JAJSH51C August 2000 – March 2024 BUF634
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: TO-220 and TO-263 Packages
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: Wide-Bandwidth Mode for SOIC Package
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: Low-Quiescent-Current Mode for SOIC Package
- 6.8 Typical Characteristics: TO-220 and TO-263 Packages
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics: SOIC Package
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- KTT|5
発注情報
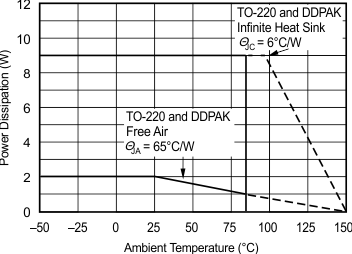
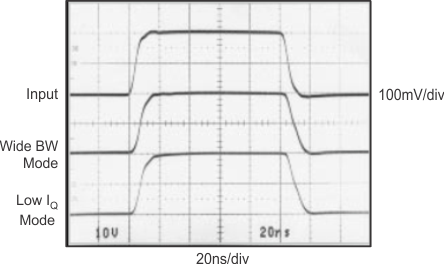
6.8 Typical Characteristics: TO-220 and TO-263 Packages
at TA = 25°C, VS = ±15 V (unless otherwise noted)
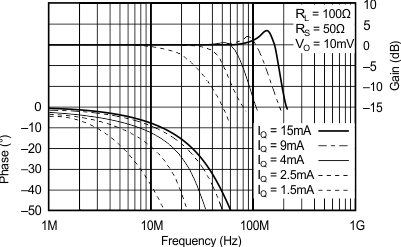
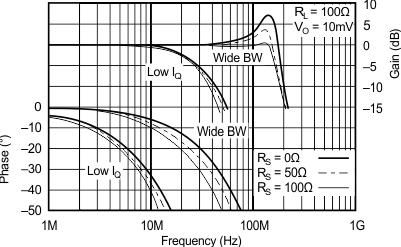
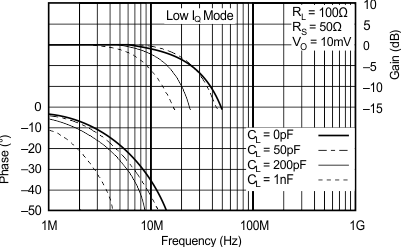
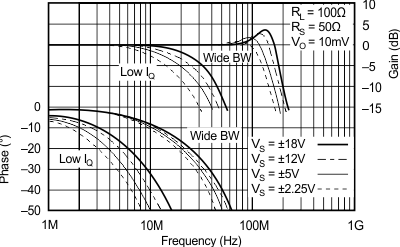
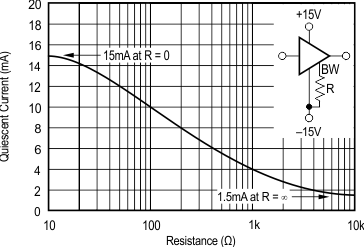
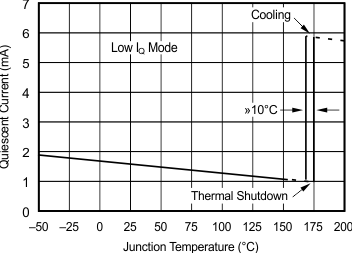
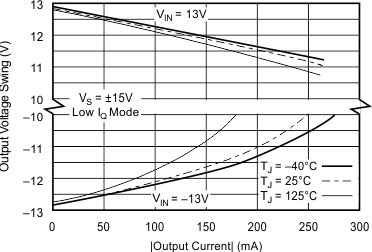
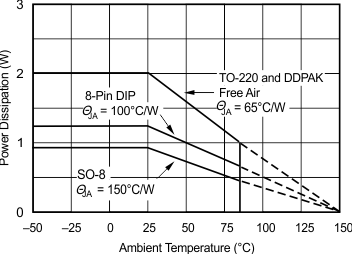
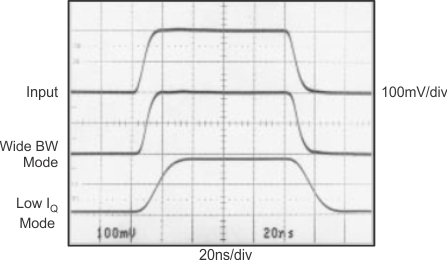
| RS = 50 Ω, RL = 100 Ω | ||
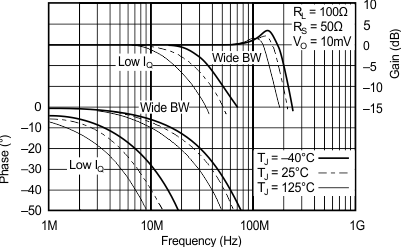
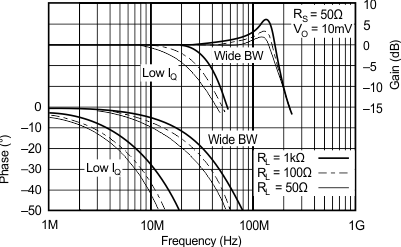
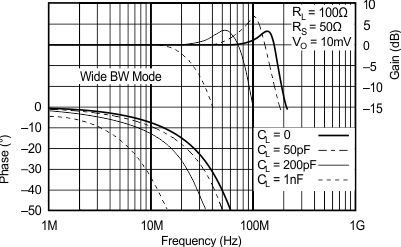
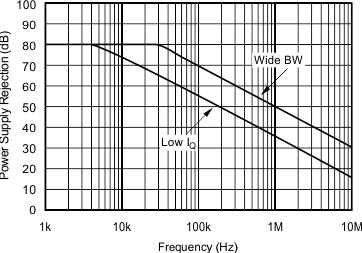
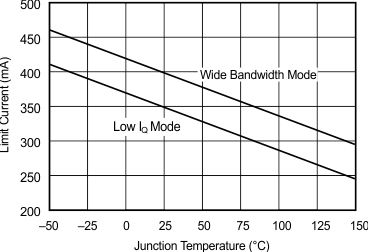
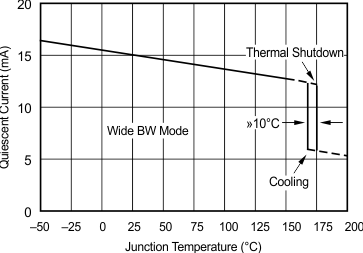
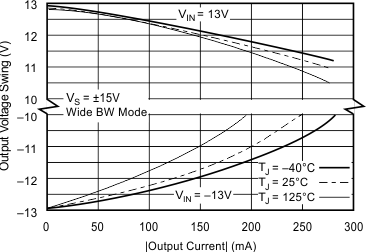
| RS = 50 Ω, RL = 100 Ω | ||