 5 V while the IC is sinking or sourcing current. An input pulse of 250 ns is applied at a frequency of 1 kHz in the proper polarity for the respective test. In each test there is a transient period where the current peaked up and then settled down to a steady-state value. The noted current measurements are made at a time of 200 ns after the input pulse is applied, after the initial transient. [1]
The first circuit in Figure 8-2 is used to verify the current sink capability when the output of the driver is clamped around 5 V, a typical value of gate-source voltage during the Miller plateau region. The UCCx7323 is found to sink 4.5 A at VDD = 15 V and 4.28 A at VDD = 12 V.
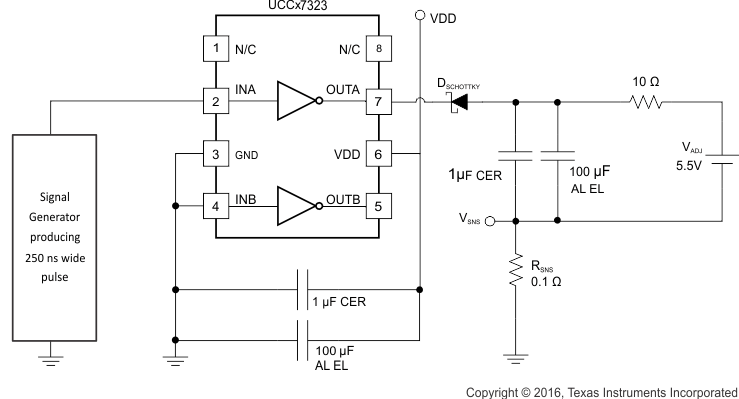 Figure 8-2 Current Sink Capability Test
Figure 8-2 Current Sink Capability TestThe circuit shown in Figure 8-3 is used to test the current source capability with the output clamped to around 5 V with a string of Zener diodes. The UCCx7323 is found to source 4.8 A at VDD = 15 V and 3.7 A at VDD = 12 V.
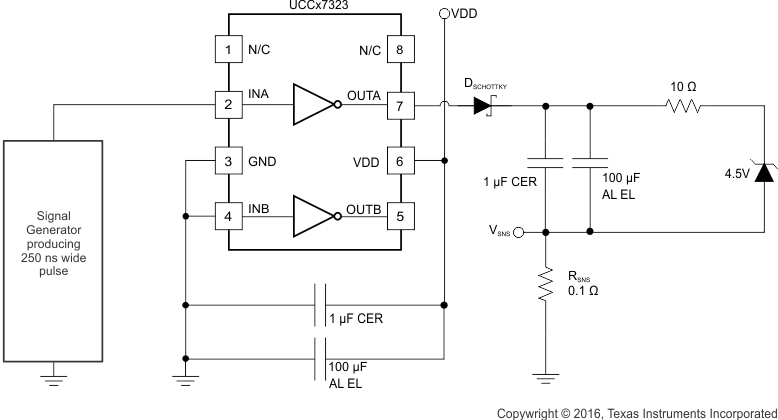 Figure 8-3 Current Source Capability Test
Figure 8-3 Current Source Capability Test